Image: ShutterStock
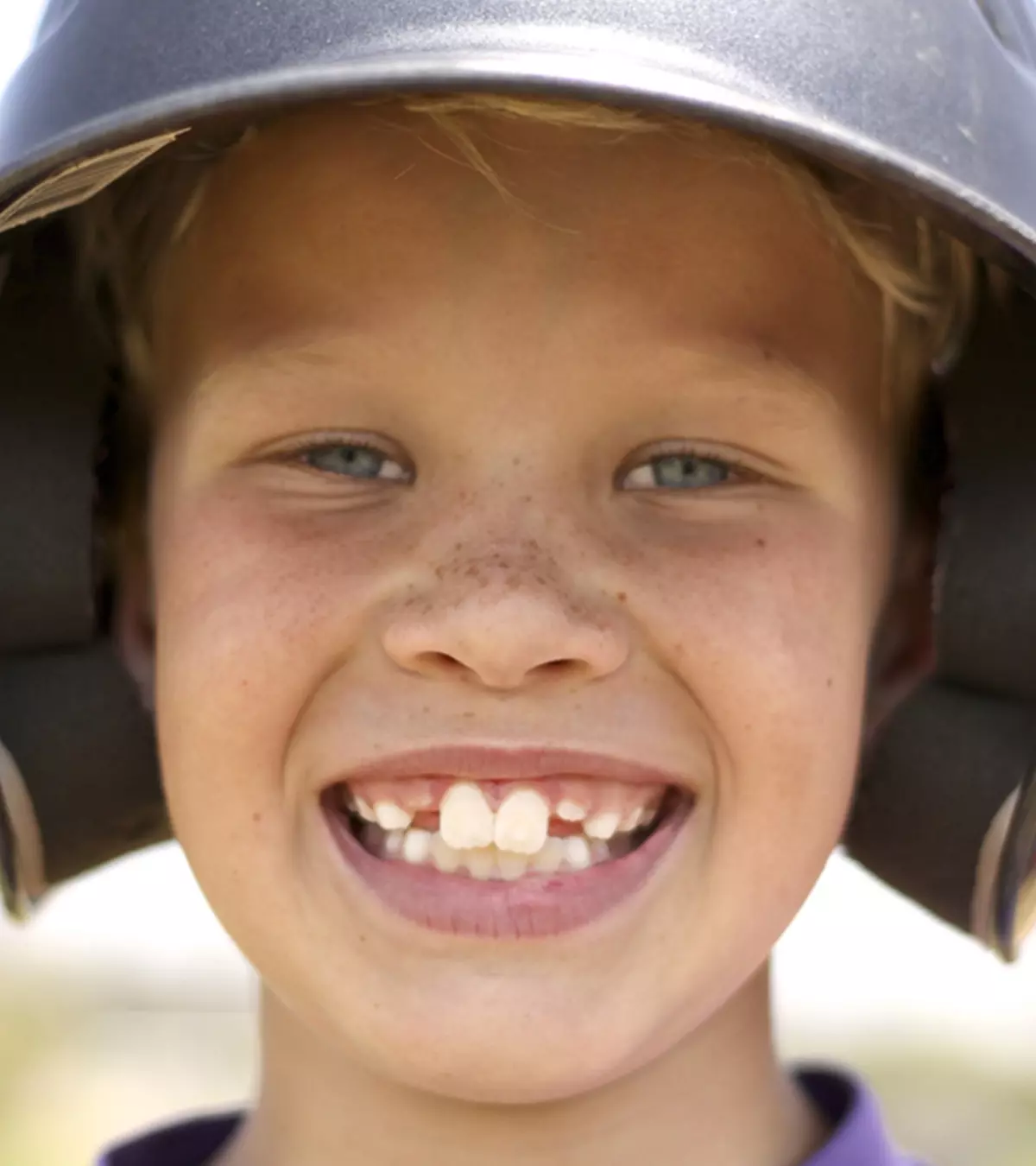
Buck teeth in kids refer to the misalignment of the upper and lower front teeth. The condition is characterized by an irregular protrusion of the upper front teeth, usually causing them to cover the lower lip. Buck teeth may lead to certain health issues in some children based on the malalignment’s severity.
Buck teeth lead to horizontal and vertical dental protrusions. The horizontal overlap of the upper front teeth over the lower front teeth is often called an overjet, while the vertical overlap is an overbite. Generally, the normal range for an overjet is about 1.5–2.5 millimeters (1). Experts advise early treatment of buck teeth to prevent complications.
Read this post to know the causes, treatment, and management options for buck teeth in children.
