Image: ShutterStock
The body’s nutritional demands escalate during pregnancy and lactation, making it vulnerable to nutritional deficiencies. Malnutrition during pregnancy may result in various maternal complications such as anemia, premature delivery, or postpartum hemorrhageiHeavy blood discharge from blood vessels after childbirth . In addition, it may adversely affect the developing fetus, increasing the risk of low birth weight and infant mortality (1).

Therefore, a balanced diet is essential to ensure the safety and health of the mother and developing baby. Continue reading this post, where we explain the causes of malnutrition during pregnancy, how it can affect you and your baby, and how to prevent it.
Key Pointers
- Malnutrition during pregnancy is a severe condition that is caused when an expecting mother doesn’t get enough nutrients required for fetal development.
- Causes of malnutrition during pregnancy can include poor dietary habits, certain medications, and health conditions such as morning sickness.
- Insufficient micronutrients during pregnancy may lead to preterm birth, anemia, a weakened immune system, and miscarriage or stillbirth.
- It can cause congenital abnormalities, neural tube defects, poor skeletal, and mental developments in the baby.
- Regular prenatal checkups, a well-balanced diet, and supplements can help prevent malnutrition in pregnant women.
What Is Malnutrition In Pregnancy?
Malnutrition is a serious condition that occurs when an individual’s diet contains insufficient nutrients that do not meet the requirements of her body. It can cause damage to the vital organs and can adversely affect the functioning of the body.
What Are The Causes Of Malnutrition?
Malnutrition during pregnancy may be a result of the following factors.
- Lack of availability of nutritious diet due to socio-economic conditions of the family.


 Quick fact
Quick factHealth Risks For The Mother
Women who are undernourished at the time of conception may also fail to meet the increased nutritional requirements during pregnancy. It can lead to insufficient gestational weight gain during pregnancy and increase the maternal mortality risk.
Deficiency of micronutrients during pregnancy could lead to the following:
- Zinc and Magnesium deficiency could cause preeclampsia and preterm birth.

Effects of malnutrition during pregnancy can be adverse. It can affect the mother’s health in the following ways:
- It can lower immunity and lead to infections.
- It can cause anemia and weakness.
- It can lower productivity.
 Did you know?
Did you know?Health Risks For The Baby
According to a study, in utero malnutrition could adversely affect the growth of the baby in the early years. It can also increase the baby’s risk of obesity, diabetes, and other metabolic complications like liver disease (4).
Micronutrient deficiency during pregnancy could adversely affect the baby in the following ways (5):
- Iodine deficiency can cause – congenital abnormalitiesiA structural or functional abnormality present from birth , neurological cretinismiA congenital thyroid hormone deficiency resulting in intellectual impairment and a dwarf stature , mental deficiency, spastic diplegiaiA type of cerebral palsy caused by a neurological disorder that affects the legs, causing difficulty with movement , myxoedematous cretinismiA rare form of cretinism caused due to iodine deficiency, characterized by stunted growth, mental impairment, and physical deformities , etc. It can also increase infant mortality risk.
- Low Zinc levels can cause fetal growth retardation and congenital abnormalities.
- Deficiency of Vitamin D during pregnancy can lead to ricketsiA bone disease caused by lack of vitamin D, calcium, or phosphorous resulting in bone deformities in children in the fetus.
- Folate deficiency can cause neural tube defects in the infant.
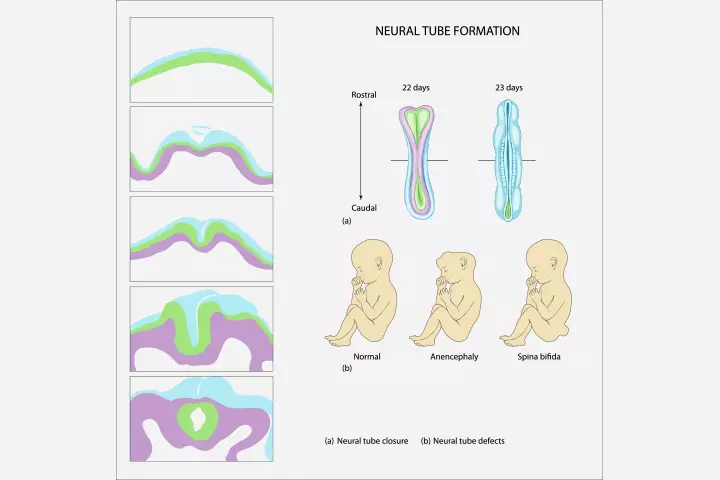
- Calcium deficiency can lead to poor fetal skeletal development.
- Low iron levels in the mother’s body and protein deficiency can cause fetal growth restriction.
An unbalanced diet during pregnancy could take a toll on the newborn’s health in the following ways (5):
- It can lead to stillbirth.
- It can cause a premature birth.
- It can increase newborn mortality risk.
- It can lead to neurological, respiratory, intestinal and circulatory complications in the infant.
- It may lead to birth defects and brain damage.
Maternal under-nutrition can make a child prone to the following health complications, in the long run (5):
- Renal dysfunction.
- He may face cardiovascular issues like – hypertensioniHigh blood pressure , atherosclerosisiHardening of the arteries due to accumulation of fats, cholesterol, and other substances , stroke, and coronary heart disease.
- OsteoporosisiA condition that weakens bones, increasing the chance of sudden, unsuspected bone fractures .
- Breast Cancer.
- Organ dysfunction of testes, ovaries, brain, heart, liver, and small intestine, etc.
Maternal malnutrition can also negatively affect mental development and school performance of a child.
Prevention

