Image: Shutterstock
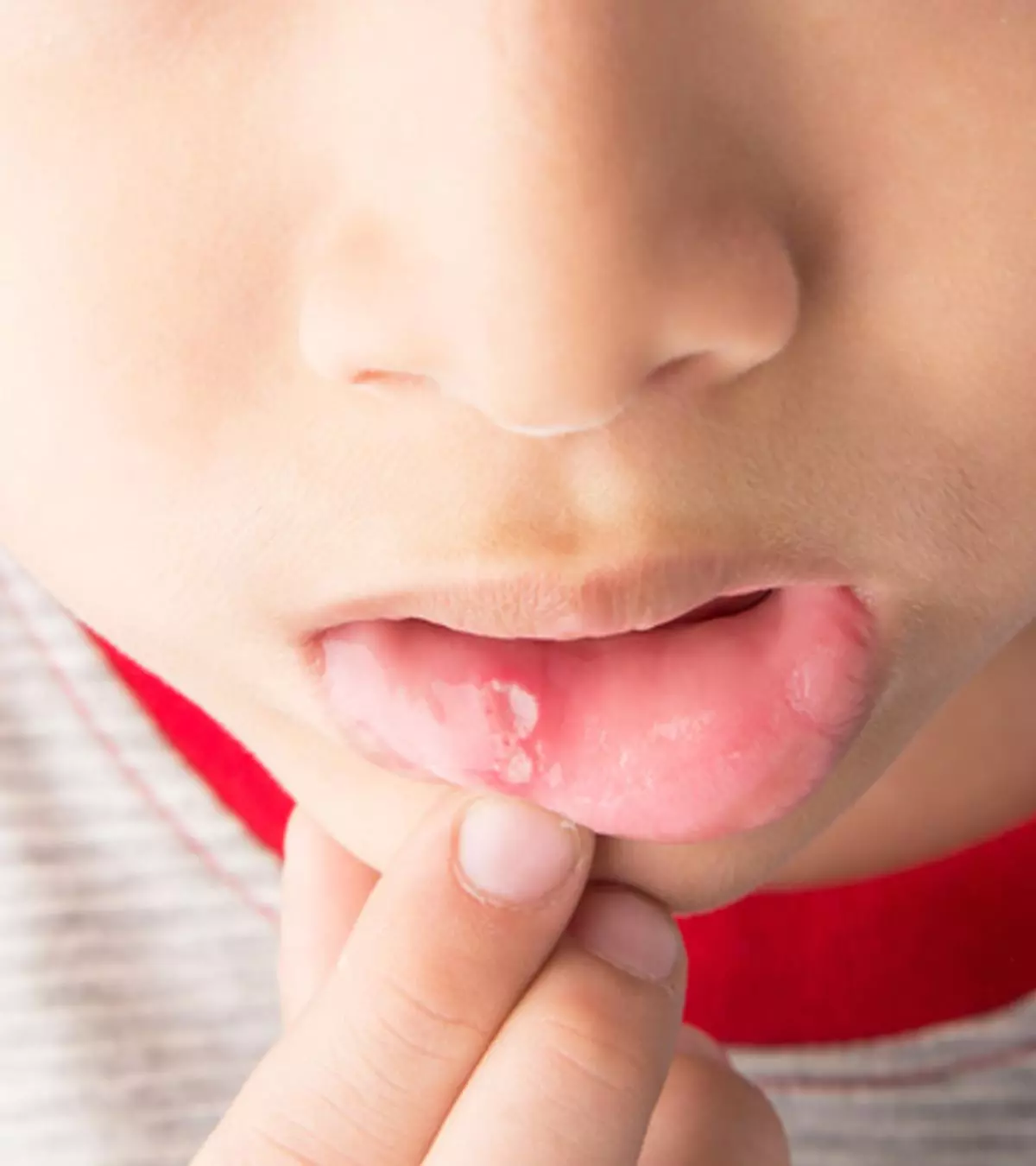
An Abscessed tooth in a child is characterized by the collection of pus inside the teeth, gums, or surrounding bone. It occurs as a result of bacterial infection.
An abscess at the end of the tooth is called a periapical abscess, and an abscess within the gum is called a periodontal abscess.
A dental abscess is painful most times, but not always. It helps if you take your child to the dentist for timely treatment and management. Read this post to learn more about the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment for dental abscesses in children.
Key Pointers
- An abscessed tooth in children results from a bacterial infection that causes pus accumulation in gums, teeth, and bones.
- Bacteria enter gums due to cavities and periodontal diseases, leading to abscess formation.
- Symptoms of an abscessed tooth in children include severe pain, tooth sensitivity, swollen gums, earache, swollen jaw, fever, and bad breath.
- Home remedies for tooth abscess in children include avoiding hot and cold foods, eating soft foods, applying ice packs, and rinsing with warm salt water.
- You can prevent tooth abscesses in children by teaching them to maintain good oral hygiene and getting regular dental check-ups.
Causes Of Tooth Abscess In Children
Dental abscess is caused due to bacteria inside the teeth. The bacteria irritates the gum and causes inflammation. Gradually, the tooth becomes loose. The bacteria pools in the gap between the tooth and the gum causing an abscess (1).
Cavities lead to a periapical abscess. When the dental decay reaches the center of the tooth, it damages the tooth nerve, and the infection collects at the tip of the tooth root to form an abscess.