Key Pointers
- Genetics, thumb sucking, macrodontia, certain pacifiers, and tongue thrust can cause buck teeth in children.
- Children with buck teeth may face issues such as dry mouth, bad breath, speech problems, enlarged tonsils and adenoidsiMass of soft tissues found behind the nasal cavity that help prevent the entry of microbes through the nose or mouth. , and mastication problems.
- Lip exercises, orthodontic braces, habit-breaking appliances, and surgery may help treat buck teeth in children.
Causes Of Buck Teeth
Several factors can lead to buck teeth in kids. Some of the most common causes include the following.
- Thumb-sucking: In babies and toddlers up to age five, thumb-sucking is considered normal. The eruption of permanent teeth begins at around six years, and thus, if the thumb-sucking habit persists after the age of five, it could lead to dental and speech problems, including the malalignment of the teeth (2) (3).

Image: Shutterstock
- Tongue-thrusting: It refers to the habit of pushing the tongue against or between the teeth while talking, swallowing, or resting. If this habit persists in your child beyond six years, it could lead to buck teeth and speech problems (4).
- Macrodontia: In some rare cases, buck teeth can be caused due to relative-generalized macrodontia, characterized by the presence of normal or slightly larger teeth in smaller jaws resulting in crowding. This usually is due to genetic factors, and the size of teeth can be inherited from one parent, whereas the jaw’s size can be inherited from the other parent (5) (6).
- Genetics: Buck teeth are most often hereditary. The placement of teeth in the jaw, the jaw’s shape, etc., are passed down through generations (7).
- Pacifiers: Studies suggest that the use of pacifiers should be stopped after a child reaches the age of three years. At the time of eruption of permanent teeth, if the child is habituated to using pacifiers, it may cause malalignment, malocclusioniA condition where the teeth are not appropriately aligned, causing difficulties in chewing or biting. , and other jaw developmental problems (8) (9).

Image: Shutterstock
- Extra, impacted, and missing teeth: Impacted teeth are the teeth inside the gum tissue or bone that fail to erupt. Impacted and extra teeth cause crowding in the jaw and may lead to buck teeth. Missing teeth, on the other hand, can create space in the jaw, allowing other teeth to drift and causing misalignment (7) (10).
- Cysts and tumors: Although rare, cysts and tumors in the jaw may also lead to displaced teeth, missing teeth, loose teeth, eruption of teeth at different sites than normal, and change in jaw position, any of which could cause buck teeth (7) (11).
- Lip incompetence: It refers to a condition in which the lips remain parted even at rest. If the lower lip gets trapped behind the upper front teeth, it can push the teeth in front and cause buck teeth (12).
Health Risks Due To Buck Teeth
Buck teeth pose certain risks, and these risks could range from mild to severe:
- Breathing problem: The inability to close the mouth completely due to protruded teeth may result in chronic mouth breathing. Also, the palate shape is usually narrow and high-arched in people with extremely protruded teeth, which can cause nasal problems, such as rhinitisiAn inflammation caused in response to an allergen, also characterized by sneezing, sore throat, and congestion. (13) (14).
- Dry mouth: Incomplete mouth closure can result in dryness of the mouth and further lead to bad breath, swollen gums, oral infections, and weakening of teeth due to gum problems (15).
- Bad breath: Mouth breathing and dry mouth can cause bacterial infection in gums, oral tissues, and throat. The build-up of microorganisms can cause bad breath in kids (halitosis) (16).

Image: Shutterstock
- Enlarged adenoids and tonsils: Malalignment, open bites, and mouth breathing result in enlargement of the tonsilsiSmall oval-shaped tissues located at the back of the throat that prevent the entry of harmful microorganisms. and adenoids as the nasal filtration is surpassed in these cases. This could increase the likelihood of microbial attacks and respiratory tract infections, such as the common cold (17).
- Speech impediment: When the upper front teeth are placed far from the tongue, it might cause speech impediment in kids.
- Deep bite: This is also known as an overbite or a closed bite. In this condition, the lower front teeth are unable to meet the upper front teeth at the normal meeting point. When the upper and lower teeth are not aligned, the upper teeth can bite into the lower gums, and the lower teeth can bite into the roof of the mouth, leading to gum problems, ulcers, and enamel wear (18) (19).
- Mastication problems: Eating food properly requires each tooth to fulfill a specific role. When the upper and lower incisors do not meet correctly due to malalignment, it can cause mastication (chewing) problems and also cause pressure on the jaw joint.
- Hampered esthetics: Buck teeth can hamper a person’s appearance. Inability to close the mouth, swollen dry gums, and inward placement of lower lip are all results of untreated buck teeth. Esthetic problems can shatter a person’s confidence.
