Image: ShutterStock
The fourth week of pregnancy is when most women find out that they are pregnant. When you are four weeks pregnant, your baby is around the size of a poppy seed and is developing in the inner lining of your womb (1). At early stages of pregnancy, most pregnancy symptoms are not evident except for a few, such as a late period and tender breasts. Read on to know the signs, symptoms, changes, growth, and dos and don’ts to follow when you are four weeks pregnant.

Key Pointers
- By the fourth week of pregnancy, the shape of the baby’s face and heart develops.
- Take your prenatal vitamins and eat a well-balanced diet with folate-enriched foods.
- Miscarriage, bleeding, and ectopic pregnancy are major concerns during this week.
- You may need to take blood tests to measure pregnancy-associated plasma protein and hCG hormone.
Changes Occurring In The Fourth Week Of Pregnancy
As the pregnancy progresses, many changes occur in the embryo and in maternal health
- Amniotic saciThe water or fluid-filled sac within the womb necessary for the growth and development of the fetus /outer layer around the embryo gradually develops along with the placenta.
- Shape of the face also roughly starts to form with large circles for eyes.
- Baby’s heart develops and beats around 65 times per minute by the end of the fourth week,
- Blood circulation begins as the blood cells take shape (2).
 Did you know?
Did you know?Signs And Symptoms Of Pregnancy At 4 Weeks
Though the physical signs of pregnancy are not visible by the fourth week, the body undergoes various internal changes to accommodate the fetus and keep it nourished and protected. The following are some of the four-week pregnancy symptoms (3) (4):
- Morning sickness due to an increased level of hormones
- Frequent bouts of fatigue due to higher physical and emotional demands
- Enlarged mammary glands due to increased levels of estrogeniA sex hormone responsible for the development of female sexual characteristics and progesteroneiA female reproductive hormone that plays an important role in menstruation, pregnancy, and breastfeeding pregnancy hormones, leading to breast tenderness
- Darkening of the area around the areola (nipple)
- Frequent urge to urinate and episodes of constipation as the developing fetus starts to press against the intestines
- Mood swings due to a surge in hormone levels
- Increased sensitivity to certain odors or a stronger sense of smell
- Fatigue or feeling tired due to physical or emotional changes
- Mild cramping or pain, similar to period-related cramps
Many women begin to detect small yet substantial changes in their bodies during the fourth week of pregnancy. Caroline, a mother residing in North Carolina, shares her symptoms during the 4th and 5th weeks of her pregnancy. She says, “Lots of cramps and twinges (painful at times) that come and go quickly. Usually, about 30 minutes of nausea in the late afternoons, but that goes away after I eat something or lay down for a bit. Oh yeah, and sleepy. I can take 3-hour naps and still want to be in bed by 8 p.m. (i).”
Recalling how she managed nausea in her fourth week of pregnancy, blogger Lindsey writes, “Nausea: not pleasant, but overall not all that bad. For me, beginning around 4 weeks, this felt like a ramped-up metabolism that was very vulnerable to blood sugar crashes, leading to nausea that would set in for the day if I didn’t get it under control during the morning. My method for managing: sip juice, eat some crackers while still in bed, sit and stand up slowly, and drink instant breakfast on the way to work, if not before (ii).”
 Quick fact
Quick factThe Belly At Four Weeks
Most first-time mothers don’t start showing the belly until week 12.
However, if it is not your first pregnancy, you may start showing it earlier as your uterus muscles are still stretched from your previous pregnancies (4). Some women may notice slight bloating in the early weeks, which can make their belly appear larger, but this could be due to hormonal changes, not a baby bump (4). However, since every pregnancy is unique, if you have any concerns about body changes during this time, consult a doctor.
 Quick fact
Quick factThe Do’s And Don’ts In The Fourth Week Of Pregnancy
Do
- Sleep well: During pregnancy, get at least eight to ten hours of sleep per day to cope with the physical and emotional demands of your body and the baby.
- Have nutritious food: The food you eat is fuel for you and your developing baby. Hence, make healthy eating choices and maintain a balanced diet (5). You don’t need to eat for two!
