Image: Shutterstock
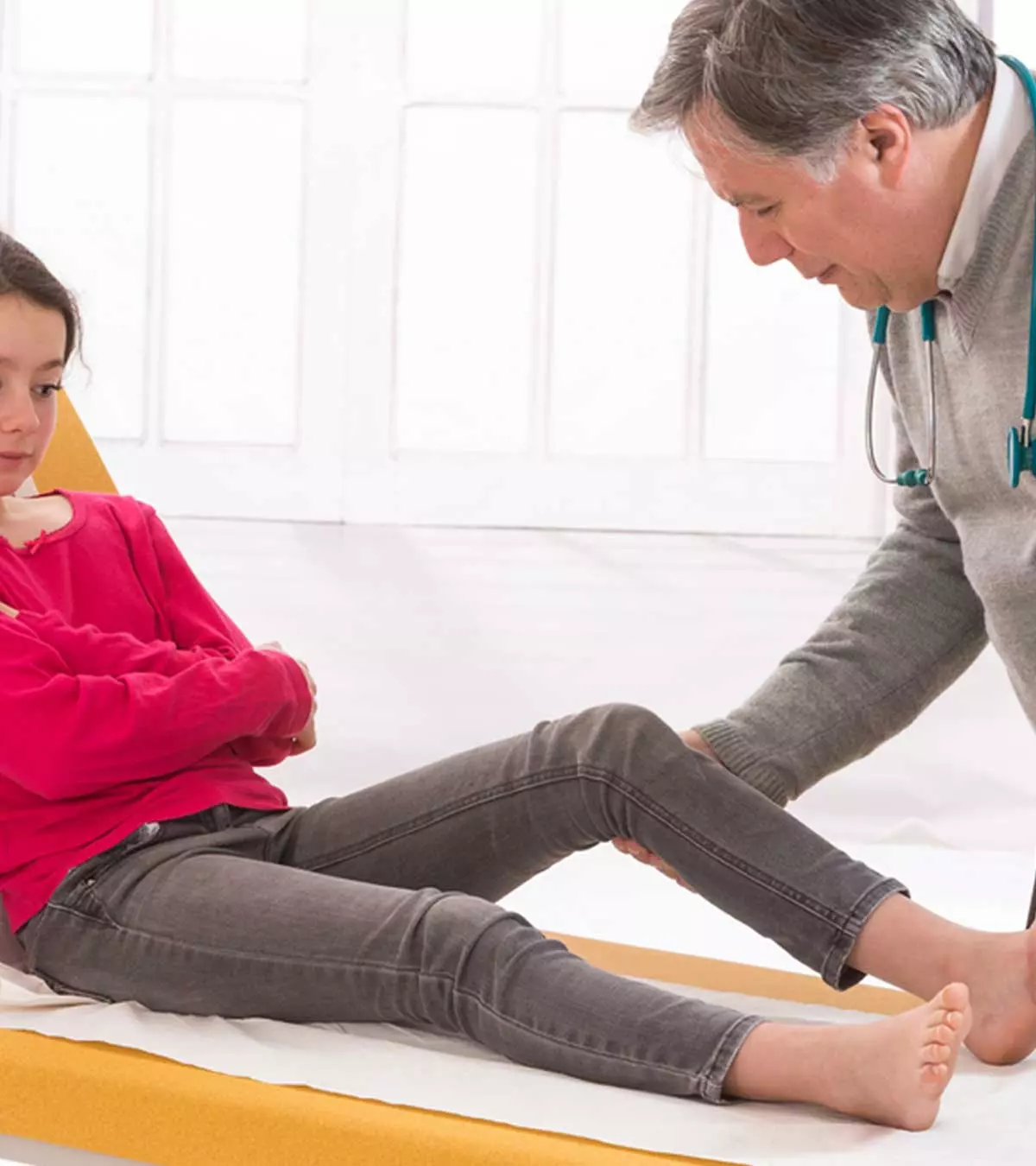
Knee pain in teenagers is a common complaint, particularly among physically active teens and those engaged in sports. It is also known as adolescent anterior knee pain and is characterized by pain in the center of the knee, beneath the patella (knee cap). Athletic teenagers are more likely to develop anterior knee pain than others.
Overuse of muscles or a training schedule without sufficient muscle strengthening or stretching exercises may also cause knee pain in teens. Otherwise, knee joint abnormalities or diseases are rare in teenagers.
Read on to know the causes, complications, treatment, and prevention of knee pain in teens.
Key Pointers
- Swelling, redness, popping sound from knees, inability to extend the knee are some symptoms of knee pain in teens.
- Some causes of knee pain include overuse, alignment issues, injuries, and growth-related problems.
- Mild forms of pain related to growth resolve with rest; however, consult a doctor for severe pain.
