Shutterstock
The benefits of fruits and vegetables for kids are numerous as they provide vital nutrients to support their growth and development. Additionally, sufficient intake reduces the risk of major chronic diseases, such as type-2 diabetesiA condition where the body cannot use insulin properly. and hypertension.

However, feeding children adequate amounts of fruits and veggies is a challenge since children tend to be picky eaters. But first, we must be aware of how much fruits and veggies children need daily.
Keep reading to understand how you can encourage children to eat fruits and veggies, their possible health benefits, and some interesting facts about these food groups that your child will love to know.
Key Pointers
- Fruits and vegetables provide essential nutrients for growth and development, combat chronic health issues, enhance immunity, and support healthy dietary practices.
- They offer health benefits for energy, digestive health, gut health, immunity, bone health, cognitive health, and overall health.
- Involving kids in shopping, being a role model, experimenting with cooking, keeping a fruit bowl, and diversifying fruit use in meals promote healthy eating.
- Cooking and preparing fruits and vegetables with children and growing them together can also increase their intake.
Why Are Fruits And Vegetables Important For Kids?

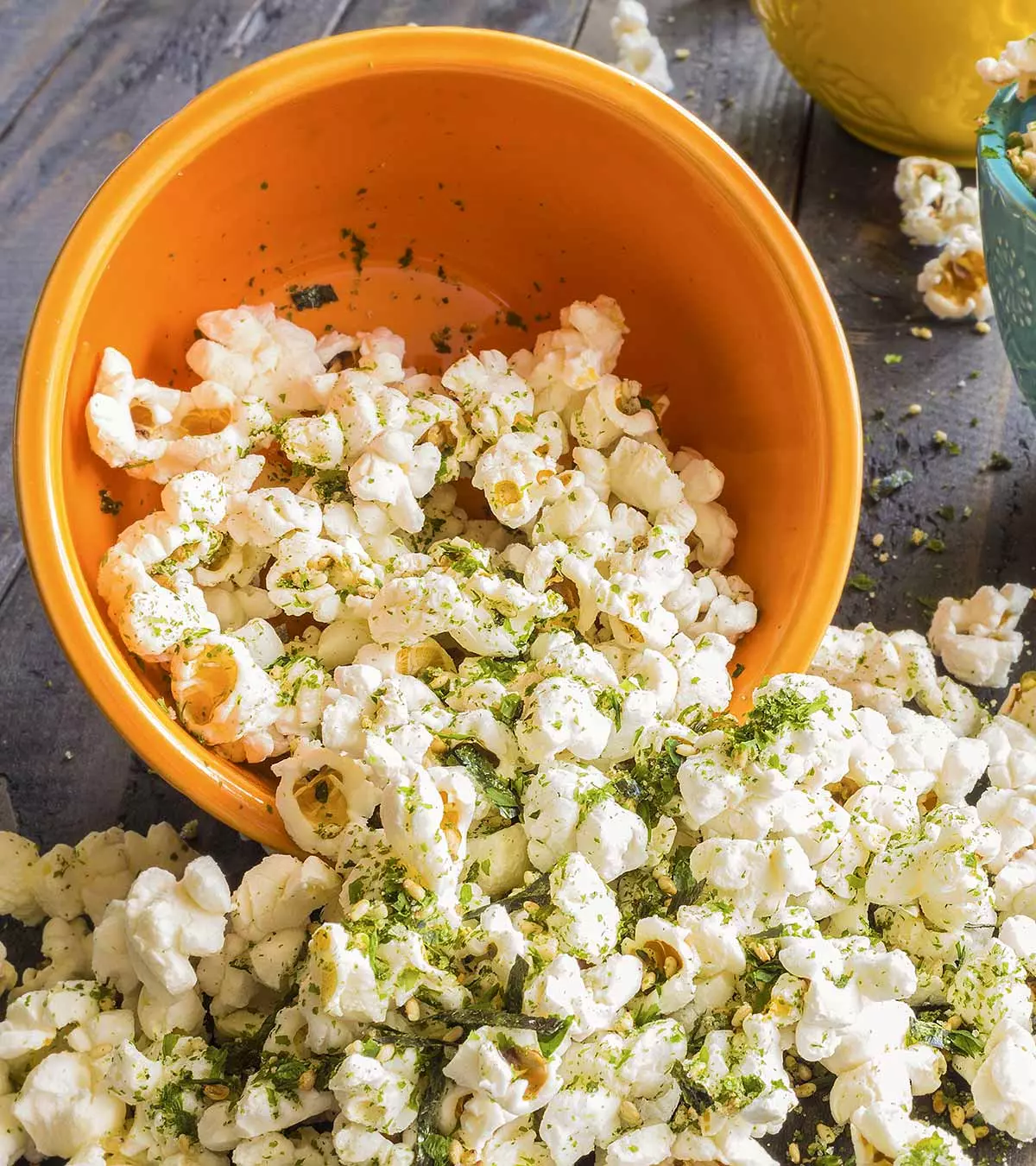
Fruits and vegetables help provide several nutrients necessary for the rapid growth and development of children. Foods from these two groups help in:
- Enhancing the immune system and thus fighting-off oxidative stressiA condition of several free radicals and a lack of antioxidants to remove them. (1)
