Image: Shutterstock
The brain is the most complex organ in the human body. As a part of the nervous system, the brain manages and coordinates all important bodily functions. Learning about the parts of the brain and their functions can be intriguing for children.
The brain controls senses, motor skills, emotions, thoughts, respiration, memory, hunger, and body temperature. Read this post to know more about how the brain functions and other interesting information.
Key Pointers
- The brain functions like a computer, but its ability to process emotions makes it different from a machine.
- The huge network of nerves enables communication between the brain and the rest of the body.
- The human brain is made up of 60% fat, makes up to 2% body weight, functions well when you are hydrated, and many other fascinating facts as you scroll down.
How Does The Brain Work?
The brain works like a computer. However, what makes it different from a machine is its ability to process emotions that lead to the human mind and intelligence. The brain consists of billions of nerve cells or neurons that receive information from different sensors or receptors of the body through synapses. This information is processed, and a relevant stimulus is sent back to various parts of the body (1).
The complex and huge network of nerves, which connect the brain to the rest of the body, enable communication in a fraction of a second (2). Different parts of the brain have specific functions, but they work together to regulate all the processes.
Parts Of The Brain And Their Functions
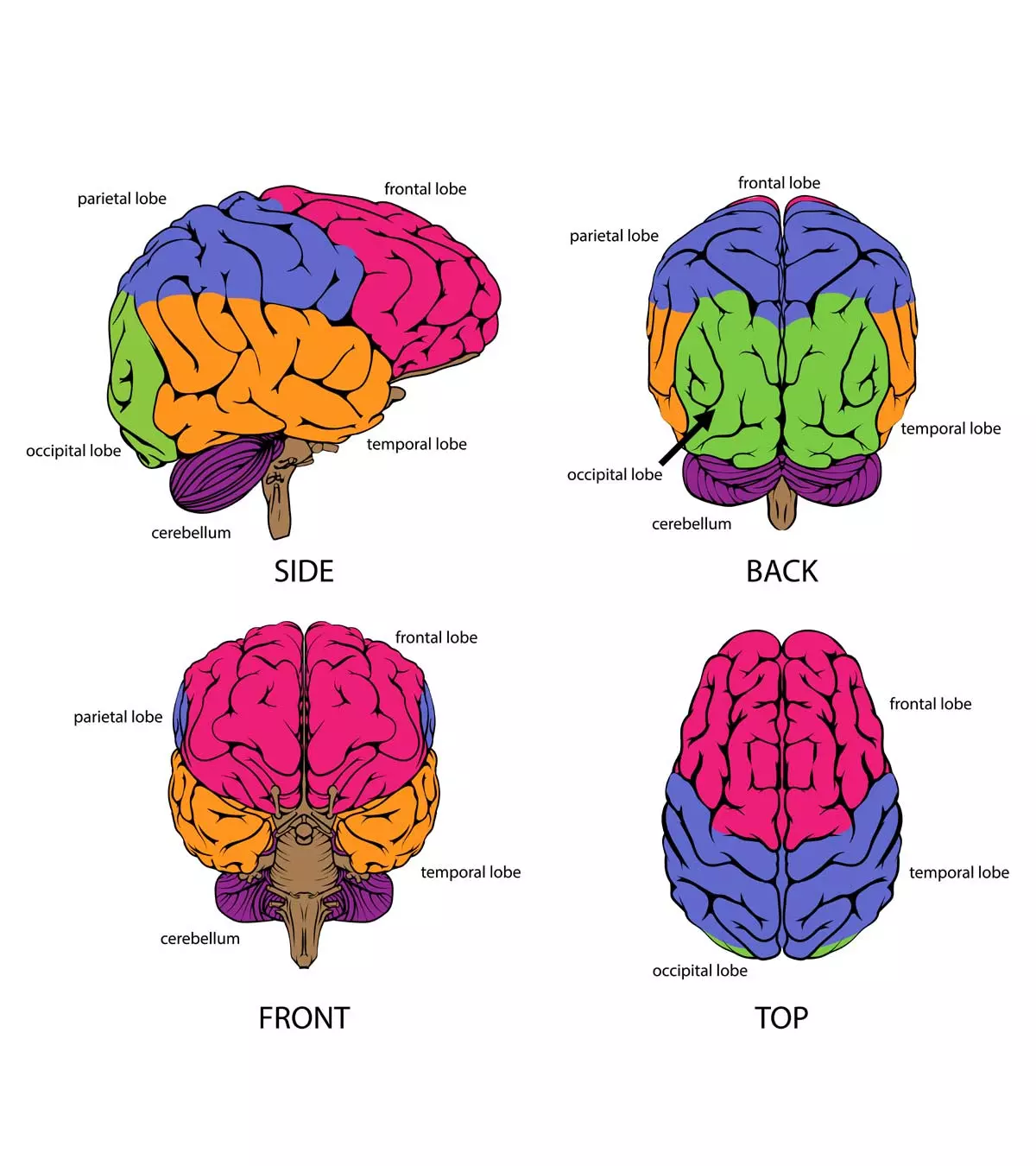
The brain and spinal cord are part of the central nervous system (CNS). The brain weighs just about two to three pounds and appears like a walnut. The brain is composed of three main regions — cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem (3).