Linda, a mother of two, who is in her fifties shares her experience on her blog of when she was eight years old in school and had buck teeth and had to go for braces. She says, “I think I was around eight years old when I went to the dentist for the first time. My permanent teeth had come in, and I was a buck-toothed child. I was headed for braces. I was in sixth grade when I got braces. I remember being really excited about getting them because I hated my buck teeth. I could hardly close my mouth because my front teeth were so big and protruded so much. Before I could get braces, I had to have four teeth pulled, two on each side to make room for my teeth to move (ⅰ).’’

Image: IStock
Treatment For Buck Teeth
At times, parents and caregivers may fail to recognize buck teeth as a problem. But, often, the solution lies in correcting buck teeth when the first signs start to appear. Addressing buck teeth early prevents dental issues and helps avoid future complications. A dentist or orthodontist performs the treatment for buck teeth.
Let’s discuss the buck teeth treatment modalities in detail.
- Habit-breaking appliances: A dentist prepares customized appliances from the mold of a person’s teeth. A habit-breaking appliance for tongue-thrusting and thumb-sucking can be given to a child as young as six. The appliance can be of fixed or removable type, but fixed appliances are advisable.
- Orthodontic braces: This is the traditional way of correcting misaligned teeth by an orthodontist. Orthodontic braces for kids can be removable or fixed and are usually made of flexible metal wires. Sometimes, an orthodontic brace can be paired with habit-breaking appliances. It takes months to achieve the desired results through wire-based corrections. The treatment is often done to straighten or move teeth to the desired position (20).
 Quick fact
Quick fact- Mouth guards: These are given to patients with deep bite, bruxismiA condition in which a person clenches or grinds their teeth while in stress or anger. , and abrasive teeth problemsiDental conditions caused when the teeth come in contact with external materials. . The guards protect the teeth from wear and fracture due to teeth grinding and while playing contact sports (21).
- Palate expansion: A narrow and high-arched palate can cause rhinitis, blocked nose, breathing problems, and mouth breathing. This can be corrected through palatal expansion and is best done when the child is below 14. A customized palate expander is made for every patient, and it helps create space to accommodate all the teeth and solve crowding (22).
- Invisalign: It is used for correcting minor malalignments. It requires fewer visits to the dentist, looks transparent and esthetic, and corrects the malalignment without much discomfort. Oral hygiene can be maintained better using Invisalign (23).
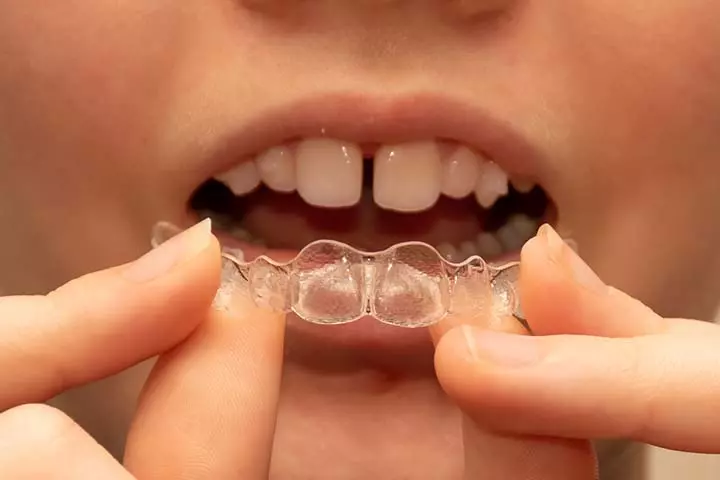
Image: IStock
- Extraction of teeth: In some cases, your child’s dentist may recommend extraction of buck teeth for bite correction (24).
- Surgery: Orthognathic surgeriesiSurgeries performed to fix the problems of the jaw. are performed, and the jaw’s size and placement are adjusted according to the occlusion. Some cases of protruded teeth cannot be resolved with surgery alone. Thus, a combination of orthognathic surgery, orthodontic braces, and habit-breaking appliances are needed to achieve perfect results.
- Lip exercises: In the case of lip incompetence, a dentist may suggest some lip exercises to be done for months to activate the lip and oral muscles. Activation of lip muscles can sometimes help in complete lip closure.
 Do remember
Do rememberManaging Buck Teeth In Kids
If one chooses to live with buck teeth, here are some self-care tips to avoid the associated risks:
- Practice good oral hygiene.
- Massage the gums with castor oil once every week.
- Gargle your mouth with warm water and salt daily as a part of oral hygiene.
- Visit the dentist regularly.
- Include citrus fruits and crunchy fruits and vegetables in your diet for healthy gums.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can buck teeth be treated at home?