 Quick tip
Quick tip- Include folate in your diet: If you did not add folate or folic acidiA natural form of vitamin B9 necessary for optimal fetal development and is found in foods like fruits, vegetables, and nuts to your diet before getting pregnant, do so now. Consuming at least 400mcg of folate per day is important in the first trimester to help prevent two major congenital disabilities—anencephalyiA severe birth defect in which the baby is born without some parts of the brain and the skull and spina bifidaiA congenital disorder where the spinal cord doesn't fully develop, leading to physical and neurological complications According to the statistics from the CDC, approximately 1,200 babies are affected by spina bifida, and 700 babies are affected by anencephaly in the US (19).
- Take prenatal vitamins: Prenatal vitamins are important for maintaining good nutrition during pregnancy and for the baby’s proper growth and development (6). Experts at the American Pregnancy Association (APA) recommend that women take at least 4mg (400 micrograms) of folic acid starting this week (20).
- Stay hydrated: Staying hydrated helps prevent preterm labor, kidney infection, and headaches. It also helps reduce the risk of constipation and hemorrhoids.

Don’t
- Smoke: Studies conducted by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) report that pregnant women who smoke may have a higher risk of miscarriage (7).
- Drink alcohol: According to the CDC, all types of alcohol are harmful to the baby during pregnancy (8). The alcohol may pass on to the baby through the umbilical cord and cause miscarriage or physical or intellectual disabilities known as fetal alcohol spectrum disordersiA group of conditions that can occur in fetuses exposed to alcohol while being in the mother’s womb (FASDs).
- Consume too much caffeine: Research suggests that consuming less than 200mg of caffeine is acceptable in the first trimester (9). However, excessive caffeine could affect the fetus’ heart rate.
- Visit the sauna: Hot tubs or saunas increase the body’s core temperature, which may adversely affect the baby’s development and double the risk of miscarriage (5).
What To Eat
Consuming a balanced diet can help reduce nausea and constipation and aid in having a healthy pregnancy.
Below are some advantageous foods for you and your baby (10).
- Proteins: peas, nuts, beans, lean beef, pork, salmon, and trout
- Vegetables: carrots, pumpkin, red sweet peppers, tomatoes, and spinach

- Grains: cooked or ready-to-eat cereals
- Fruits: bananas, mangoes, cantaloupes, prunes, apricots, oranges, and grapefruit
Potential Risks In The Fourth Week Of Pregnancy
Most cases of miscarriage or ectopic pregnancyiA life-threatening condition in which the fertilized egg gets implanted outside the uterus, mainly in the fallopian tubes occur in the early months after conception (11). Some common potential risks during pregnancy include
- Miscarriage: Miscarriage in the early months of pregnancy is known as a chemical pregnancy. The most common cause of a miscarriage in the first trimester is a chromosomal abnormalityiNumerical or structural abnormalities in chromosomes (12).
- Bleeding: Some women may experience light spotting or bleeding in the early days of pregnancy but have an overall healthy pregnancy throughout. However, any signs of bleeding or rupture of blood vessels during pregnancy should be reported to your healthcare provider to avoid complications.