- Combating chronic health issues in the long run (2)
- Maintaining overall well-being by developing and supporting healthy dietary practices (3)
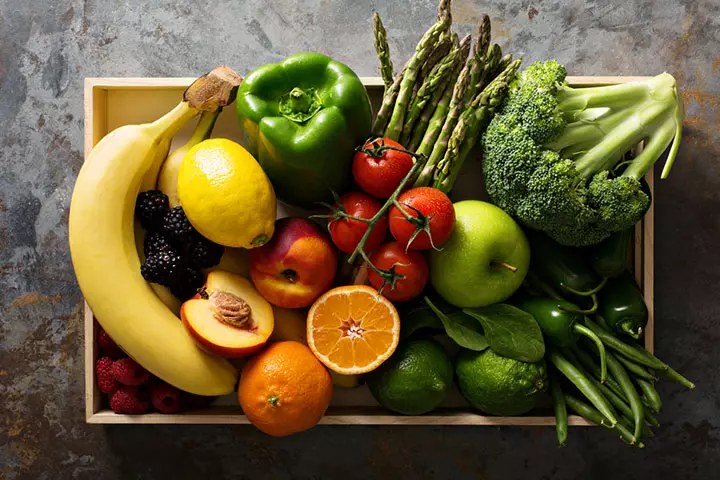
How Much Of Fruits And Vegetables Should Children Eat Every Day?

The Dietary Guidelines For Americans 2015-2025 recommends the following number of cup-equivalents per day for different age groups of children (4) (5).
Recommendation for boys
| Age (years) | Vegetables (cups-equivalent per day) | Fruits (cups-equivalent per day) |
|---|---|---|
| 1-3 | 1 – 1.5 | 1 – 1.5 |
| 4-8 | 1.5 – 2.5 | 1 – 2 |
| 9-13 | 2 – 3 | 1.5 – 2 |
Recommendation for girls
| Age (years) | Vegetables (cups-equivalent per day) | Fruits (cups-equivalent per day) |
|---|---|---|
| 1-3 | 1 – 1.5 | 1 – 1.5 |
| 4-8 | 1.5 -2.5 | 1 – 2 |
| 9-13 | 1.5 – 3 | 1.5 – 2 |
* Cup-equivalent refers to the amount of food from each food group with similar nutritional content (6)
The total number of cups of fruits and vegetables can be spread across multiple servings per day. Consuming the recommended amount of fruits and vegetables ensures health benefits to kids in the long run.
Health Benefits Of Fruits And Vegetables For Children

Including phytonutrient-rich fruits and vegetables in your child’s diet can provide them with numerous health benefits. Fruits and vegetables are rich in essential micronutrients, dietary fiber, and bioactive compoundsiMolecules present in plants and foods with antioxidant properties and health-promoting effects. . These substances can provide several health benefits, as mentioned below (7).
