Image: Shutterstock
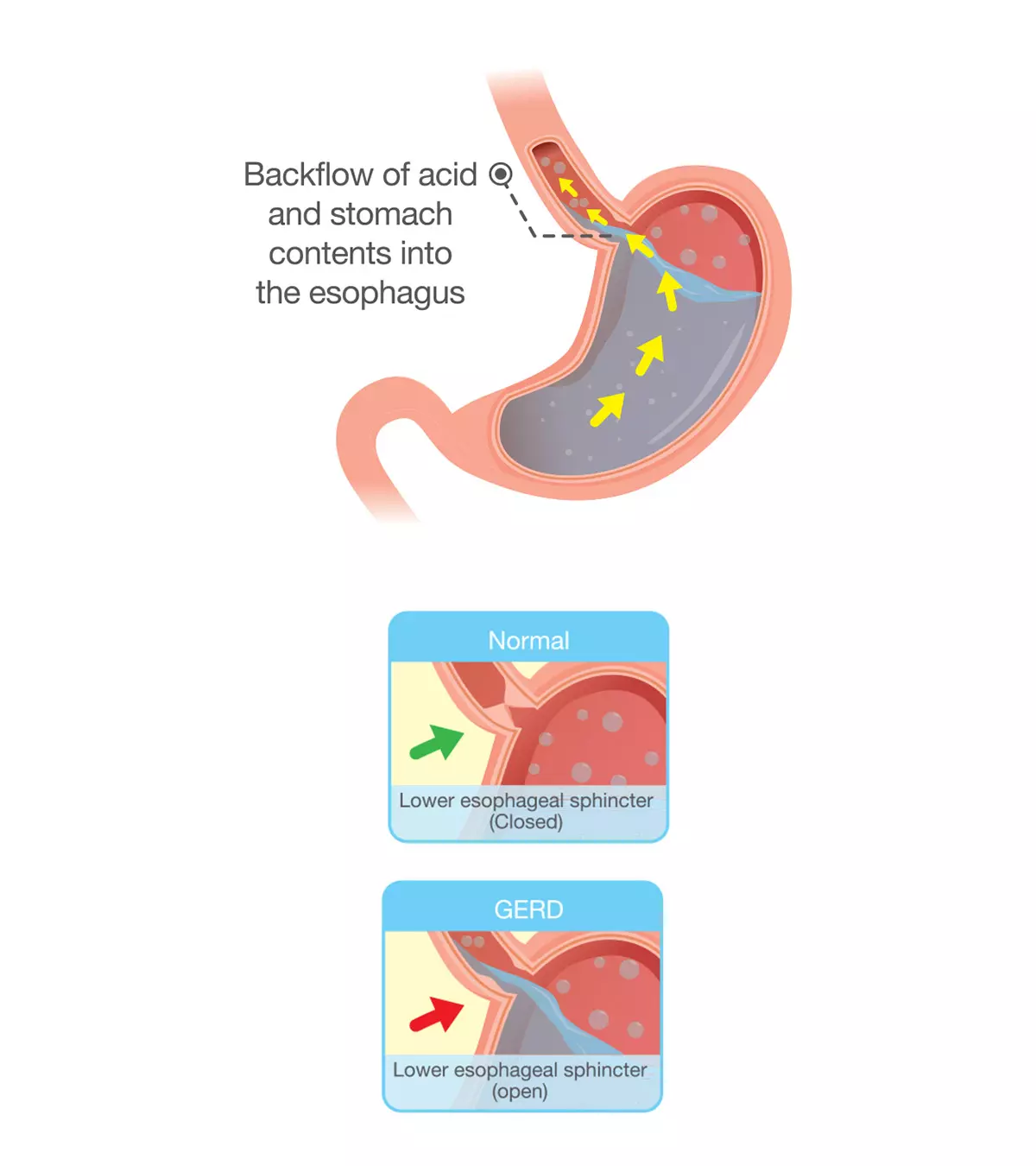
Appendicitis is the inflammation of the appendix, a pouch-like organ that projects from the coloniThe large intestine. on the lower right side of the abdomen. The location of pain and other classic symptoms or signs may not be present in appendicitis while pregnant. Therefore, it is recommended to seek medical care for the new onset of abdominal pain during pregnancy to identify and treat the underlying cause.
