Image: iStock
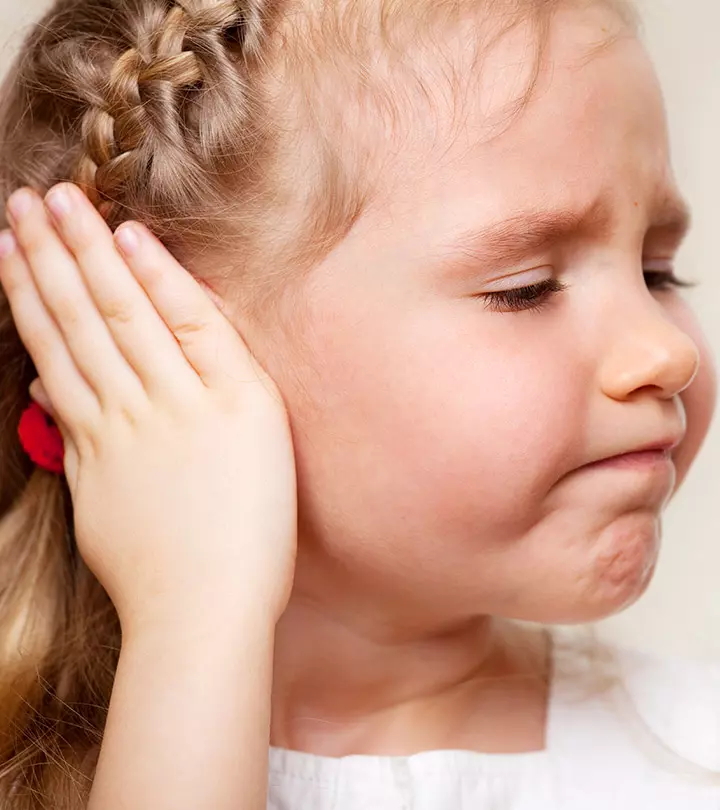
Earache in kids is common and can result from different causes. For example, your child may complain about pain in the ears during a respiratory tract infection (RTI) due to the spreading of the RTI up to the ears, causing earaches. The earaches might also develop from ruptured eardrums (1) (2).

Diagnosing the cause and providing the necessary treatment would protect the ear from further complications. Although ear pains in children are harmless, they may cause irritation, interfere with daily activities, recur and persist for longer.
Read on to know about the causes, symptoms, treatments, home remedies, and preventive measures for earache in children.
Key Pointers
- Children are more susceptible to frequent earaches due to ear architecture, an underdeveloped immune system, and diseased adenoids.
- Ear infections, ear canal injury, swimmer’s ear, altitude changes, ear piercings are some causes of ear pain in children.
- Neck stiffness, redness in or around the ear, fluid discharge from the ear, fever, increased crankiness, constant crying are signs of earache in children.
Is It Normal For Children To Have Earaches?

Earaches in children are common since their ears could get triggered even during the common flu. Furthermore, the following factors make children even more prone to earaches than adults (1).
- The eustachian tube of a child is smaller than that of an adult; hence, making the drainage of fluids from the ear difficult when the tube swells or gets blocked due to a respiratory illness or cold.
- A child’s immunity is still developing, thus making them more susceptible to infections.
- The adenoids, a lymphatic tissue behind the nose that balances the body’s fluids and fights infections, can become infected. The infection could then extend to the eustachian tube and the ear.
 Quick fact
Quick factHow Does The Ear Work?
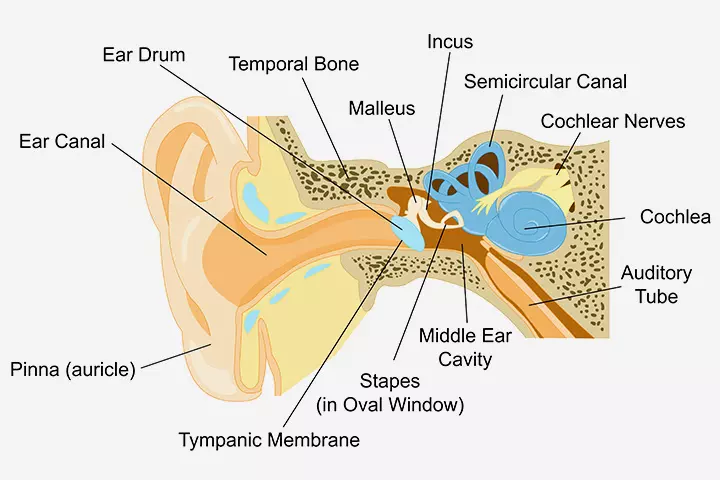
The working of the ear entails a series of complex events that occur almost simultaneously. First, any sound we hear through the external ears (pinnae) travels and reaches the eardrum through the ear canals. Next, the sound vibrations from the eardrum stimulate the three tiny bones—the malleus, incus, and stapes—of the middle ear, which in turn transfer the vibrations to the inner ear (3) (4).