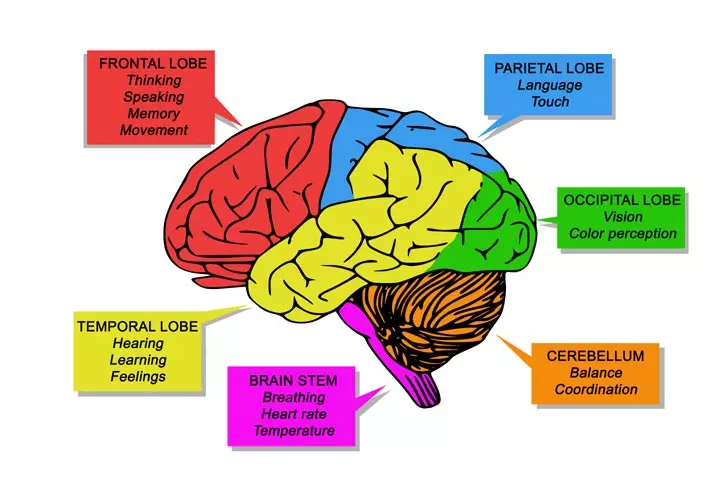
Image: Shutterstock
Let us discuss these parts and their functions in detail (1) (3) (4).
- Cerebrum: The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain. The outermost layer is called the cerebral cortex or the ‘gray matter’. The cerebrum, divided into four ‘lobes’ or regions, controls higher functions, such as learning, reasoning and speech, and senses, such as vision and hearing.

Image: Shutterstock
 Quick fact
Quick fact- Occipital lobe: Located at the back of the cerebrum, the occipital lobe is the primary visual area of the brain. The occipital lobe processes visual information for your eyes. In other words, the occipital lobe helps you make sense of the shapes, colors, and spatial orientation (position or direction of objects in space).
- Frontal lobe: Located at the front part of the brain, the frontal lobe is responsible for concentration, problem-solving, creativity, thinking, planning, organizing, short-term memory, movement, and motor planningi, and personality characteristics. So, if you are wondering what keeps your kids organized at school or keeps your emotions under control, it is this lobe.
- Temporal lobe: Located near the ears, this lobe is responsible for auditory perceptioni or cognition, speech, hearing, memory, and smell recognition.
- Parietal lobe: Located between the frontal and occipital lobe, the parietal lobe helps in processing sensory information, such as taste, touch, pain, and temperature. The lobe helps in understanding spatial relationships, which is the relative movement of objects and people in a space.
- Cerebellum: This is the second-largest part of the brain. Located at the back of the head, the cerebellum is responsible for coordinating muscle movements, particularly those that help maintain the body’s balance, equilibrium, and posture. The cerebellum combines all the sensory information from the eyes, ears, and muscles to coordinate movements.
