Image: Shutterstock
A child is said to have a flat foot or flat feet when they lack curvature in the foot/feet, causing their entire feet to touch the floor flat. Flat feet in children is a common condition that usually disappears around six years of age (1). Still, one to two children out of every ten continue having a flat foot or feet as they grow older (2).
Generally, every child is born with flat feet, and they start developing a curvature at around three years (1). But if they have flat feet, it could be any one of the two types — rigid or flexible (3). A flexible flat foot is normal. However, if a child has a rigid flat foot, it may be due to an underlying joint or bone problem, warranting treatment.
Read on to know more about the causes of flat feet in children and what you can do to help it.
Key Pointers
- If a child is over six to seven years old, flatfoot may be due to a deformity caused by low or high muscle tone, heredity, and other reasons.
- Flatfoot can be diagnosed in children with the help of X-rays.
- Children are usually born with flatfoot, making it difficult to diagnose the condition early.
Is Flatfoot A Disability?
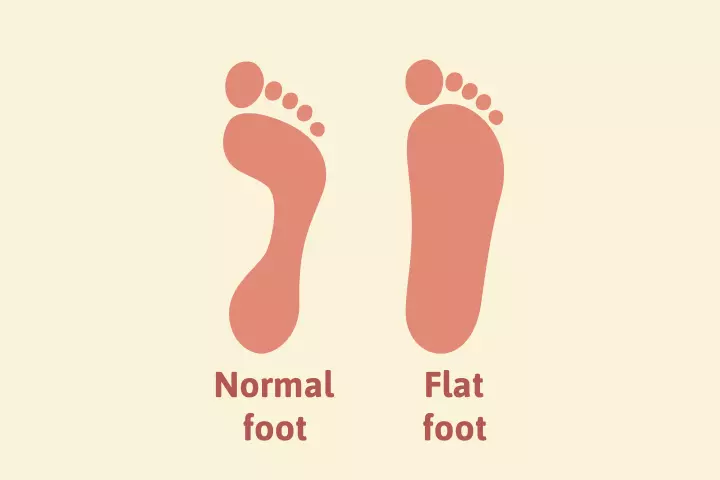
Image: Shutterstock
When children are young, their arches are yet to form, and so they naturally have flat feet. A twenty-year meta-study by the Beijing Sports University indicated that flat foot was prevalent among 25% of children. But, it corrects by itself as the child grows. However, if a child is over six or seven years of age and still continues to have flat feet, it is due to a deformity or anomaly of the heel wherein the heel bone or calcaneus rotates inward, causing the arch of the feet to collapse. While flat feet may be a deformity, it is not a disability.
Causes Of Flat Feet In Children
Not every child has the same cause of flat feet. Here are a few common ones.
1. Low muscle tone
In children with low muscle tone, their ligamentsi A connective tissue that connects bones in the joints, providing stability and flexibility are slightly more stretchy, allowing joint motion over the normal range. It results in the heel bone rotating inwards, causing the arch to collapse and give rise to flat feet (4).
2. High muscle tone
In children with high muscle tone, the Achilles tendoniA flexible fibrous collagen tissue that joins calf muscles (of the lower leg) to the heel bone pulls the foot inward, causing an arch collapse and flat feet (5).
3. Hypermobile joints
In the case of hypermobile joints in a child’s feet where the ligaments holding the joints are too loose, the foot’s arch collapses under the body’s weight, thus disturbing the biomechanics and resulting in flat feet (1).
4. Heredity
Some children inherit the flat feet trait from their parents due to genetics (4).
5. Overweight

Image: Shutterstock
Research shows that overweight children tend to have flat feet (3).
Children develop normal feet as they grow older, but they can continue having flat feet in their adulthood due to a few systemic conditions. Some of these include (6):
- Obesity
- Diabetes
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Foot or ankle injuries
- General aging process
 Quick fact
Quick factWhat Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Flat Feet In Children?
Though most children with flat feet usually have no signs, some common ones observed are (6):
- Foot pain, pain in the heel, knee, or sometimes the entire leg
- Outward tilting of the child’s heel
- Unusual or awkward gaitiA pattern of movement of limbs (legs), including walking and running
- Walking with different types of shoes can cause discomfort
- Reduced efficiency or inability to run fast as compared to children with normal feet
- Reduced energy while participating in high-intensity activities
- A tendency to withdraw from or show disinterest in sports and physical activities
Are There Any Risks And Complications of Flat Feet?
Flat feet may have an impact on your child’s overall posture, gait, and muscle health. The condition could set up a chain of reactions that include (1):
- Joint pains
- Muscle weakness

Image: Shutterstock
- Exhaustion
- The tendency of toe walking can cause posture and gait problems
- Limping while walking or running
- Affects the development of the child’s feet
At What Age Can Flat Feet Be Diagnosed?
Flat feet in children are usually diagnosed when they are around six or seven years of age (2). As the child grows and their bones develop, the arches form in their feet. Though there is no right age to diagnose flat feet in children, most parents usually approach their pediatrician or a podiatristiMedical professional who addresses the problems or ailments related to the leg (including foot and ankle) about their child’s flat feet if the condition is not corrected by the time they turn ten or 11 years old.
How Is A Flat Foot Diagnosed?
A flat foot is diagnosed by physical examination and X-rays. For making a diagnosis, a foot and ankle surgeon will first examine the feet and evaluate how the child stands, sits, and walks. They even examine the child’s range of motion. X-rays may be required to detect deformities in the feet(if any).
Diagnosis is essential for determining the best treatment option for flat feet. Rigid flat feet usually require additional investigations. If the flat feet affect the child’s hips or knees, or the child shows signs of nerve or muscle problems, X-rays and other tests may be required (6).
Treatment For Flat Feet In Children
Treatment for flat feet in children can be of two types, based on the nature and severity of the condition:
1. Non-surgical methods