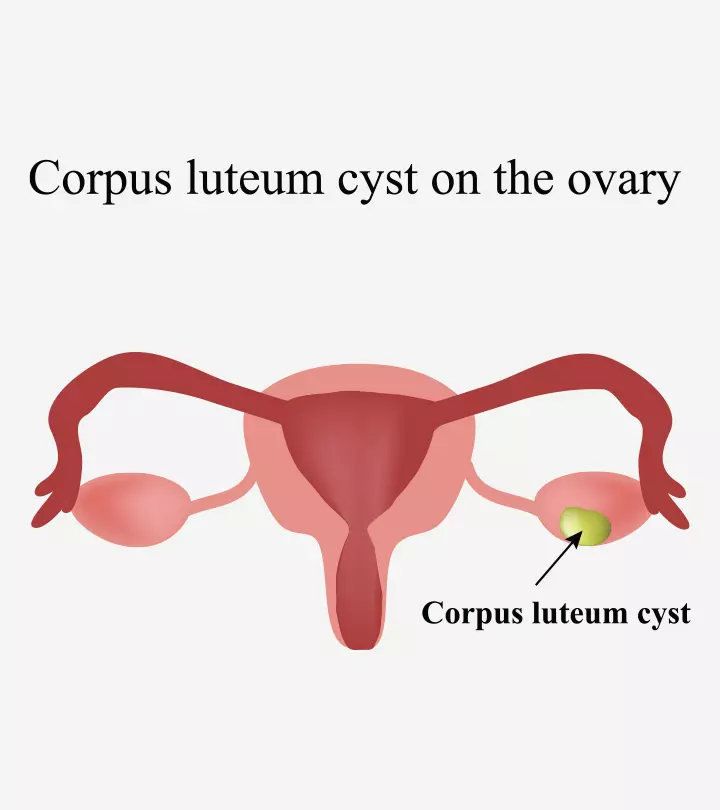
- Ectopic pregnancy: Ectopic pregnancy is common and occurs in around one in 80 pregnancies in the UK. In this condition, the fertilized egg implants itself in the fallopian tube instead of the endometrium. In the later stages of an ectopic pregnancy, the baby’s growth may severely damage the fallopian tube and cause pain and bleeding (13).

Screening Tests In The Fourth Week
Getting certain tests and ultrasounds done in the early weeks of pregnancy can help determine pregnancy or fetal complications.
Blood tests measure the amount of pregnancy-associated plasma protein and the pregnancy hormone human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG). Abnormal quantities of either may indicate the risk of chromosomal abnormality in the fetus (14). These tests are usually ordered by the doctor or the obstetrician.
 Quick fact
Quick factWhen To Seek Medical Care
At four weeks pregnant, mild symptoms are common, but certain signs may need medical attention. Consult a doctor if you experience one or more of the following symptoms (21).
- Heavy bleeding: Light spotting is not uncommon during this week, but if you have heavy bleeding with clots or bright red blood, seek medical help.
- Severe cramping or abdominal pain: Mild cramping is normal in the initial weeks, but if the pain is sharp, intense, or mostly on one side, see a doctor.
- Fever or weakness: If you develop a fever or feel unusually weak, contact your doctor, as it could indicate an infection.
- Pain or trouble while urinating: If you experience pain or notice blood in your urine, seek medical advice, as it could signal a urinary tract infection.
- Unusual vaginal discharge: A slight vaginal discharge is normal, but if it suddenly increases, smells bad, or looks different, talk to your doctor.
 Point to consider
Point to considerFrequently Asked Questions
1. What is my risk of miscarrying?
The risk of miscarrying at four weeks of pregnancy stands at around 25% (15).
2. How is pregnancy calculated?
Pregnancy is calculated from the first day of your last menstrual period. You can also use a pregnancy or due date calculator to calculate your approximate due date.
3. What should I avoid at four weeks pregnant?
At four weeks pregnant, you should avoid (16) (17):
- Chemical exposure to cleaning products, mothballs, wall paints, fake tan products (containing dihydroxyacetone), and hair treatment products
- Handling cat litter as it increases the risk of toxoplasmosis
- Undercooked meat and eggs. They may increase the risk of contracting infections such as listeriosis and toxoplasmosis, which may lead to serious illnesses
4. Is it normal to experience cramping at 4 weeks?
Mild, occasional cramping may happen this week, but if you have persistent cramps like menstrual pain along with vaginal bleeding, contact your healthcare team, as it could indicate a miscarriage (11).
Four weeks of pregnancy is when you are excited to confirm pregnancy and begin to experience pregnancy symptoms. This is when the pregnancy hormones become more active, and you begin to feel various physical and mental changes of pregnancy. Sticking to regular exercise and following a balanced diet can be beneficial. It is also crucial to follow prenatal care, especially prenatal vitamins and supplements, and avoid harmful things since your baby begins to develop its organs and organ systems.