No, buck teeth cannot be treated at home. For displacing or moving the teeth without damage, a specific amount of force is applied at a particular point on the tooth. This can only be done by an orthodontist or a dentist.
2. Will sucking the thumb as a child cause “buck teeth”?
Babies and toddlers suck their thumb in response to rooting and suckling instincts. When the habit extends beyond the age of five, it could cause buck teeth as the thumb exerts unwanted pressure on erupting permanent teeth, resulting in abnormal positioning of the teeth.
Consult a dentist or orthodontist if your child has buck teeth and discuss the treatment options to prevent future complications. In adults, treatment is needed if buck teeth cause pain or discomfort. If a person has no problems associated with such teeth arrangement and is confident of their looks, the treatment can be avoided.
3. How can children smile with buck teeth?
Children should practice oral hygiene to have a good smile with buck teeth. It is because these teeth show significantly when they smile. Also, practicing different styles of smile may eventually help them smile with more comfort and confidence.
Consult a dentist or orthodontist if your child has buck teeth and discuss the treatment options to prevent future complications. In adults, treatment is needed if buck teeth cause discomfort. If a person has no problems associated with such teeth arrangement and is confident of their looks, the treatment can be avoided.
Buck teeth in children mostly occur due to excessive thumb sucking, tongue thrusting, or genetics. Consulting an orthodontist or a dentist and discussing the treatment options for this condition can help in the prevention of any complications in the future. In addition, having misaligned, crooked, or unequal teeth during their childhood days might take a hit on their self-image and self-esteem. Therefore, it is advised that you talk with your child about the condition and give them enough support to go through this period.
Infographic: What Are The Reasons For Buck Teeth In Children?
Buck teeth, also known as protruding front teeth or malocclusion, are a common dental issue in children that can affect their appearance and oral health. In the infographic below, let’s look at the possible causes for their development in children to ensure effective management and prevent complications later in life.

Illustration: Momjunction Design Team
Illustration: Buck Teeth In Kids: Causes Health Risks Pictures & More

Image: Dall·E/MomJunction Design Team
Personal Experience: Source
MomJunction articles include first-hand experiences to provide you with better insights through real-life narratives. Here are the sources of personal accounts referenced in this article.
ⅰ. A Flashback Friday To Sink Your Teeth Into.https://mochawithlinda.blogspot.com/2011/02/flashback-friday-to-sink-your-teeth.html
References
1. What’s the difference between an overbite and an overjet?; Orthodontics Australia
2. Thumb-Sucking; Regents of the University of Michigan
3. Thumb sucking and pacifier use; American Dental Association
4. Tongue Thrust; Intermountain Healthcare
5. Ebru Canoglu, et al.; Isolated bilateral macrodontia of mandibular second premolars: A case report; European Journal of Dentistry (2012).
6. Manogari Chetty, et al.MACRODONTIA: A brief overview and a case report of KBG syndrome; Elsevier (2021)
7. Malocclusion of teeth; MedlinePlus
8. Pacifier Pros and Cons; University of Rochester Medical Center Rochester
9. James Poyak; Effects of pacifiers on early oral development; International Journal of Orthodontics (2016).
10. Impacted tooth; MedlinePlus
11. 5 Causes of Protruding Teeth; Bethesda Family Dentistry
12. Protruding Teeth; Health Online Unit, Ministry of Health Malaysia
13. Rhinitis; Johns Hopkins Medicine
14. Nina Lakhani, Michelle North, and Anne K. Ellis; Clinical Manifestations of Allergic Rhinitis; Journal of Allergy & Therapy (2012).
15. Dry Mouth: Home Treatment and Prevention; Regents of the University of Michigan
16. Lara Jansiski Motta, et al.; Association between halitosis and mouth breathing in children; Clinics (Sao Paulo) (2011).
17. Enlarged tonsils and adenoids: Overview; Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care
18. 7 Common Bite Problems in Children and Adults; American Association of Orthodontists
19. What is a Deep Bite?; American Association of Orthodontists
20. Orthodontic treatment; Oral Health Foundation
21. Mouthguards; Cleveland Clinic
22. Dental: Wearing a Palatal Expander; Nationwide Children’s Hospital
23. What is Invisalign?; Mon OrthoDontiste
24. Why tooth extractions are sometimes necessary in orthodontic treatment; Orthodontics Australia
25. Braces; Nemours Kids Health
Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our nurturing community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with fellow parents.
Read full bio of Dr. Tazeen Raees
Read full bio of Dr. Ritika Shah
Read full bio of Rebecca Malachi
Read full bio of Shinta Liz Sunny