- Energy: Fruits and vegetables contain natural sugar, glucose, and fructoseiA natural sweetener present in fruits, honey, and vegetables. . Both these sugars are condensed sources of energy and are a healthy replacement for high-sugar processed items like candies, colas, and cakes. Eating fruits and vegetables, in recommended portions, can help manage your child’s weight and thus combat lifestyle-related health issues, such as obesity, in the long run.
 Quick fact
Quick fact- Digestive health: Whole fruits and vegetables (with peel) are rich in dietary fiber, which includes soluble and insoluble fiber. Insoluble fiber present in the fruit helps add bulk to the diet. Besides, it helps in smooth intestinal motility. Both these qualities help regular bowel movement and thus avoid constipation (8).
- Gut health: Whole fruits and vegetables provide fermentable dietary fiber such as pectin, inulin, resistant starch, and lignin (9). These fermentable fibers act as ideal prebiotic support that might enhance gut microflora (10). A healthy gut promotes absorption of necessary nutrients for growth.
- Immunity: Regular consumption of recommended amounts of fruits and vegetable aid in enhancing gut microflora. A healthy gut microbiota helps improve general health by maintaining the immune system (11). Besides, fruits and vegetables provide essential vitamins, minerals, and bioactive compounds, which also play a role in maintaining immunity (12) (13).
- Bone health: Several epidemiological studies indicate the direct relationship between bone health and regular consumption of high amounts of fruits and vegetables (14). The prime evidence is the possible ability of fruits and vegetables to enhance potassium uptake (15). Besides, fruits and vegetables contain vital vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that could also help maintain bone health.
- Cognitive health: It is well-known that green leafy vegetables such as kale, collards, and broccoli boost the functioning of the brain. This ability of these vegetables is attributed to the presence of micronutrients such as vitamin K, lutein, folate, and beta carotene. Fruits rich in flavonoidsiA group of naturally occurring antioxidant and anti-inflammatory compounds found in plants and fruits. and essential micronutrients such as berries also help in maintaining cognitive health (16) (17).
- Overall health: Whole fruits and vegetables are rich in almost all the vitamins except vitamin B12. Similarly, they are rich in minerals and bioactive compounds such as phenolsiCompounds in plants with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. , flavonoids, and carotenoidsiColored pigments found in plant-based foods that act as a precursor in the synthesis of vitamin A and protect cells from damage. . These nutrients have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects that help in supporting general health (18).
The nutrients of fruits and vegetables together provide several general health benefits (19).
Fruits And Vegetables Chart For Kids
A plant-based diet is a great way to improve your child’s cognitive function and overall health. Ensuring your child stays hydrated is crucial for their health and well-being, and consuming fruits and vegetables can help with that. Incorporating a variety of plant-based superfoods such as fruits and vegetables into your child’s diet can help them discover new flavors and develop a love for healthy foods.
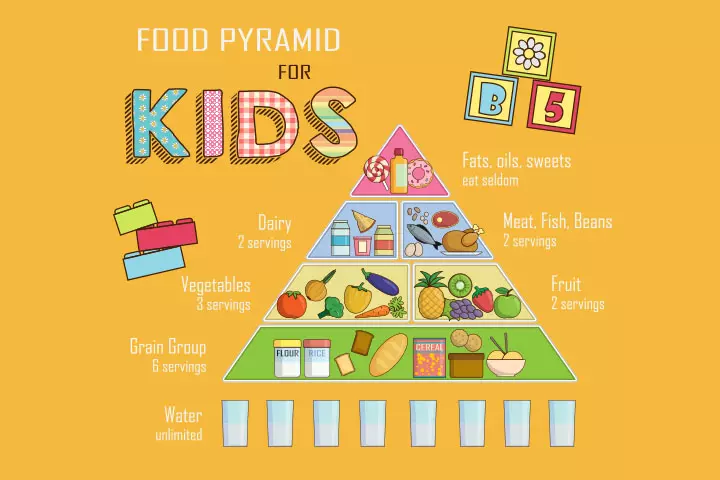
It is good to select seasonal varieties of fruits and vegetables as they are fresh and readily available (20). However, you can also include their alternative forms, such as frozen, canned, and dried produce. You may find it helpful to refer to the food pyramid for kids, which presents the suggested daily portions of various food groups, taking into account your child’s age and gender. The following chart provides additional information.
