Image: ShutterStock
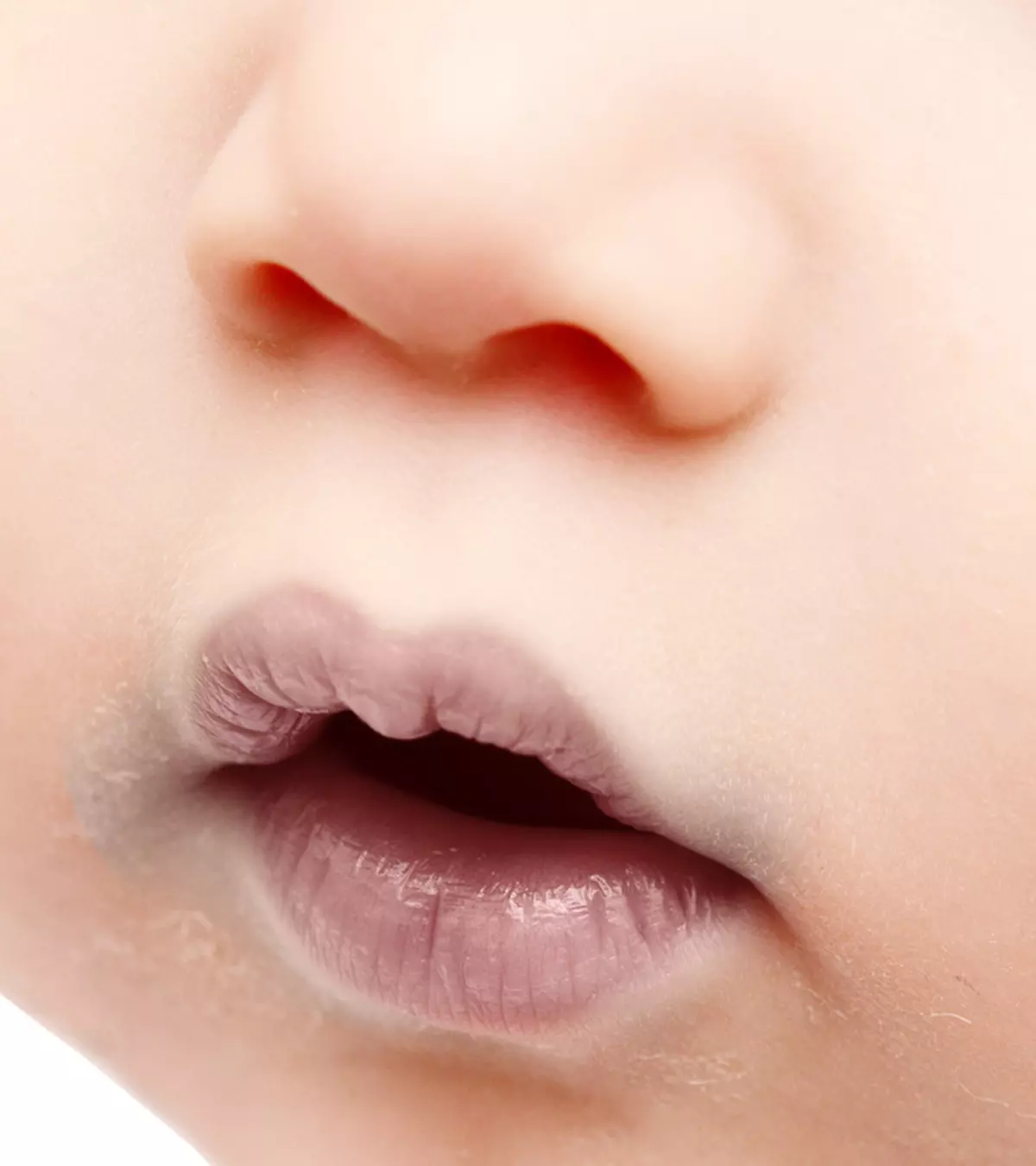
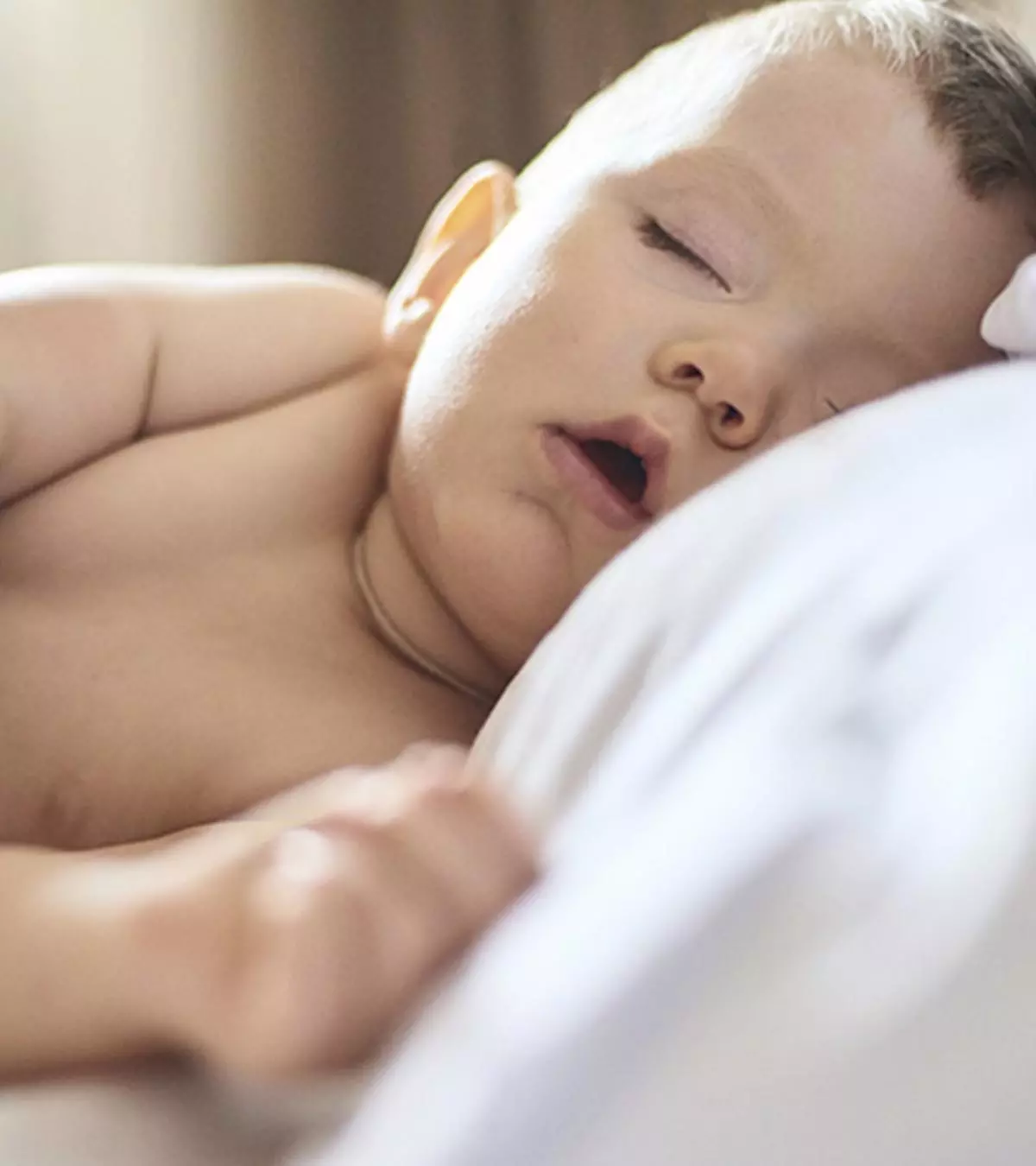
Circumoral cyanosis is a type of cyanosis that occurs when there is discoloration around the mouth. Here, the term “cyanosis” describes a bluish discoloration or tint in the skin caused by various conditions related to blood circulation and reduced oxygen levels in the bloodstream.