Infographic: Tips To Reduce Miscarriage Risk At Four Weeks Pregnant
The 4th week of pregnancy is the initial and crucial phase of the first trimester. As you embark on your pregnancy journey, this infographic can guide you with vital things to consider during this week to prevent pregnancy loss and sustain a healthy pregnancy.
Some thing wrong with infographic shortcode. please verify shortcode syntax
Learn about what is happening inside your during the fourth week of your pregnancy and how developed the fetus is, in this interesting video.
Personal Experience: Sources
MomJunction articles include first-hand experiences to provide you with better insights through real-life narratives. Here are the sources of personal accounts referenced in this article.
i. Pregnancy week by week: 4 & 5.https://myprettylittlethoughts.blogspot.com/2011/02/pregnancy-week-by-week-4-5.html
ii. The Pregnancy Process- TMI ahead.
https://familystyleliving.wordpress.com/2013/11/21/the-pregnancy-process-tmi-ahead/
References
- You and your baby at 4 weeks pregnant.
https://www.nhs.uk/pregnancy/week-by-week/1-to-12/4-weeks/ - Fetal development: stages of growth.
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/7247-fetal-development-stages-of-growth - The first trimester.
https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/wellness-and-prevention/the-first-trimester - Week-by-week guide to pregnancy.
https://www.nhs.uk/start-for-life/pregnancy/week-by-week-guide-to-pregnancy/1st-trimester/week-4/ - Do’s and don’ts during the first trimester of pregnancy.
https://news.sanfordhealth.org/womens/dos-and-donts-during-first-trimester-pregnancy/ - The ABCs of vitamins in pregnancy.
https://news.sanfordhealth.org/womens/prenatal-vitamins/ - Smoking During Pregnancy.
https://www.cdc.gov/tobacco/about/cigarettes-and-reproductive-health.html?CDC_AAref_Val=https://www.cdc.gov/tobacco/basic_information/health_effects/pregnancy/index.htm - About Alcohol Use During Pregnancy.
https://www.cdc.gov/alcohol-pregnancy/about/index.html - How much coffee can I drink while I’m pregnant?
https://www.acog.org/womens-health/experts-and-stories/ask-acog/how-much-coffee-can-i-drink-while-pregnant - Nutrition during pregnancy.
https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/wellness-and-prevention/nutrition-during-pregnancy - Early pregnancy problems.
https://www.thewomens.org.au/health-information/pregnancy-and-birth/pregnancy-problems/early-pregnancy-problems - Signs of miscarriage.
https://americanpregnancy.org/getting-pregnant/pregnancy-loss/signs-of-miscarriage/ - What is an ectopic pregnancy?
https://ectopic.org.uk/what-is-an-ectopic-pregnancy - Common tests during pregnancy.
https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/wellness-and-prevention/common-tests-during-pregnancy#first - Miscarriage: your questions answered.
https://www.nct.org.uk/pregnancy/miscarriage/miscarriage-your-questions-answered - Things to avoid during pregnancy.
https://www.pregnancybirthbaby.org.au/things-to-avoid-during-pregnancy - Do’s and don’ts during the first trimester of pregnancy.
https://news.sanfordhealth.org/womens/dos-and-donts-during-first-trimester-pregnancy/ - 4 weeks pregnant.
https://raisingchildren.net.au/pregnancy/week-by-week/first-trimester/4-weeks - Data and Statistics on Birth Defects
https://www.cdc.gov/birth-defects/data-research/facts-stats/?CDC_AAref_Val=https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/birthdefects/data.html - 4 Weeks Pregnant
https://americanpregnancy.org/healthy-pregnancy/week-by-week/4-weeks-pregnant/ - First trimester (weeks 0 to 12)
https://www2.hse.ie/conditions/stomach-pain-cramps-pregnancy/ - I had a positive pregnancy test – now what?
https://www.osfhealthcare.org/blog/first-time-pregnant-heres-what-to-expect/
Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our nurturing community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with fellow parents.
Read full bio of Dr. Ben Abbes Taarji Hicham
Read full bio of Sanjana Bhattacharjee
Read full bio of Rebecca Malachi
Read full bio of Reshmi Das