Read this post to know more about the incidence rates, causes, risk factors, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and complications of appendicitis during pregnancy.
Key Pointers
- Acute appendicitis affects less than 1% of pregnant women.
- Hardened stool, inflammatory bowel disease, and appendicolith are some common causes of this condition.
- The symptoms of appendicitis include anorexia, vomiting, dysuria, and diarrhea.
- Abdominal ultrasound imaging is the primary method for diagnosing appendicitis during pregnancy.
Is Appendicitis Common During Pregnancy?
Appendicitis is rare in pregnancy. However, it is one of the common causes of acute abdomen (abdominal condition requiring urgent treatment) in pregnancy, affecting around one in 1500 pregnancies. The overall incidence of acute appendicitis in pregnant women is 0.05-0.07%.
Appendicitis incidence rates in each trimester are (1):
- 19-36% in the first trimester
- 27-60% in the second trimester
- 15-33% in the third trimester
Although data from several sources show a higher incidence rate of appendicitis in the second trimester, some studies reported 59% of cases in the third trimester.
What Causes Appendicitis?
Appendicitis can occur due to various reasons. The cause may not be known in some cases. The possible causes of appendicitis may include (2):
- Hardened stool due to constipation, parasites, etc. blocking appendix
- Appendicolith (stone in the appendix)
- Enlarged tissue in the wall of the appendix due to infections in the digestive tract or other parts of the body
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Appendiceal tumors such as carcinoid tumors.
When any of these factors block the lumen of the appendix, bacteria builds up in the lumen and results in inflammation and infection of the appendix.
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Appendicitis In Pregnancy?
None of the clinical signs or symptoms are reliable for diagnosing appendicitis in pregnancy due to the change of appendix location and body changes and pains. In addition, the classic appendicitis signs such as Rovsing’siPositive indication of appendicitis when there is right lower abdominal pain upon pressing the left lower abdomen. and psoas signsiA muscle pain affecting the flexibility of thighs, often experienced by the appendicitis patients. are also not clinically significant during pregnancy. Therefore, ultrasound evaluation is recommended to confirm the diagnosis in all suspected cases (1).
Sudden onset of severe symptoms is seen in acute appendicitis, whereas milder symptoms often come and disappear in chronic appendicitis. Appendicitis symptoms in pregnancy may include (1):
- Right lower quadrant abdominal pain or discomfort
- Anorexia (eating disorder)
- Vomiting
- Nausea
- Uterine contraction
- Diarrhea
- Dysuria (painful urination)
- Rectal pain and vaginal tenderness in the first trimester
Fever and tachycardia may not be seen in appendicitis symptoms during pregnancy. In addition, the appendix changes its location during pregnancy, so that pain may be felt in the upper right side of the abdomen, especially in later trimesters.
 Research finds
Research findsHow Is Appendicitis Diagnosed In Pregnancy?