Cyanosis affects different body parts, including the nails, fingers, earlobes, and mouth or mucous membranes (1), and can be divided into distinct categories depending on the discolored body parts.
Read on to know more about circumoral cyanosis in babies, including its symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment options.
Key Pointers
- Circumoral cyanosis refers to the blue or grayish discoloration around a baby’s mouth.
- Respiratory issues, pain, and fever are common signs of circumoral cyanosis.
- Spreading discoloration to the tongue, cheeks and other parts is a cause for concern.
- In most cases, this condition resolves unless there is an underlying condition present.
What Is Circumoral Cyanosis?
Circumoral cyanosis is defined as the blue-gray discoloration around the mouth, especially the upper lip area
. It is the most common type of cyanosis in babies and children. With dark skin, the tint may also appear gray or white (2).
Although the condition can be worrisome for parents, you may check a few things to rule out a medical emergency.
Main Categories Of Cyanosis
Let us now discuss the two main types of cyanosis (1) (3).
- Central cyanosis: It occurs in the central part of the body, including the mouth, torso, and head. In newborns, this condition is not considered normal and is usually associated with low oxygen levels in the blood. Central cyanosis can also occur due to a problem in the heart, lungs, or blood.
 Quick fact
Quick fact- Peripheral cyanosis: It occurs in the extremities, including toes, fingertips, and hands. It can also occur in the circumoral area. This type of cyanosis is usually not life-threatening, but understanding the cause can help prevent further complications.
What Causes Circumoral Cyanosis In Babies?

Image: Shutterstock
Circumoral cyanosis is usually considered a type of acrocyanosis, which is common in babies as long as it doesn’t affect the central parts of the body (1). Sometimes, acrocyanosis in newborns may occur after a swim or bath in cold water. However, it usually resolves once the body is warmed up.
However, in some cases, the condition does not go away even after warming up and may be due to underlying heart or lung problems, such as Tetralogy of Fallot, a type of congenital heart disease (4).
Cyanosis may also occur when the lungs do not properly oxygenate the blood or the body is not receiving enough oxygenated blood. It most commonly occurs (5):
- If the baby is crying incessantly and strongly

Image: Shutterstock
- Immediately after feeding, bowel movement, or waking up
- If the baby is dehydrated
- If there has been smoke inhalation
- If there is a foreign body obstructing the airway (choking) or suffocation (asphyxia)
According to a case report published in the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) publications, perioral cyanosis without signs of respiratory distress was seen in a baby with COVID-19 infection (6)
. Coexisting signs and tests may help diagnose the exact causes of cyanosis around the mouth in babies.
 Quick fact
Quick factSigns And Symptoms Of Circumoral Cyanosis In Infants

Image: Shutterstock
Babies with circumoral cyanosis will have blue discoloration around their mouth. According to the Boston Children’s Hospital, blue discoloration around the mouth and face, earlobes, and fingernails are the common symptoms of cyanosis in babies (7).
You may also look out for the associated signs and symptoms in babies (8):
- Respiratory issues – difficulty breathing, fast breathing, chest indrawing
- Sweating
- Fainting
- Discomfort
- Fever
When To See A Doctor?

Image: Shutterstock
If the cyanosis is visible on the lips, tongue, head, or torso, it is central cyanosis and should be immediately checked by the doctor (1).
Additionally, talk to your pediatrician or cardiologist
- If your baby has experienced cyanosis for the first time
- If the frequency of cyanosis increases, it may be due to a heart condition
- If the cyanosis condition lasted for more than one minute
How Is Circumoral Cyanosis Diagnosed?