How To Make Your Kids Eat Fruits And Vegetables?

It is not easy to convince a child to eat adequate vegetables and fruits. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s survey revealed that approximately one in two of the children surveyed failed to consume a vegetable on a daily basis. At the same time, one in three did not include fruit in their daily diet. Hence, here are a few tips to motivate them to eat sufficient fruits and vegetables every day (21) (22).
- Involve your kids in grocery shopping. This way, you can show them the variety of seasonal fruits and vegetables that could be included in their diet. Take their opinion about what vegetables and fruits should be brought for the week and what dishes you can make with them. In addition, opting for organic and locally grown fruits and vegetables can ensure that your child isn’t exposed to harmful chemicals.
- Be a role model. Do not say no to any fruit or vegetables in front of your child. Eat a variety of fruits and vegetables with your child so that they may also learn to do the same.
- The presentation of food is important for everyone. However, its importance is higher when it comes to attracting kids. Thus, experiment with interesting ways of cooking. The use of different colors of vegetables and fruits in a dish is a wise start. You may also try out different vegetable snacks for kids. Sarah, a mother of three, highlights the importance of food presentation for children’s enjoyment. She says, “They (her children) go Bonkers for fruit slices on skewers, ‘ghosty bananas’ (half bananas with two chocolate chips for eyes), or their names written with carrot sticks (i).”
- Try to keep a bowl of fresh fruit on the table at all times. This will help them munch on fruits whenever they are craving for snacks.
- Share healthy alternatives to your kid’s favorite unhealthy choices. For example, you can replace colas with fresh smoothies and fruit juices with fruit salad and vegetable snacks.
- Stick to whole fruit and vegetables. Avoid giving your kids fruit juices as they can elevate blood sugar faster than whole fruits do.
- Educate them to eat raw vegetables, preferably with skin as much as possible. If they do not like raw vegetables, then try giving soft-cooked vegetables as an alternative. Some kids might prefer raw vegetables, while others might not.
- To diversify the use of fruits, prepare fruit-based desserts such as pies, ice creams using frozen bananas, and puddings. You may also consider dry fruits for kids.
- You can try including fruits and veggies in all the meals, i.e., breakfast, lunch, and dinner.
- Cook and prepare fruits and vegetables with them! Children love being involved in the kitchen. It will effectively increase their intake of fruits and vegetables. Try easy dishes like fruit salad or vegetable salad.
- If you have the space, try to grow fruits and vegetables with your children. Studies have shown that it is effective in increasing children’s fruit and vegetable intake.
- Plan fun activities and challenges to make your kids try new fruits and vegetables and reward them for their efforts.
With the best of your efforts, kids can start eating a variety of fruits and vegetables. However, at times, they may simply refuse to eat a particular vegetable. In such a situation, you could follow some simple steps to set things right.
What To Do When Children Refuse To Eat Fruits And Vegetables?
If your child refuses to eat a fruit or vegetable, you may follow the steps given below (23).
- Do not give up if your kid is not eating a particular fruit or vegetables. It may take as many as 15 times for a child to develop a taste for a food item. So, be patient and persistent with your efforts.
- Do not force, nag, bargain, or bribe your child to eat a vegetable. Forcing might make a child lose interest in the food completely.
- Do not introduce a fruit or vegetable to your kid at dinner time. Most children are tired by dinner time and might not have an interest in trying something new.
- For extremely picky eaters, get sneaky. Use shredded or thinly sliced fruits and vegetables instead of big pieces. It will help the fruit or vegetable to stay in disguise. You may try adding broccoli florets or thinly sliced carrots to pasta or green salad. You may also try vegetable sauces if your kid is fussy about eating vegetables.
- Try adding the fruit or vegetable that your kid does not like in the dishes that they like. It will encourage them to try the vegetable or fruit through the dish. The chances are that after repeated trials, your child may start liking the vegetable.
Convincing a kid to eat what they don’t like is not easy. However, while you try, share some fun facts about fruits and vegetables with them.