The inner ear consists of a fluid-filled and spiral-shaped bone called the cochlea. As the stapes vibrates, it initiates a wave-like motion in the fluid of the cochlea. This, in turn, stimulates the microscopic hair cells in the cochlea to vibrate.
Further, each hair cell detects a specific pitch or frequency of sound it is designed to respond to and triggers the nerve impulses, which ultimately reach the brain’s hearing center called the auditory cortex via the auditory nerve and are converted into meaningful sound (3).
Causes Of Earache In Children
The outer and middle ears are the common sites of pain as infections or blockages of the ear canals could trigger an earache. Here are some common causes of earaches (4) (5) (6).
- Ear infection: A respiratory infection could spread bacteria and viruses to the ear canals and cause a middle ear infection, also called otitis media. Otitis media is one of the most common causes of earache. Approximately five out of six children will experience at least one ear infection by the time they are three years, according to the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders (NIDCD). Otitis media with effusion or glue ear may develop after middle ear infections and may affect hearing. Fluid builds up inside the middle ear due to a blockage in the eustachian tubes, and this fluid may become thick and sticky like glue. A child may feel pain or pressure in the ears. The condition may resolve on its own. However, it may take up to three months for the fluid to clear up (7).
- Ear canal injury: Accidental scraping off the ear canal by a cotton bud or any foreign object could lead to an ear canal injury.
- Swimmer’s ear: It is an infection of the outer ear canal commonly seen in swimmers.
- Blockage: A lump of ear wax could block the ear canals and increase the pressure within, thus causing pain. Regular usage of earbuds is a common cause of ear canal blockage, as these buds may push the wax deeper into the ear.
- Altitude changes: Earache is a common complaint during altitude changes. The sudden altitude changes during mountain climbing or landing of an airplane could cause earaches.

- Pierced ear infection: Ear piercing for kids is another common cause of earache in children and can cause excruciating pain if not treated on time.
- Other causes: In some cases, earache could also be caused by teething, sore throat, allergies, dental abscessesiA bacterial infection characterized by pus-filled, swollen gums and dental cavities, causing intense pain and fever. , and sinusitisiAn infection in which the tissues that line the sinus (hollow, air-filled spaces in the skull) get swollen or inflamed. .
 Quick fact
Quick factSigns And Symptoms Of Earache In Children
Sharp pain in the ear is the major sign of earache. Your child may also manifest the following symptoms (4) (5) (8).
- Pain in and around the ear
- Pink or red swelling behind the ear
- Red, swollen, and painful outer ear
- Stiff neck and associated discomfort
- Muffled hearing
- Fluid discharge from the ear
- Constant pulling or rubbing of the ear
- InsomniaiA sleep disorder that makes it difficult for one to fall asleep, stay asleep, or get a sound sleep.

- Loss of balance
- Decreased response to auditory cues
- Fever
- Irritability and constant crying
- Headache
- Disinterest in eating (due to severe pain while swallowing)
Diagnosing Earache In Children
The preliminary analysis for earache includes physical examination using any of the following options (1) (4).
- Otoscope: It is an illuminating tool to check the condition of the eardrum and ear canal. An otoscope helps identify any inflammation or redness of the eardrum. A healthy eardrum is transparent with a pink-greyish hue.
- Pneumatic otoscope: This tool helps identify if the tympanic membraneiA thin transparent membrane that differentiates the outer and middle ear, commonly known as the eardrum. is filled with fluid. A medical professional would blow air towards the eardrum using the pneumatic otoscope. If the eardrum doesn’t move flexibly, it is an indication that it is filled with fluid.
- Tympanometry: It is another painless method to test for fluid accumulation in the eardrum. It tests the mobility of the tympanic membrane using air pressure.
- Other tests: The health professional may test the child’s throat for signs of respiratory infections or tonsillitisiThe inflammation of the tonsils (tissues located at the back of the throat) usually caused by an infection. .