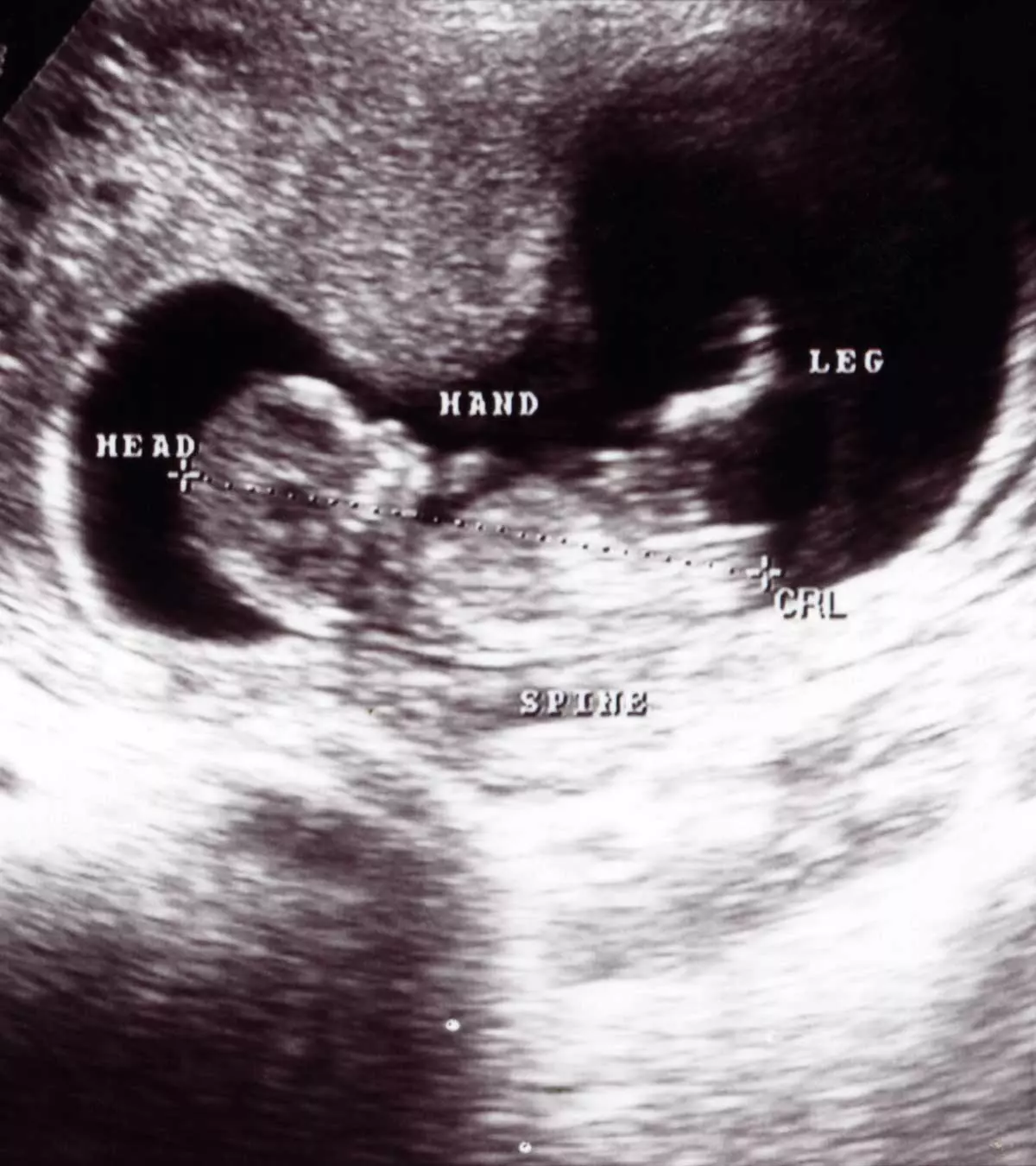
Imaging techniques help diagnose appendicitis in pregnancy. Abdominal ultrasound imaging is the first choice since it is easily available and safe. Ultrasound can also provide information about fetal health and obstetric causes of symptoms. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) without contrast is recommended if the ultrasound image is unclear (3).
Other tests and procedures ordered to diagnose appendicitis in pregnancy include (4):
- Medical history to know other possible causes of similar signs and symptoms. This should be the first step.
- Physical examination, including abdominal tenderness and rigidity.
- Complete blood count (CBC) to determine white cell count. Although WBC levels can be high in infection, it is not specific in pregnant women since high WBC levels are usual in pregnancy.
- Urinalysis or urine tests to look for red and white blood cells in the urine.
- Mild elevation of bilirubiniA byproduct of old broken down red blood cells, found in the liver, that is excreted from the body. may indicate appendix perforation in pregnancy.