Interesting Facts About Fruits And Vegetables

Learning more about a fruit or vegetable might make a child curious enough to try it. So, when you introduce any new vegetable or fruit to your child, share some interesting facts with them to keep them intrigued. You can also use these interesting facts during family trivia night or party for children.
Interesting fruit facts for kids
The fruit is the simplest food available as it needs no cooking. It can be used as an ingredient in a meal or a food item, or eaten raw! Here are a few fruit facts you can share with your kids.
- Ever thought an apple looks as beautiful as a rose? Well, it belongs to the rose family.
- A banana is actually an herb, while tomato is a fruit.
- Does your kid love mangoes? Then, that’s one thing he or she has in common with orangutans and the rest of the world. Mango is the most loved fruit around the world.
- Apple floats on water as 25% of it is filled with air.
- Did you know that there are around 7,000 varieties of apples in the world?
- On average, a strawberry has 200 seeds, which are actually the plant’s ovaries.
- Pumpkins and avocados are fruits, not veggies. Eggplants are also fruits and are botanically classified under berries.
- Pineapples are called so because they look like huge pine cones.
 Trivia
TriviaInteresting vegetable facts for kids
Here are some fun facts about veggies.
- Edible broccoli is a part of the bigger flower. We eat the baby part of the flower as the mature parts of the green vegetable are bitter. Cauliflower is also a flower.
- Vegetables need a warm climate to grow; a few vegetables like kale, carrots, leeks, spinach, parsnips, lettuce, and cabbage grow in cold climates.
- The highest amount of nutrients in a vegetable is found in the layer right under the skin.
- Vegetables are nutritious in any form, frozen or fresh. So are fruits.
- You can cook vegetables in any way you want but the lesser you cook them, the better it is. Vegetables are known to lose their nutritional content when boiled. Try steaming and baking or eating them raw to save the nutrients in vegetables.
- The tomato was declared a vegetable by the US Supreme Court in 1893.
- Cabbage and cucumbers are among the oldest known vegetables in the world.
- Carrots were originally purple. They have a high content of vitamin A and can improve night-vision – who needs night vision goggles, eh?
- Garlic is said to keep mosquitoes away.
- Vegetables with a strong or pungent smell are highly nutritious, as they contain high quantities of vitamin K, C and folate, and minerals like potassium, magnesium, and calcium. Such veggies include cabbage, radish, scallions, and spring onions. The next time your kid complains of a smelly vegetable, tell them it is for their own good!
 Did you know?
Did you know?Frequently Asked Questions
1. Are there any risks associated with eating too many fruits for children?
Children may consume excessive fruits if they consume more servings of smoothies and juices. The high sugar intake in such cases may cause dental caries and obesity (26).
2. Are there any fruits or vegetables that are not recommended for children to eat?
Children should eat all types of whole and fresh fruits and vegetables as a part of a balanced diet. However, they should avoid processed products, such as fruit bars and fruit straps, as they are high in sugar (27).
3. What are the differences between fresh, frozen, and canned fruits and vegetables?
Fresh fruits and vegetables have limited shelf life compared to frozen and canned products. Frozen fruits and vegetables undergo processing, such as blanching (to kill bacteria and restrict spoiling) and then freezing (considered nutritionally equivalent to fresh produce), whereas canned products may undergo multiple processing steps and contain added sugars and salts. Canned foods are considered to have less nutritional value than frozen foods (28).
4. What are some easy recipes to incorporate more fruits and vegetables into my child’s diet?
Smoothies, salads, and stir-fries are some easy and quick recipes you can incorporate into your child’s diet to include many fruits and vegetables at once.
Fruits and vegetables provide the essential nutrients and fibers needed for the proper growth and development in children. Incorporating healthy foods for kids into their diet, including a variety of fruits and vegetables, is crucial for their overall well-being. Therefore, you should teach your children the importance of edible plant products and include them in their daily diet with proper meal planning. This way, you can encourage them to have it raw and in meals. However, if your little one is a picky eater, you can get sneaky with the food and try including them in dishes your child likes to eat. You may cook different interesting ways to make their diet edible and healthy.