- Doctors may diagnose the condition using different tests, such as X-ray, CT scan, blood tests, etc.
- Home measures for knee pain relief include rest, heat or ice packs, and compression bandages.
Symptoms And Signs Of Teenage Knee Pain
The location of the knee pain in children may vary depending on the underlying cause. Some children may have anterior knee pain, while others may have posterior knee pain. The following signs and symptoms can be associated with knee pain in most teens (1).
- Pain intensity increases over time
- Redness
Image: Shutterstock
- Swelling
- Tenderness
- Warmth or fever
- Pain felt during knee flexion
- Popping sounds heard from the knee during movements
- Problems in weight-bearing on leg
- Inability to keep knees fully flexed or extended
Severe knee pain and other symptoms require pediatric consultation. Doctors may help to identify the cause of pain and treat it.
Is Knee Pain In Teens Common?
Anterior knee pain due to overuse and sports are common among teens. They may also commonly experience growing pains in the knee. It is difficult to rate the exact incidence of knee pain since the definition of knee pain may vary in each cause.
How Long Does Knee Pain In Teens Last?
There is no specific duration for knee pain in teens. It may vary depending on the severity and type of underlying conditions. Knee pain due to overuse may be relieved immediately with rest. However, knee pain due to a knee injury, such as ligament tear, may continue even after treatment and until the injury heals.
Growing pains in the knee are experienced during growth spurts in teenagers. This type of pain may resolve once the growth is completed.
Causes Of Knee Pain
The common causes of knee pain in teenagers may include the following conditions (2).
- Alignment problems may increase the pressure on the knee cap during movements.
- Overuse and inflexible muscles may cause knee pain.
- Tendinitis is the irritation and inflammation of the tendons.
- Apophysitis is a stress injury or inflammation around the bone growth plates in children and teens and affects the normal anatomy and physiology of the knee.
- Developmental changes or growth-related problems, such as Osgood-Schlatter disease, can cause pain in the growth area. According to StatPearls Publishing of the National Library of Medicine, the lifetime prevalence rate of Osgood-Schlatter disease is 9.8% in adolescents aged 12 to 15. This can be due to the fast bone growth that stretches the muscles and can be localized and tender to the touch.
Recounting his persistent struggle with knee pain since his teenage years, Edward Breen, an author and scientist, says, “I’ve had problems with my knees since I was a teenager. It didn’t stop me doing anything, really, but it’s been a constant niggle ever since. It started with some pain just under my knees, especially when swimming. Subsequently, I developed tender swellings at the top of both shin bones. Long story short, I went to a specialist, and he said I had something called Osgood-Schlatter disease, a fairly common condition in adolescents where more or less what happened to me happens. I was assured that unless a spur of bone formed in my knee joint, I shouldn’t have any issues, and the symptoms should gradually lessen, but I’d have the lumps for life (ⅰ).”
- Abnormal hip rotation may also lead to knee pain due to displacement of the knee cap.
- Patellar tendonitis is the inflammation of patellar tendons.
- Quadriceps tendonitis is the inflation of the quadriceps tendon.
- Patellofemoral stress syndrome causes anterior knee pain due to abnormal movement or increased pressure between the patella and femur (thighbone).
- Growing pains may occur when there are growth spurts in teens and are usually felt at night.
- Sports injuries usually occur from sports involving running and jumping.

Image: Shutterstock
- Other knee injuries, such as ACL injury, could cause pain due to a tear of the anterior cruciate ligamentiA major ligament (connective tissue) that is responsible for stabilizing the knee joint. (ACL).
 Quick fact
Quick factAlthough teens may have growth spurts, knee pain in teens is not always growing pains. Sometimes, this may be over-labeled as a growing pain, and the underlying reasons may stay unresolved.
Risk Factors For Knee Pain
The following factors may increase the risk for knee pain in teens (3).
- Overweight and obesity may increase strain on knee joints
- Lack of muscle strength and flexibility may make the knee joint unstable during motion
- Certain sports involving repeated jumps, such as alpine skiing and basketball, may increase chances of knee pain
- History of knee injury can increase the risk of knee pain and further knee injuries
 Quick fact
Quick factComplications Associated With Knee Pain
Knee pain due to growth or overuse may not cause severe complications in most teens. Knee injuries have an increased risk of recurrence, and the pain may worsen if left unmanaged. Medical conditions, such as osteoarthritis in obese teens, may cause increased pain.
If left untreated, teens with musculoskeletal disordersiA group of health conditions that typically affect the muscles, joints, and bones, causing pain, swelling, and muscle weakness. may also have an increased risk for worsening knee pain over time.
Prevention Of Knee Pain In Teens

Image: Shutterstock
All cases of knee pain cannot be prevented. The following tips may help to reduce the risk of knee pain in some teens (4).