CT scan is rarely ordered if the MRI is unavailable or ultrasound is inconclusive. However, doctors may order CT scans below the threshold to help reduce the risk of ionizing radiation to the baby. The decision may also depend on the weeks of pregnancy since the fetal malformations due to radiation are high in the first trimester. However, the risk lowers after the completion of organ development (3).
The following obstetric and non-obstetric conditions may mimic appendicitis in pregnancy (1):
- Ovarian cyst
- Salpingitis (inflammation of the fallopian tubes)
- Placental abruption
- Chorioamnionitis
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Preeclampsia
- Adnexal torsioniTwisting of the ovaries around the surrounding tissues due to a large cyst.
- Round ligament syndrome
- Preterm labor
- Gastroenteritis
- Mesenteric adenitis
- Pancreatitis
- Nephrolithiasis (kidney stones)
- Urinary tract infections
- Cholecystitis (inflammation of gall bladder)
- Cholelithiasis (gallstones)
- Hernia
- Bowel obstruction
- Pyelonephritis (type of UTI)
- Right lower lobe pneumonia
- Sickle cell disease
How Is Appendicitis Treated In Pregnancy?
After the evaluation, if there is no risk of perforation, doctors may recommend antibiotic treatment for pregnant women. This may help reduce the infection and related symptoms. Second-generation cephalosporins cover gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, and clindamycin or metronidazole cover anaerobic bacteria (3).
In some cases, the surgical intervention is planned within 24 hours since delaying may increase the risk of free perforation. For example, open or laparoscopic appendectomy is performed to remove the appendix in pregnant women. However, the surgical procedures are modified to avoid injury to the pregnant uterus. Following hospitalization, doctors may recommend rest at home for a week or more to aid recovery and promote healing (3).
An anonymous blogger who experienced appendicitis when she was eight weeks pregnant shares her story of getting a laparoscopy. She says, “They (the medical staff) examined the baby, and everything looked good. The heartbeat was strong. She (the doctor) then poked and prodded me from the inside, and as soon as she landed on one spot in particular, I started screaming, ‘That’s it! Whatever you are on right now. That’s where the pain is coming from.’ They admitted me to the hospital. I had laparoscopic surgery that went without a hitch. I spent the next few days in the hospital healing (i).”
 Point to consider
Point to considerHow Is The Perforated Appendix Treated In Pregnancy?
The treatment for a perforated appendix may depend on the type of perforation. Urgent appendectomy with irrigation and drainage of the abdominal cavity (peritoneal cavity) is needed for free perforation. The pus and fecal material are leaked into the abdominal cavity after the appendix bursts. This may cause sepsis, preterm labor and delivery, and even fetal loss if left untreated.
The appendix is surrounded by other abdominal structures such as the intestines and peritoneum. So, when there is a perforation, it can get walled off. The other theory is that when there is an inflammation of the appendix, the mobile fat layer omentumiA fatty tissue layer that stretches from the stomach to all the organs and covers the inflamed areas to heal them. , known as “policeman of the abdomen,” can move the appendix and contain the infection. This may result in a pus-filled abscess outside the appendix covered by the omentum (3).
What Are The Complications Of Appendicitis During Pregnancy?
Appendicitis in pregnant women is associated with a higher risk for morbidity and perforation than non-pregnant women. There can be a 55% of perforation rate in appendicitis during pregnancy. This may increase the risk for miscarriage (fetal loss) and preterm delivery if not intervened on time. Multiple research institutions in the United States conducted a collaborative study on managing complex appendicitis during pregnancy. The findings revealed that among expectant mothers with complicated appendicitis, for each additional day of delay in having the surgery, the likelihood of experiencing preterm delivery, preterm labor, or abortion increased by 23%. Ensuring timely diagnosis and treatment is crucial in safeguarding maternal health and preventing life-threatening risks.
There is up to 2% risk for maternal mortality and 1.5-9% risk for fetal loss in unruptured appendicitis. The risk may increase with perforation. The complications such as rupture of the appendix are high in the third trimesters (1) (5).
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is it safe to have appendix surgery while pregnant?