Treatment For Earache In Children
The treatment for earache in children depends on the causative factors (4).
- If the pain is due to an ear infection, the cause of the infection is determined.
- The medical advisor may put your child on antibiotics for a few days if the pain is due to a bacterial infection. Antibiotic treatment may be preferred if the child is under two years old, has a severe infection with pain and fever, has symptoms lasting several days, or has a weakened immune system. However, if prescribed, ensure your child completes all the antibiotic doses to prevent the infection from recurring. You may also consider adding probiotics to protect your child’s gut from the side effects of antibiotics (9).
- The doctor would treat an underlying upper-respiratory-tract infection accordingly.
- The pediatrician may suggest pain medications, such as acetaminophen and ibuprofen, and also prescribe ear drops.
- If the pain is due to a physical injury, the child needs immediate medical care. Your health professional may suggest performing an ear tube surgery.
- In the case of frequent ear infections, an ENT specialist may also recommend ear tubes.
Prevention Of Earache In Children
Earaches usually subside on their own in children. Nevertheless, you could take a few measures to reduce recurring earaches in your child (1) (4).
- Get them vaccinated against the common flu.
- Instill the importance of regular hand-washing as this reduces the spread of viruses.
- Prevent your child from sharing toys, bottles, or utensils with a sick person
- Breastfeed your child for the first year since studies have shown that breast-fed children are less susceptible to ear infections (10).
- Make them drink fluids in an upright position to prevent any liquids from entering the eustachian tubesiA passage connecting the middle ear to the pharynx/back of the throat. . You must also not let them take a nap with a bottle in their mouth.
- Avoid smoking around your baby as secondhand smoke may cause frequent ear infections in children.
- Never use a cotton swab to clean your child’s ears. Cotton swabs may push the ear wax further inside the ear canal, causing discomfort and injury (11).
- Restrict your children from placing any object in the ears as it might put them at risk of harming their eardrums, which can cause hearing loss.
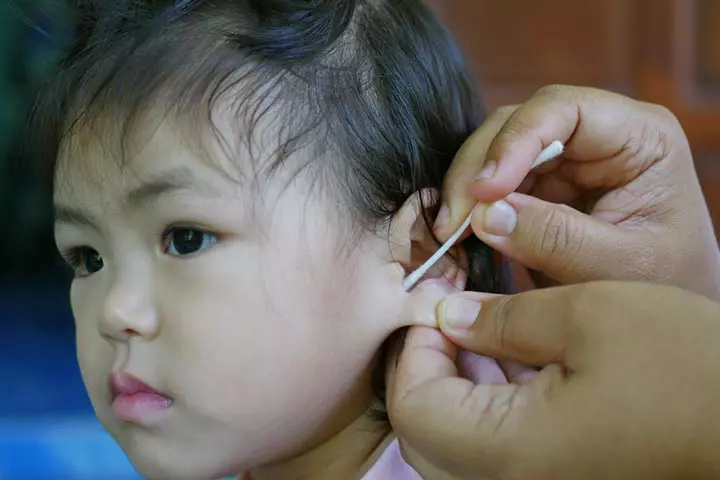
Home Remedies For Earache In Children
You could use the following home remedies to lessen the pain (12).
- Use hot or cold compress pads to soothe the pain temporarily.
- You could give over-the-counter medications such as ibuprofen and acetaminophen to reduce ear pain in children. Consult a pediatrician to know the dosage for a child. Children under 16 should not take Aspirin as it may lead to Reye’s syndrome (13).
- Make them sleep in an elevated position to reduce strain on the ears. Also, sleep on the alternating ear.
- Apply ginger juice or ginger-infused oil on the outer ear. Do not put oil directly into the ear.
- You may also fry garlic or onion and apply the strained oil around the ears.
- Hydrogen peroxide irrigates any blockage and could be used to remove wax buildup. Refer to a medical professional regarding its usage.
- Divert children’s minds off the pain by engaging them in their favorite activities.
- For pain radiating from the neck, a gentle massage could be relaxing. Apply pressure downwards for better results.
Nicole Spring, a mother of four, shares her experience using natural home remedies when her daughter cried out of earache. She says, “I ran upstairs to our kitchen and grabbed some garlic and extra virgin olive oil, and then I proceeded to make her an ear remedy. I put some in her ear, and she fell asleep. She slept for hours but still woke up in pain. I gave her another dose of the ear drops, and she slept again. The next time she woke up, she was feeling better. By the third dose, she could sit up and play with her baby brother again. Thank goodness for natural remedies made from things we have readily available in our home (i)!”