The three primary steps that your doctor may perform to diagnose circumoral cyanosis may include (1):
- Medical history of the baby
- Physical examination
- Oxygen saturation level to determine whether the oxygen levels are low or normal
Doctors may use pulse oximetry to measure blood oxygen levels, and physical examinations to observe symptoms. They may also require chest X-rays or echocardiograms for thorough evaluation.
Depending on the above findings, the doctor may recommend further confirmatory tests or evaluation. Also, the urgency of the condition may warrant consultation with a heart or lung specialist or a visit to the emergency room.
How Can Circumoral Cyanosis Be Treated?
In most cases, if the cyanosis is due to acrocyanosis, babies may not require any treatment. However, if there is an underlying heart or lung problem, the treatment may depend on the condition (1). Further, the doctors may monitor the baby’s oxygen levels, provide supplemental oxygen if necessary, and address any underlying conditions, such as congenital heart defects, that may be causing the cyanosis.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Which congenital heart diseases are characterized by cyanosis at birth?
Congenital heart diseases characterized by cyanosis include valve defects such as (9) (10):
- Truncus arteriosusiA congenital heart defect where the crucial arteries transporting blood from the heart are malformed
- Tetralogy of Fallot
- Tricuspid, Pulmonary or Aortic valve narrowing
- Transposition of the great arteries
- Total anomalous pulmonary venous return
- Hypoplastic left heart syndromeiA severe condition characterized by malformation of the left side of the heart affecting the blood circulation process
- Pulmonary valve atresiaiA congenital condition where the valve that regulates blood circulation from the heart to the lungs fails to develop
- Ebstein's anomalyiA rare cardiac abnormality where the tricuspid valve (involved in the blood circulation) is positioned incorrectly
- Complete interruption of the aorta
2. How are cyanosis and hypoxia related?
Hypoxia refers to the condition where body tissues have low oxygen levels. Cyanosis may be the clinical manifestation of tissue hypoxia (11)
3. Can anemia cause cyanosis?
Anemia plays a role in cyanosis but is not a common cause. A patient with severe anemia may not have cyanosis (11).
Circumoral cyanosis is evident by blue or gray discoloration around a baby’s mouth. It is considered a type of acrocyanosis caused by oxygen deprivation. In newborns, the condition usually resolves once circulation is established. Blue coloration around the mouth is not serious if it is not on the lips. It may fade once the baby is warmed up. However, seek immediate medical attention if you notice warning signs such as fainting, difficulty breathing, excessive sweating, and a bluish appearance around the head, torso, and tongue.