LaparoscopiciA surgical technique that enables a surgeon to reach the belly and pelvis from the inside through a small incision. appendectomy can be safely performed during pregnancy. The correct surgical techniques do not affect the mother or fetus irrespective of gestation age. Laparoscopy is often preferred over open surgeries since it has less risk for postoperative complications (7).
2. Can appendicitis cause a miscarriage?
Non-perforated appendicitis can progress to appendiceal rupture associated with miscarriage and childbirth complications such as early delivery, or fetal loss. An accurate and rapid diagnosis of the appendix is always established in pregnant women to avoid these risks (8).
3. Does appendix removal affect pregnancy?
Appendectomy and scarring may increase the risk of ectopic pregnancy in the future. However, it may not impact future fertility in women (9).
4. What if the appendix bursts in pregnancy?
Emergency surgery or appendectomy removes the appendix if it bursts during pregnancy. Pregnant women are at high risk for developing appendix rupture and sepsis if there is spillage of infectious content to the abdominal cavity (4).
Appendicitis in pregnancy has nonspecific symptoms. You may seek medical care to diagnose the cause of abdominal pain during pregnancy since taking pain medication may mask the pain and lead to complications. Abdominal ultrasound is pregnancy-safe, and it is always done before planning the appendix surgery to avoid unnecessary interventions.
Infographic: Possible Signs Of Appendicitis During Pregnancy
The appendix’s location and the ongoing pregnancy may make the usual symptoms of appendicitis unreliable. Therefore, you must check for certain unusual or uncommon signs. The following infographic lists these indicators, helping you stay alert and get timely treatment. Illustration: Momjunction Design Team
Illustration: Appendicitis During Pregnancy: Signs Causes And Treatment

Image: Stable Diffusion/MomJunction Design Team
Pregnant women can experience acute appendicitis. This video gives valuable insight into the clinical features, diagnosis, and treatment of appendicitis during pregnancy in this video.
Personal Experience: Source
MomJunction articles include first-hand experiences to provide you with better insights through real-life narratives. Here are the sources of personal accounts referenced in this article.
i. Appendicitis while pregnant.
https://writtenwindowtomysoul.wordpress.com/2020/11/25/appendicitis-while-pregnant/
References
- Appendicitis In Pregnancy.
https://www.jabfm.org/content/19/6/621 - Symptoms & Causes of Appendicitis.
https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/appendicitis/symptoms-causes - Gad Aptilon Duque and Stephen Mohney; Appendicitis In Pregnancy.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK551642/ - Appendicitis In Pregnancy. Medical Attention Is Highly Needed When A Pregnant Woman Complains Of New Abdominal Pain.
https://www.bangkokhospital.com/en/content/be-aware-appendicitis-while-pregnant - Anne-Kathrine Carstens, et al; Nonoperative Treatment of Appendicitis during Pregnancy in a Remote Area.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5830160/ - Libin Huang et al.; Comparison of Antibiotic Therapy and Appendectomy for Acute Uncomplicated Appendicitis in Children.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5470362/#:~:text=The%20presence%20of%20appendicolith%20is,undergo%20more%20detailed%20clinical%20evaluation - Jesper Frølund Laustsen et al.; Laparoscopic appendectomy during pregnancy is safe for both the mother and the fetus.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27477796/#:~:text=Conclusion%3A%20Laparoscopic%20appendectomy%20is%20safe,risk%20of%20post%2Doperative%20complications - L. Aggenbach et al.; Impact of appendicitis during pregnancy: No delay in accurate diagnosis and treatment.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1743919115000436#:~:text=emergency%20during%20pregnancy.-,A%20rapid%20and%20accurate%20diagnosis%20of%20appendicitis%20is%20particularly%20critical,3%5D%2C%20%5B4%5D - Tarig Elraiyah et al.; The effect of appendectomy in future tubal infertility and ectopic pregnancy: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25303785/
Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our nurturing community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with fellow parents.
Read full bio of Dr. Karla S. Sanchez-Banos
Read full bio of Dr Bisny T. Joseph
Read full bio of Rebecca Malachi
Read full bio of Reshmi Das