 Caution
CautionAlthough the home remedies mentioned above could temporarily alleviate the pain, always consult a doctor before trying any home remedy for your child’s earache.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. When should I take my child to the doctor for an earache?
Below are the concerning earache symptoms you need to look out for in your children (5). In case you observe any of the below mentioned symptoms, refer to an ear specialist or ENT doctor at the earliest:
• Unable to stand or too weak
• Earache not improving even after taking medicine
• High fever
• Painful swollen red ears
• Earache accompanied by a cough or runny nose for over a week
2. Can a child’s ear hurt but no infection?
Yes, earache is not always due to an ear infection and may result from other factors such as ear canal injury and swimmer’s ears, as mentioned above in the article.
3. How long does an ear infection last in a child?
An ear infection may improve within three days. However, you must watch out for concerning symptoms such as fever in children and teens, earache persisting for more than three days, or fluid oozing out of the ears to seek timely medical attention (14).
4. What are the long-term effects of untreated ear infections in children?
If ear infections in children are left untreated, they can cause long-term issues such as hearing loss, speech delays, and repeated infections. Hence, it is essential to monitor your child’s ear health and consult a doctor if the symptoms persist (9).
Earache is common among children due to their short eustachian tube and developing immunity. However, if your child complains of constant earache, consult a pediatrician. Identifying the cause is important for intervention and alleviating the symptoms. Since respiratory tract illnesses could cause frequent earaches in children, ensure your child receives their flu shots on time every year. Further, avoid potential triggers and try home remedies, such as applying ginger juice to the outer ear to alleviate the pain, after running them past your doctor.
Infographic: How To Manage Earache In Children At Home?
Earache can cause pain in children and even lead to difficulty in eating, distressing both the child and the parents. While seeking medical care is important to address the underlying issue, immediate home remedies can provide some relief to the child. Explore the home management tips for earache in children in the infographic below.
Some thing wrong with infographic shortcode. please verify shortcode syntaxIllustration: Effective Home Remedies That Soothe Earache In Kids

Image: Stable Diffusion/MomJunction Design Team
Earaches are relatively common in children. Help your child to manage the pain and discomfort with the following video on how to manage their earache.
Personal Experience: Source
MomJunction articles include first-hand experiences to provide you with better insights through real-life narratives. Here are the sources of personal accounts referenced in this article.
i. Smitten and sick.https://frontierdreams.blogspot.com/2012/02/smitten-and-sick.html
References
- Ear Infections in Children.
https://www.nidcd.nih.gov/health/ear-infections-children#10 - Perforated Eardrum
https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/perforated-eardrum/#:~:text=Symptoms%20of%20a%20perforated%20eardrum,itching%20in%20your%20ear - How the Ear Works.
https://www.hearinglink.org/your-hearing/about-hearing/how-the-ear-works/ - Ear Infection (Otitis Media).
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/8613-ear-infection-otitis-media#prevention - Earache.
https://www.seattlechildrens.org/conditions/a-z/earache/ - Ear Pain in Children.
https://www.mottchildren.org/posts/your-child/ear-pain-children - Glue ear
https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/glue-ear# - Ear Infections in Babies and Toddlers.
https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/ear-infections-in-babies-and-toddlers - Ear Infections in Children: Information for Parents.
https://www.healthychildren.org/English/health-issues/conditions/ear-nose-throat/Pages/Ear-Infection-Information.aspx - Sabirov. A. et al.; (2009); Breastfeeding is associated with a reduced frequency of acute otitis media and high serum antibody levels against NTHi and outer membrane protein vaccine antigen candidate P6.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2783794/ - Using Cotton Swabs in Children’s Ears.
https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/wellness-and-prevention/using-cotton-swabs-in-childrens-ears - 3 Home Remedies for an Ear Infection.
https://health.clevelandclinic.org/home-remedies-for-ear-infection - Aspirin.
https://www.versusarthritis.org/about-arthritis/treatments/drugs/aspirin/ - Ear infections.
https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/ear-infections/
Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our nurturing community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with fellow parents.
Read full bio of Dr. Dur Afshar Agha
Read full bio of Sindusha MS
Read full bio of Dr. Ritika Shah
Read full bio of Dr. Joyani Das