- Weight loss may help to reduce knee pain in obese teens. Activities such as swimming and aerobics can be tried for weight loss in the initial stages since they have a low impact on the knees.
- Condition the muscles for sports activities. This may increase the flexibility and strength of the muscles.
- Practice sports with perfect techniques. A trainer or coach can help the teen learn movement patterns and sports techniques that minimize knee injury risk.
- Avoid overtraining to prevent overuse injuries.
- Stretching before exercise and using an ice pack after exercises may help to reduce knee pain.
Limiting high-impact activities may reduce pain in some children. Seek medical care in case of chronic knee pain since early interventions may prevent the worsening of underlying causes.
When To See A Doctor?
It is not ideal to use pain relievers, such as ibuprofen, to mask the pain and participate in sports. This may worsen the injuries and pain over time. Seek medical care for effective pain management in the following circumstances (5).
- Knee pain lasting more than two weeks
- Limping due to pain
- Unable to do sport activities
- Pain while playing sports
- Performance is affected by the pain
- Knee injuries
Never force your teen to participate in sports with knee pain. All cases of knee pain are not related to growth. An orthopedic doctor should evaluate the teen to identify the exact cause.
Diagnosis Of Knee Pain
Doctors may examine the knee movement and local signs of inflammation during physical examination. The following imaging tests are often ordered to identify the cause (3).
- X-ray imaging of knee joint helps to visualize degenerative joint diseases and fractures.
- Computed tomography (CT) scan may help visualize subtle fractures and gout.
- Ultrasound imaging of the knee helps to look at the soft tissues around the knee.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may also be used to visualize soft tissues, such as tendonsiStrong fibrous tissues that act as a bridge between muscles and bones and aid in stabilized bone movements. , ligaments, cartilages, and muscles in the knee.
- Blood tests may help to identify infection or inflammation markers.
- Arthrocentesis involves needle aspiration of synovial fluid from the knee joint and its laboratory analysis.
Blood tests, X-rays, and physical examination of knee flexibility, range of motion, and strength may often confirm the diagnosis. Other tests are usually ordered if these examinations are not enough for diagnosis.
Home Care For Knee Pain
The following self-care measures may help to reduce knee pain in some teens (3).
- Rest: Reducing knee strain by avoiding high-impact activities may help in recovery.
- Ice packs: This may help to reduce inflammation and pain. You may use it for less than 20 minutes at a time.
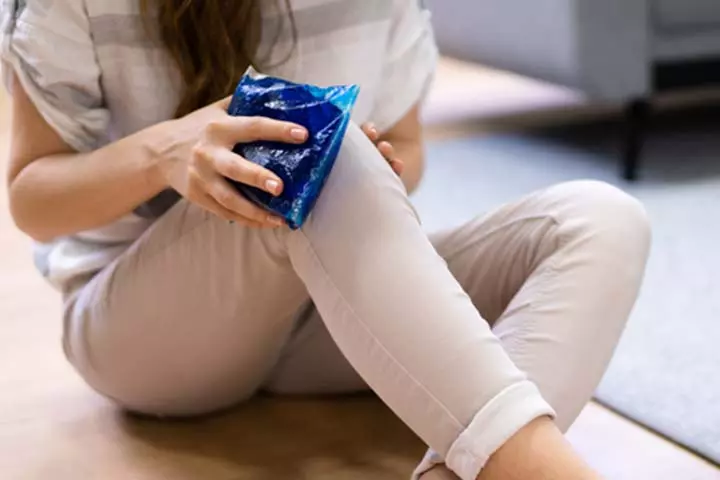

Image: Shutterstock
- Heat pack: This may help to relieve pain in some teens.
- Compression bandage: A breathable compression bandage may help prevent fluid build-up and provide better stability for the knees.
- Elevation: Keeping legs on a pillow or using a recliner may reduce swelling.
Treatment For Knee Pain
Treatment options may vary depending on the underlying cause of knee pain. The following treatments are usually prescribed for teens (3).
- Medications: Pain relievers are often prescribed for teens. Conditions such as gout and rheumatoid arthritis are also treated with medications.
- Physical therapy: This may help to strengthen the muscles by specific exercises. This may also improve flexibility and balance.
- Correction of sports techniques: If the knee pain is related to inappropriate sports techniques, your teen may feel better after correcting it.
- Arch supports: Wedges on one side of the heel may reduce pressure on the knee. This can be useful in the case of osteoarthritisiA common degenerative form of arthritis caused when the tissues of the joints gradually break down due to overuse or physical damage. .
- Knee braces: This may help support and protect the knee.
Some conditions may require direct injection of medication or other substances to the knee joint. Arthroscopic surgeries are often recommended for knee injuries.