Infographic: Effective Tips To Make Children Eat Fruits And Vegetables
Fruits and vegetables are loaded with nutrients and bioactive compounds that support healthy growth and development in children. However, it can be challenging to get your children to eat them voluntarily. So check out the infographic below for practical advice on getting your children to eat fruits and vegetables. Illustration: Momjunction Design Team
Illustration: Fruits And Vegetables For Kids: Importance Benefits And Tips

Image: Stable Diffusion/MomJunction Design Team
Eating fruit and veg is important for growing bodies! Learn why in this fun video for younger kids.
Personal Experience: Source
MomJunction articles include first-hand experiences to provide you with better insights through real-life narratives. Here are the sources of personal accounts referenced in this article.
i. 10 ways to help kids eat fruit & vegetables;https://alovelettertofood.blogspot.com/2015/02/10-ways-to-help-kids-eat-fruit.html
References
1. How to boost your immune system; Harvard Health
2. Maxine Sharps and Eric Robinson; Encouraging children to eat more fruit and vegetables: Health vs. descriptive social norm-based messages; National Center For Biotechnology Information
3. How to Eat Healthy; U.S. Department of Health and Human Service
4. Shifts Needed To Align With Healthy Eating Patterns; Health.gov
5. Fruit-and-veggie-toolkit-for-kids; Heart.org
6. Cup- and Ounce-Equivalents; Health.gov
7. Fruit and vegetables; Better Health Channel.
8. Mark L. Dreher; Whole Fruits and Fruit Fiber Emerging Health Effects; National Center For Biotechnology Information
9. Devinder Dhingra et al.; Dietary fibre in foods: a review; National Center For Biotechnology Information
10. Jiefen Cui et al.; Dietary Fibers from Fruits and Vegetables and Their Health Benefits via Modulation of Gut Microbiota; Wiley Online Library
11. Victoria Bell et al.; One Health, Fermented Foods, and Gut Microbiota; National Center For Biotechnology Information
12. Rui Hai Liu; Health-Promoting Components of Fruits and Vegetables in the Diet; National Center For Biotechnology Information
13. Liu RH; Dietary bioactive compounds and their health implications.; National Center For Biotechnology Information
14. Rui Qiu et al.; Greater Intake of Fruit and Vegetables Is Associated with Greater Bone Mineral Density and Lower Osteoporosis Risk in Middle-Aged and Elderly Adults; National Center For Biotechnology Information
15. New SA; Intake of fruit and vegetables: implications for bone health.; National Center For Biotechnology Information
16. Foods linked to better brain power; Harvard Health Publishing
17. Jeremy Spencer;The impact of fruit flavonoids on memory and cognition; British Journal of Nutrition, Cambridge University Press
18. Shashirekha MN et al.; Status of bioactive compounds in foods, with focus on fruits and vegetables.; National Center For Biotechnology Information
19. van Breda SGJ and de Kok TMCM; Smart Combinations of Bioactive Compounds in Fruits and Vegetables May Guide New Strategies for Personalized Prevention of Chronic Diseases.; National Center For Biotechnology Information
20. Macdiarmid JI; Seasonality and dietary requirements: will eating seasonal food contribute to health and environmental sustainability?; National Center For Biotechnology Information
21. How to Get Your Child to Eat More Fruits & Veggies; Healthy Children; American Academy of Pediatrics
22. Encouraging Your Child to Eat Fruits and Vegetables; University of California San Francisco
23. How to get your kids to eat fruit and veggies; Queensland Government
24. Are apples better than coffee?; Cornell University
25. Fun Facts about Potatoes; Montana State University
26. Smoothies—Helpful or Harmful?;; Utah State University
27. Children’s diet – fruit and vegetables; Better Health Channel
28. Canned Versus Frozen Fruits and Vegetables: What’s Better for You?;; UCLA Health
Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our nurturing community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with fellow parents.
Read full bio of Charmaine Dominguez
Read full bio of Swati Patwal
Read full bio of Rohit Garoo
Read full bio of Shinta Liz Sunny
