The bacteria present in the plaque can cause gum irritation, gum swelling, gum disease and periodontal infection. Periodontal space is present between the gums and teeth. Bacteria can collect in this space and may form abscesses (1).
Signs And Symptoms Of Tooth Abscess In Children
The following are the signs and symptoms of tooth abscess in children (1) (2) (3).
- Sharp or throbbing pain in the affected tooth or gum
- Teeth are sensitive to hot or cold food or drinks, and pressure
- Red discoloration on the gums
- Swollen gums
- Ear pain on the same side of the affected tooth
- Pain worsens on lying down and might cause sleep disturbance
- Pus discharge from the gum
- Swollen jaw and jaw pain in children
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Swollen neck
- Fever
- Bitter taste in the mouth
- Bad breath in kids
In severe cases, one may experience difficulties opening the mouth or problems with swallowing or breathing.
Risks And Complications Of Tooth Abscess
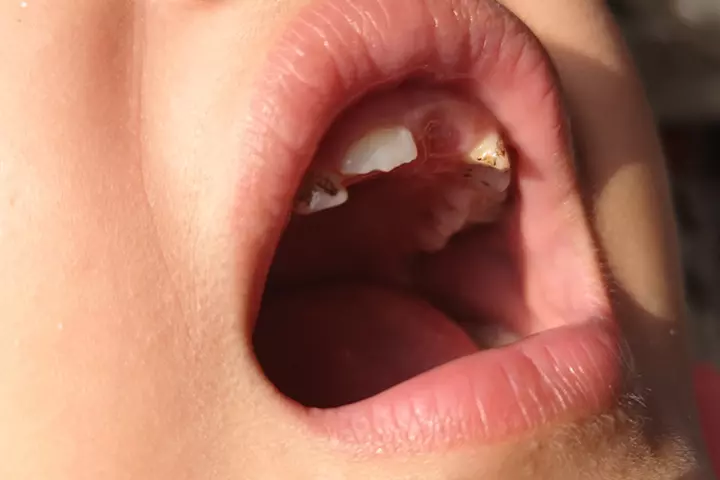
Untreated dental abscesses may lead to the following complications (4).
- Loss of tooth
- Blood infection
- Spread of infection to adjacent soft tissues
- Spread of the tooth infection to the jaw bone
- Spread of the oral infection to the other areas of the body, therefore causing brain abscess, heart inflammation, pneumonia, etc.
Signs You Need To See A Doctor
Contact the pediatric dentist if you notice any of these symptoms (2).
- Fever
- Nausea or vomiting
- Persistent redness or swelling
- Difficulty in breathing
- A swollen or painful eye, or sudden vision problems
- Excessive swelling in the mouth
 Be watchful
Be watchfulDiagnosing Dental Abscess In Children
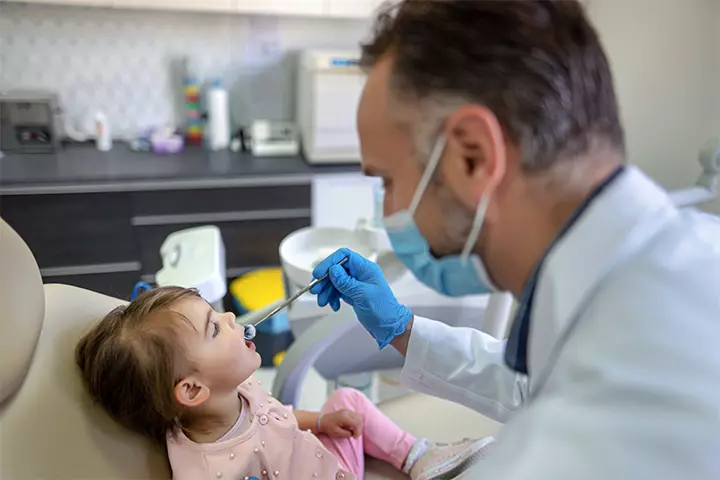