 Quick tip
Quick tipPhysical Therapy For Knee Pain
Physical therapy may help strengthen the muscles with the help of specific exercises. It may also improve flexibility and balance. If your doctor suggests physical therapy, a physical therapist will thoroughly examine your teen. This assessment includes evaluating your teen’s knee strength, range of motion, balance, and functional abilities like walking and stair climbing. With an understanding of your goals, a personalized treatment plan would be devised to relieve knee pain and enhance mobility.
Physical therapy for knee pain typically involves stretching, strengthening, balance, gait training, joint mobilization, and stabilization. Additional modalities such as heat, ice, ultrasound, electrical stimulation, or athletic taping may be incorporated. The therapist may also guide on braces, orthotics, and assistive devices. Furthermore, a comprehensive home exercise program ensures ongoing progress and an improved quality of life beyond therapy sessions (6).
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can dehydration cause knee pain in teens?
Experts suggest that dehydration may impact the lubrication of joints, which might cause frequent muscle cramps or joint pains (5).
2. Can lack of calcium cause knee pain in teens?
There is not much scientific evidence to prove this statement. However, a study conducted on more than 2500 adults (aged above 40) demonstrated that low serum calcium levels might be linked to radiographic knee osteoarthritis (OA) (7).
3. How can a teenager with knee pain maintain an active lifestyle while recovering?
To maintain an active lifestyle while recovering from knee pain, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional and follow the recommended treatments. Engage in low-impact activities or physiotherapy exercises focusing on strengthening the supporting muscles without causing further injury. Prioritize warm-up exercises and consider using supportive gear if necessary.
Knee pain in teenagers may occur due to overuse, excessive pressure on the knee cap, tendon inflammation, growth pains, or injuries during sports. Obesity and insufficient muscle strength may increase the risk of knee injury and pain. While some pains may go away with rest, others may require physical therapy, medications, or external support. Consult a doctor if the pain persists beyond two weeks or the pain makes you limp. Further, following a warm-up routine and stretching before strenuous activities can go a long way in preventing injuries. Teens can continue participating in sports once the underlying issue resolves and acute pain subsides.
Infographic: Exercises To Manage Knee Pain In Teens
Suitable physical activities, such as exercises, can help manage knee pain, potentially leading to less pain in the long run. A well-structured physical rehabilitation program can also help you regain strength and flexibility in the knees. Save this infographic where we enlist safe knee exercises along with detailed steps. Illustration: Momjunction Design Team
Illustration: Main Causes Of Knee Pain In Teens Its Symptoms & Treatment
Image: Dalle.E/MomJunction Design Team
Knee pain in adolescents can be a difficult issue to manage. Learn more on how to deal with knee pain in adolescents by an expert in this video
Personal Experience: Source
MomJunction articles include first-hand experiences to provide you with better insights through real-life narratives. Here are the sources of personal accounts referenced in this article.
i. A sore Knee, Is it me?.https://medium.com/@edbreen/a-sore-knee-is-it-me-ac7e12a393d4
References
- 8 Signs Your Child’s Knee Needs To Be Examined; Nationwide Children’s Hospital
https://www.nationwidechildrens.org/specialties/sports-medicine/sports-medicine-articles/8-signs-your-childs-knee-needs-to-be-examined - Knee Pain; Physio.co.uk
https://www.physio.co.uk/what-we-treat/paediatric/conditions/children/knee-pain.php#:~:text=The%20most%20common%20reason%20for - Anterior Knee Pain; Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia
https://www.chop.edu/conditions-diseases/anterior-knee-pain-children-and-teens - Preventing Knee Pain; RUSH University
https://www.rush.edu/news/preventing-knee-pain - Dehydration and Joint Pain: How Your Hydration is Affecting Joint Health; Orthopedic Associates.
https://orthopedicassociates.org/dehydration-and-joint-pain-how-your-hydration-is-affecting-joint-health/ - Physical therapy’s role in addressing knee pain.
https://www.beaumont.org/health-wellness/blogs/physical-therapys-role-in-addressing-knee-pain - Hui Li et al., Serum Calcium Concentration Is Inversely Associated With Radiographic Knee Osteoarthritis; Medicine (Baltimore).
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4753953/ - Anterior Knee Pain in Children and Teens.
https://www.chop.edu/conditions-diseases/anterior-knee-pain-children-and-teens# - The Impact of Wearing High Heels.
https://www.sutterhealth.org/ask-an-expert/answers/the-impact-of-wearing-high-heels - Knee injuries.
https://kidshealth.org/en/parents/knee-injuries.html#
Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our nurturing community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with fellow parents.
Read full bio of Dr. Dur Afshar Agha
Read full bio of Dr Bisny T. Joseph
Read full bio of Dr. Ritika Shah
Read full bio of Vidya Tadapatri