- Brainstem: Brainstem is the third region of the brain that anchors the spinal cord. Located in front of the cerebellum, the brainstem consists of the ponsiLargest structure of the brainstem involved in information processing and various other brain functions. , medullaiThe lowest part of the brainstem that connects the brain to the spinal cord. , and the midbrainiA topmost region of the brainstem, involved in vital brain functions such as hearing, motor color, and sleep regulation. . The brainstem is involved in essential life functions, such as breathing, regulation of blood pressure, and heart rate. It also plays a vital role in the movement of the eyes and mouth, consciousness, sneezing, coughing, vomiting, sleeping, swallowing, and other involuntary muscle movements.
Facts About The Brain For Kids
Here are some fun facts about the brain that can intrigue your kids and inspire them to learn more about how it works.
- The sperm whale has the biggest brain among animals, weighing almost 20 pounds.
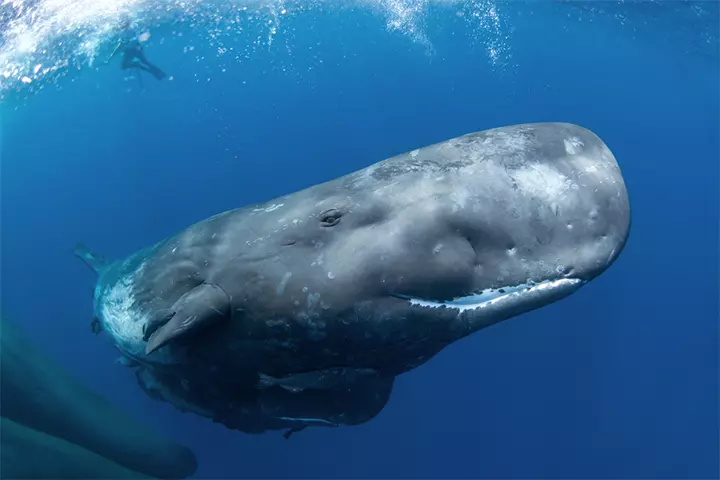

Image: Shutterstock
- It is a myth that humans use only 10% of their brains.
- Human brain consists of around 100 billion nerve cells and approximately 10 times more glial cellsiNon-neuronal cells that protect the nerve cells and support the functions of the central nervous system. .
- Human brain is made up of 60% fat.
- The size of the brain decreases with age.
- The brain size of the earliest humans was similar to that of chimpanzees. Human and chimpanzee brains have evolved over a period of time (5)(6).
- Human brain makes up to 2% of the body’s weight but uses approximately 20% of the oxygen supply (7).
- Human brain uses about two-thirds of its energy to generate nerve signals, and the remaining energy is used for cell maintenance (8).
- Nerve impulses can travel as fast as 275 miles per hour or 120 meters per second (9).
- Human brain and the spinal cord are covered by three layers of tissue collectively known as the meninges. A clear fluid called cerebrospinal fluid flows between these layers (10) (11).
 Did you know?
Did you know?- The left part of the brain is responsible for analytical thinking. The right part helps in creative thinking (12).
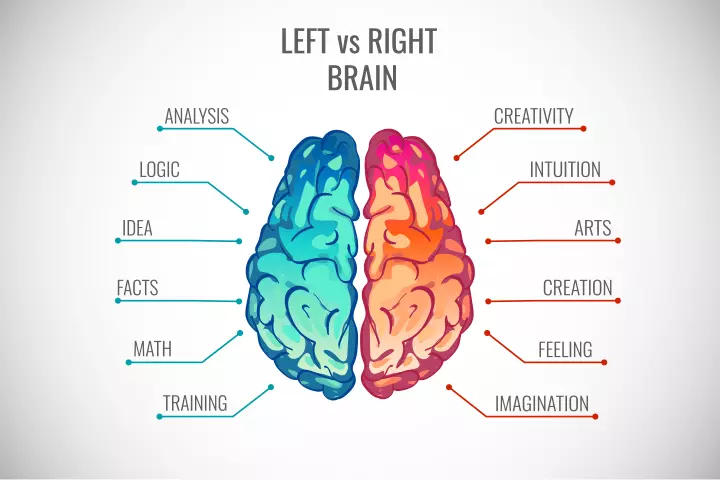
Image: Shutterstock
- The left part of the brain is responsible for analytical thinking. The right part helps in creative thinking (12).