Infographic: Indicators Of Circumoral Cyanosis In Infants
Circumoral cyanosis is a type of discoloration of a baby’s skin in the central and peripheral regions. It can occur for many clinical and non-clinical reasons, and the baby would need immediate care. The infographic gives some signs that can help you detect the condition as soon as possible.
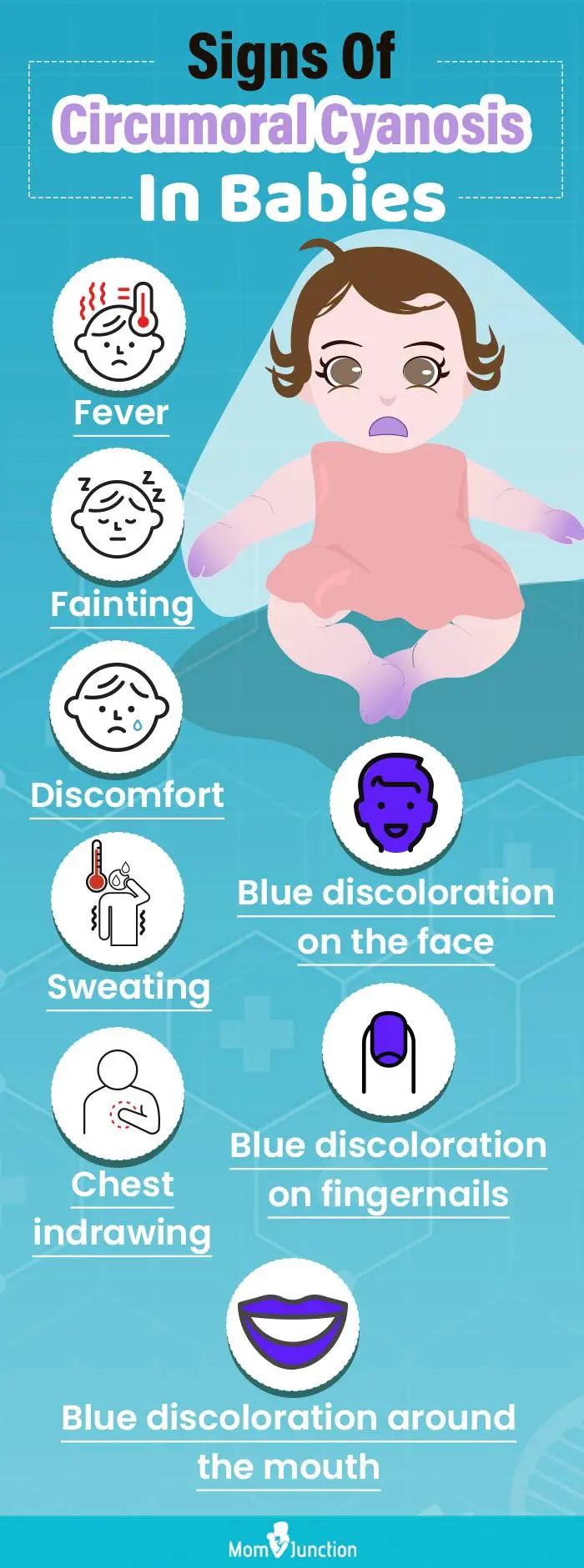
Illustration: Momjunction Design Team
References
- Cyanosis in infants and children; Cincinnati Children’s
https://www.cincinnatichildrens.org/health/c/cyanosis - J Bernard; Blue Lips or Skin (Cyanosis): Symptoms & Treatment; K Health (2020)
https://khealth.com/learn/symptom/cyanosis-blue-lips-skinskin - P Pahal and A Goyal; Central and Peripheral Cyanosis: StatPearls Publishing LLC. (2021)
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK559167/ - M. Ushay; Cyanosis; Textbook of Pediatric Care (Chapter 136)
https://archives.cjr.org/language_corner/our_funny_language.php - D Passàli et al; Foreign body inhalation in children: an update. (2010)
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2881610/ - Mariateresa Sinelli et al; Early Neonatal SARS-CoV-2 Infection Manifesting With Hypoxemia Requiring Respiratory Support; American Academy of Pediatrics
https://publications.aap.org/pediatrics/article/146/1/e20201121/37067/Early-Neonatal-SARS-CoV-2-Infection-Manifesting - Cyanosis; Boston Children’s Hospital
https://www.childrenshospital.org/conditions-and-treatments/conditions/c/cyanosis - Cyanosis (Blue colouration of lips feet body): Diagnosis and Treatment; Narayana Health
https://www.narayanahealth.org/diseases/cyanosis - Cyanotic Heart Disease; Nicklaus Children’s Hospital
https://www.nicklauschildrens.org/conditions/cyanotic-heart-disease - Cyanotic heart disease; MedlinePlus
https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/001104.htm - Adebayo Adeyinka and Noah P. Kondamudi; Cyanosis: StatPearls Publishing LLC.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482247/ - Overview of cyanosis in the newborn.
https://www.uptodate.com/contents/overview-of-cyanosis-in-the-newborn#:~:text=Cyanosis%20is%20a%20common%20clinical,pulmonary%20disorders%20(table%201)
Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our nurturing community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with fellow parents.
Read full bio of Dr. Neema Shrestha
Read full bio of Dr Bisny T. Joseph
Read full bio of Rohit Garoo
Read full bio of Shinta Liz Sunny