Having a balanced diet by consuming fresh and healthy meals during pregnancy can help you enjoy a safe pregnancy. Consume a lot of fruits and vegetables to gain vitamins, minerals and fiber. Include healthy protein sources like fish, eggs, pulses, beans, and poultry in your diet. Choose whole grains over refined grains for better nutrition, and include sources of healthy fats, such as clarified butter, avocados, and nuts, to support fetal brain development. Also, add starchy foods like cornmeal, pasta, noodles, bread, and potatoes to meet your increased carbohydrate requirement (6).
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the signs and symptoms of malnutrition during pregnancy?
In general, malnutrition may produce symptoms such as weight loss, reduced appetite, a constant feeling of being weak and tired, feeling cold, low mood or depression, and taking more time to recover from illness (7). These symptoms may indicate malnutrition during pregnancy as well.
2. Can malnutrition during pregnancy be reversed?
Nutritional support for pregnant women diagnosed with malnutrition may help reverse its adverse effects (8). Dietary supplements taken under the guidance of healthcare providers may also be helpful.
3. How is malnutrition during pregnancy diagnosed?
Blood tests for specific nutrients such as calcium, vitamin D, and B-group vitamins may be suggested by your doctor to diagnose deficiencies during pregnancy.
4. What should I do if I experience nausea during pregnancy?
To help manage nausea during pregnancy, you may consider having smaller meals and ensuring adequate hydration. If you are averse to the smells and textures of warm food, opt for easily digestible foods and consume them either chilled or at room temperature. Also, consider eating a high-protein snack before bed and light foods like crackers before starting your day. Lastly, resting in an elevated posture after eating may also relieve some of the symptoms of nausea.
Pregnancy increases the nutritional demands of the body to support fetal growth. Excess vomiting, underlying conditions affecting eating and digestion, or socio-economic factors may be responsible for malnutrition during pregnancy. Excessive consumption of junk and fast food during pregnancy may also lead to malnutrition, as it takes the place of food dense in crucial prenatal vitamins. Congenital abnormalities such as neural tube defects, growth retardation, premature birth, and miscarriage may be attributed to specific nutritional deficiencies caused by malnutrition. Most of the issues may be prevented with dietary and lifestyle changes. However, you should consult a doctor to identify the required prenatal nutrition and supplements to avoid deficiencies.
Infographic: Notable Health Risks Of Malnutrition To Mother And Fetus
Not getting enough nutrients during pregnancy can harm the woman and her unborn baby. This infographic shows the harmful effects of malnutrition during pregnancy and how it can affect the fetus. Save it and share it with other expectant mothers to encourage a healthy and adequate diet.
Some thing wrong with infographic shortcode. please verify shortcode syntax
Illustration: Serious Causes Of Malnutrition During Pregnancy

Image: Dall·E/MomJunction Design Team
Pregnancy is a special time, but malnutrition can put both mother and baby at risk. Learn how to prevent it in this video.
References
- Impact of Malnutrition.
https://www.unicef.org/nutrition/maternal - Causes of Malnutrition.
https://www.news-medical.net/health/Causes-of-malnutrition.aspx - Data and Statistics on Stillbirth.
https://www.cdc.gov/stillbirth/data-research/index.html - Malnutrition during pregnancy may affect the health of future generations.
https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2014/05/140501123447.htm - Alison D. Gernand et al.; (2016); Micronutrient deficiencies in pregnancy worldwide: health effects and prevention.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4927329/#:~:text=Deficiency%20of%20micronutrients%20including%20vitamin - Have a healthy diet in pregnancy.
https://www.nhs.uk/pregnancy/keeping-well/have-a-healthy-diet/#close - Symptoms-Malnutrition.
https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/malnutrition/symptoms/ - M.P. O’Connell et al.; (2000); Pregnancy outcome in a patient with chronic malnutrition: Case report.
https://academic.oup.com/humrep/article/15/11/2443/635083 - Ebele Philomina Meniru, et al.; Malnutrition in Pregnancy: Causes and Prevention.
https://journals.aphriapub.com/index.php/IJoHKHE/article/view/1457/1395 - Undernutrition during Pregnancy
https://www.intechopen.com/chapters/64950
Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our nurturing community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with fellow parents.
Read full bio of Jennifer House
Read full bio of Ria Saha
Read full bio of Swati Patwal
Read full bio of Dr. Joyani Das