- Human brain has blood vessels that can run up 100,000 miles, long enough to circle Earth approximately four times (13).
- Although our brain processes the sensation of pain, the organ itself lacks pain receptors. That’s the reason why neurosurgeons can operate on the brain without having to numb the organ (14) (15).
- Our brain is composed of 75% of water. Therefore, keeping yourself hydrated is important.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Which part of the brain is the largest?
The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain, and it controls movement, speech, problem-solving, emotions, and reasoning. The cerebrum is also responsible for the functioning of the senses, such as sight, hearing, and touch (3).
2. At what age is my brain the sharpest?
For ages, scientists believed that the ability to think and recall information quickly peaked at 20 years and then slowly declined. However, current research shows that different components of such intelligence peak at different points, some even at 40 years (16).
3. What are the differences between a child’s and an adult’s brains?
The main differences between a child’s and an adult’s brains lie in size, plasticity, and developmental stages. A child’s brain is much smaller at birth but grows rapidly, doubling in size in the first year and reaching 90% of its adult size by age 5. The child’s brain is also more plastic and capable of rewiring parts of its circuit for new learning than an adult’s brain, with over a million new neural connections forming every second during early childhood. As the child’s brain matures, it undergoes a pruning process, eliminating weaker or unused connections to increase efficiency and create more complex circuits (17) (18) (19).
4. How can I keep my child’s brain healthy?
A healthy brain can impact the overall growth and development of children. To keep their brain healthy, encourage them to have a proper sleep, engage in regular physical activity, eat a balanced diet, take enough rest, and engage in cognitive activities such as solving puzzles and reading (20).
5. What activities can children do to help stimulate their brain development?
Different fun activities can boost a child’s brain development. These activities and brain games for kids include reading, playing with puzzles and blocks, singing, exploring different textures or playing with mirrors to let them observe their reflection, and going outside to the park (21) (22).
6. What is the role of neurotransmitters in the brain?
Chemical messengers called neurotransmitters are present in the brain to send signals between neurons. They are crucial in regulating various functions such as mood, cognition, behavior, and bodily processes, facilitating communication and coordination among different body parts and the brain (23).
7. What are some practical ideas to teach kids about the brain?
You could use posters and diagrams of the brain with labels for different parts or use brain 3D models to teach them about the brain. You may also encourage them to make art and craft projects of the brain or conduct quiz activities.
The brain comprises billions of neurons that send and receive information, connecting the brain to various parts of the body. The brain has different parts, each of which has specific functions. For example, the cerebrum controls learning, speech and reasoning, and the senses; the cerebellum helps maintain balance and posture, and the brain stem is involved in life functions such as breathing and heart rate. Introducing children to these fascinating facts about brain parts and functions can help pique their interest in learning more about the human body.