The dentist will thoroughly examine the tooth and the surrounding structures. The diagnosis includes tapping on the tooth using the blunt end of the mouth mirror. Pain on tapping or closely biting the teeth can indicate a dental abscess. The mobility of the teeth or the presence of cracks in the tooth are also checked. Dental caries is also evaluated in the teeth around the abscess.
Dental x-rays help the dentist determine the tooth causing the problem and gauge the infection (4).
Treatment For Dental Abscess In Children
Removing the source of infection and draining away the pus is important for treating a dental abscess. The following are the possible dental treatments based on the location and the severity of the oral infection (2) (4) (5).
- OTC pain killers
OTC painkillers may help in providing some relief from toothache and fever.
- Antibiotics
Antibiotic therapy helps reduce the severity of tooth infections. However, not all cases of dental abscess need antibiotics. Ensure completion of the entire course of antibiotics for your child upon prescription.
- Root canal treatment

Root canal therapy is one of the most commonly used dental procedures to treat tooth abscesses. The infected dental pulp and abscess are removed from the tooth root before filling and sealing it.
- Removal of the affected tooth
Tooth extraction might be recommended for severely infected teeth that cannot be saved by root canal treatment.
- Incision and drainage
A small cut is made on the gum to drain the pus/abscess. It might relieve the swelling. However, this is only a temporary solution, and further dental treatment is suggested.
For severe dental infections, hospitalization may be needed. However, more extensive surgical procedures are rarely required and may be performed under general anesthesia (3).
 Caution
CautionHome Remedies For Tooth Abscess In Children

The following measures may help your child get some relief from an abscessed tooth (1) (2).
- Avoid cold and hot food and beverages.
- Chew with the opposite side of your face and eat soft foods.
- Switch to a softer toothbrush and avoid flossing around the affected area.
- Local application of ice packs for up to 20 minutes multiple times a day can help reduce pain and swelling.
- Avoid using ointments or medicines internally or externally over the abscess without the doctor’s consent.
- Warm salt water rinses may offer relief by reducing irritation, gum swelling, and pain.
Prevention Of Dental Abscess

Dental abscesses can be prevented by taking measures to keep your teeth and gums healthy that promote dental health. The following tips can help your child prevent dental abscesses (2).
- Ensure your child maintains proper dental hygiene to prevent cavities. Have your child brush their teeth twice daily with fluoridated toothpaste and a soft-bristle toothbrush. Moreover, as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reports, drinking fluoridated water prevents tooth decay in about 25 percent of children and adults (6).
- Flossing the areas between the teeth can prevent plaque formation and gum diseases.
- Have your child’s oral health evaluated by the dentist regularly.
- Avoid giving excessive sugary food and drinks.
- Offer a balanced diet with all vegetables and fruits.
- Give a child-friendly mouthwash.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is a dental abscess an emergency?
A dental abscess that causes unbearable pain can require immediate treatment. Dental abscess-related emergency visits are common, and the incision and drainage may be treated in an emergency room with follow-up oral care (7).
2. Are dental abscesses common in children?
Although not all children may experience dental abscesses, it is fairly common and needs prompt medical attention. A study conducted on 300 children showed the prevalence of tooth abscesses primarily in preschoolers aged 3-5 years (8).
3. Can I pop a tooth abscess with a needle?
Do not pop a tooth abscess or press against it, as you may complicate it further. Instead, visit a doctor who will drain an abscess appropriately (9).
A dental abscess does not heal by itself and needs medical attention. The symptoms might sometimes improve, but a thorough dental evaluation is still necessary. Undergoing dental treatment and regular check-ups improves the lifespan of the teeth. Do not ignore your child’s symptoms of a dental abscess and seek an expert’s opinion.
Infographic: Facts About Root Canal Treatment In Children
Root canal, or the removal of the damaged tooth pulp, is done to preserve the integrity and function of the oral tissue among children. Although it is commonly done in children older than 12 years, it can be done for younger children in certain situations. Go through the infographic to learn more about root canal treatment in children. Illustration: Momjunction Design Team
Illustration: Abscessed Tooth In Child: Causes Risk Treatment And Prevention

Image: Stable Diffusion/MomJunction Design Team
An abscessed tooth can be painful and cause discomfort in children and adults. Learn about the causes, signs and symptoms, diagnosis, and how to treat and manage this condition in this video.
References
- Dental abscess.
https://www.nhsinform.scot/illnesses-and-conditions/mouth/dental-abscess/ - Dental abscess.
https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/dental-abscess/ - Dentoalveolar Infections.
https://www.childrenshospital.org/conditions/dentoalveolar-infections - Tooth abscess.
https://www.gosh.nhs.uk/conditions-and-treatments/general-medical-conditions/tooth-abscess/ - Toothache (Pulpitis) in Children.
https://www.nationwidechildrens.org/conditions/health-library/toothache-pulpitis-in-children - CDC Scientific Statement on Community Water Fluoridation.
https://www.cdc.gov/fluoridation/about/statement-on-the-evidence-supporting-the-safety-and-effectiveness-of-community-water-fluoridation.html - Justin L. Sanders and Richard C. Houck; Dental Abscess.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK493149/ - Vinay K Srivastava; (2022); Prevalence of Abscesses Associated with Carious Primary Teeth in Preschool Children and its Association with Age, Gender, Location, and Parent’s Education and Social Class: An Observational Study.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9357539/ - Abscess Drainage.
https://www.stanfordchildrens.org/en/topic/default?id=abscess-drainage-22-abscessdrainage
Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our nurturing community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with fellow parents.
Read full bio of Dr. Ashveeta Shetty
Read full bio of Dr. Ritika Shah
Read full bio of Rebecca Malachi
Read full bio of Vidya Tadapatri