Infographic: Human Brain Facts For Children
The brain is the most complex and fascinating organ of the human body and also the most crucial and dynamic one. It involves more than billions of nerve cells and connections to store and process immense amounts of information. Let your child explore more intriguing facts about the brain with the help of our infographic. Illustration: Momjunction Design Team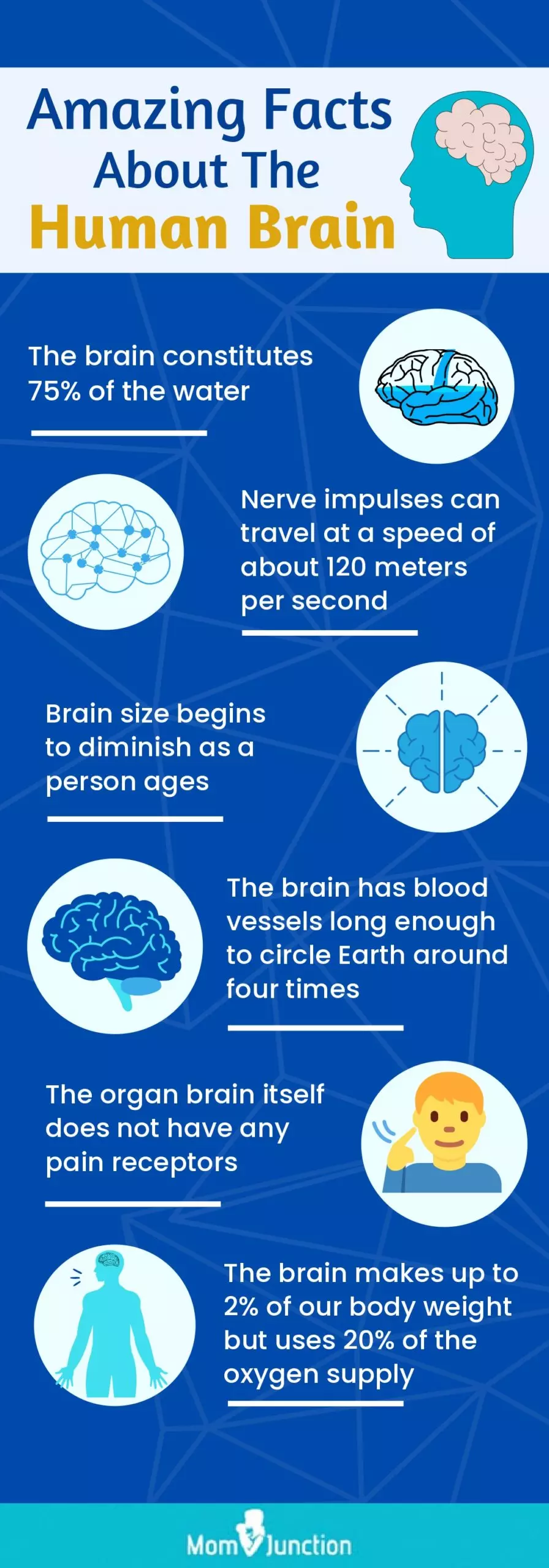
Illustration: Informative Facts Diagram & Parts Of Human Brain For Kids

Image: Dall·E/MomJunction Design Team
The brain is an amazing organ! It controls how we think, feel, and act. Learn how it works and why it’s so important in this fun video!
References
1. How does the brain work?; NCBI
2. Trafton A., In the blink of an eye; MIT News Office
3. Anatomy of the brain; John Hopkins Medicine
4. Maldonado K.A. and Alsayouri K., Physiology, Brain: NCBI
5. Brains; American Museum of Natural History
6. Herculano-Houzel S., The human brain in numbers: a linearly scaled-up primate brain; NCBI
7. Chia-Yu Chang, Der-Shin Ke, and Jen-Yin Chen, Essential fatty acids and human brain; NCBI
8. Neuroscientists explain how the sensation of brain freeze works; ScienceDaily, Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center
9. Peters R., Ageing and the brain; NCBI
10. What does it mean to be human?; Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History
11. 11 Fun facts about your brain; Northwestern Medicine
12. Chuldler E. Neuroscience for kids; Center for Neurotechnology, Seattle, Washington
13. About the brain and spinal cord; Neurological Surgery, University of Pittsburgh
14. 10 facts about the brain you didn’t know; Children’s Hospital of Orange County
15. The human brain; Rehabilitation Info Portal
16. The rise and fall of cognitive skills; Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
17. Brain Development; FIRST THINGS FIRST
18. Brain Architecture; Centre on the Developing Child, Harvard University
19. Change Is a Choice: Nurturing Neuroplasticity in Your Life; Good Therapy
20. Brain Boost; Health Powered Kids; Allina Health System
21. Thinking and play:newborns; raisingchildren.net.au
22. Play games to boost your baby’s brain development; Sanford Health
23. Neurotransmitters: Types, Function And Examples; Simply Psychology
Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our nurturing community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with fellow parents.
Read full bio of Katherine Paxton
Read full bio of Swati Patwal
Read full bio of Deepa Thomas
Read full bio of Shinta Liz Sunny