Image: Shutterstock
These are often advised when the child has no symptoms, and the condition is regularly monitored by the foot and ankle surgeon. If the child shows signs of flat feet, the surgeon evaluates the condition and may advise one or more of the following non-surgical management options (6):
- Modification of the child’s activities
- Use of orthoticsiDevices (often custom-made) designed to correct or stabilize problem areas in the foot
- Physical therapies to improve flexibility and mobility
- Medications
- Use of different types of shoes
David McQuillan, a contributor to the ‘Somatic Reflections’ blog, was diagnosed with flat feet during childhood. Sharing how he used somatic exercises to correct the condition, he says, “I was given orthotic inserts for my shoes and the standard physiotherapy exercises at the time – putting a towel under my feet & pulling it towards me with my toes (strengthening the toe flexors which support the medial arch), and standing on a balance board (to activate and strengthen the muscles which laterally support the ankle). I was not particularly motivated to do these exercises.”
Over the years, McQuillan tried different things that helped him better understand his body. He says, “Over the last two years, I have been working with a series of somatic exercises, which I’ve developed from my understanding of anatomy, kinesiology, and tai-chi and my kinesthetic sense of my body. I have noticed some real changes in the last couple of months, which I hope will continue (i).”
2. Surgery
Surgical treatment for flat feet in children is recommended only when the non-surgical methods of management are not helping, or the child is suffering from aches and pains caused by them (7).
Surgical procedures used to correct flat feet include:
- Repairing a torn or stretched tendon
- Fusing one or more bones in the ankle
- Cutting or re-shaping a bone to correct the foot alignment
- Lengthening or replacement of tendons
Home Care For Flat Feet In Children
Most children with flat feet do not show symptoms and, therefore, do not require treatment. However, since their feet are flexible, parents can use a few home care management methods to help their child (after consulting the pediatrician):
- Use of custom-made insoles or inserts that support the arch and help improve balance
- Using appropriate shoes or footwear to improve foot function
- The use of braces can be helpful
- Exercises recommended by the physiotherapist can help improve a child’s overall well-being.
 Things to know
Things to know
Image: Shutterstock
Can Flat Feet Be Prevented in Children?
Since children are naturally born with flat feet, it cannot be prevented earlier in their lives. Prevention of flat feet is not possible earlier in their lives, but if a child shows flat feet anatomy even after six or seven years of age, you can provide them shoes with extra support or shoe inserts that have arch support in them.
All babies are born with flat feet due to the anatomy of their feet. They start to develop the curvature of their feet around their third birthday as a part of normal physiology. While most children do not show any symptoms with flat feet, some common signs can be observed. The treatment for flat feet is usually begun in the most non-conservative way using orthotics, physiotherapy and medications. However, if a child’s flat feet are not successfully managed using non-surgical methods, surgery may be advised. If your child experiences pain or discomfort while walking due to flat feet, consult a healthcare provider. Diagnosing a flatfoot condition earlier on in the child’s life is useful to correct with a better prognosis.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. When should I be concerned about my child’s flat feet?
You should consult a healthcare provider if your child has not outgrown their flat feet even after five years of age, they experience painful and stiff flat feet, or they often trip or fall (8).
2. How common are flat feet in children?
Most children aged between one and five years have flat feet as a part of their normal development. 95% of children outgrow this condition with time (9).
3. Does having flat feet affect height?
Some researchers have proven that the height of a person’s foot arch does not impact their linear growth/height (10). However, more research may be required to confirm this theory.
4. When do children’s feet develop arches?
Most children develop an arch while standing at around six years of age (11).
5. What are the long-term effects of flat feet?
Unaddressed flat feet may increase the risk of certain conditions such as bone spurs, arthritis, corns and calluses, shin splints, hip pain, lower back pain, and knee pain in children (1).
All children are born with flat feet, which eventually develop a curvature as the child grows. But in rare cases, the flatness remains. The most common reasons that lead to this include overweight, heredity, and high muscle tone. However, certain modifications in their activities or surgery could help. In addition, you could help your child at home by trying out foot-strengthening exercises with a physiotherapist’s help and making them use a custom-made insole.
Infographic: Potential Reasons And Care For Flat Feet In Children
Flat feet in children can cause joint pains, limping, muscle weakness, and other complications. However, knowing the underlying cause can help correct the condition with appropriate treatment. Check out the infographic below to learn about possible causes and home care tips for flat feet in children.

Illustration: Momjunction Design Team
Illustration: Causes Of Flat Feet In Children Symptoms And Treatment

Image: Dall·E/MomJunction Design Team
Discover effective strategies to assist your child in managing the challenging condition of flatfoot. This enlightening video gives valuable insights and guidance, empowering you to support your child’s well-being.
Personal Experience: Source
MomJunction articles include first-hand experiences to provide you with better insights through real-life narratives. Here are the sources of personal accounts referenced in this article.
i. Collapsed arches – a personal account.https://somaticreflections.wordpress.com/2008/12/01/collapsed-arches-a-personal-account/
References
- Flat Foot; Cleveland Clinic
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/flat-feet-pes-planus - Flat Feet and Fallen Arches; Healthy Children.
https://www.healthychildren.org/English/health-issues/conditions/orthopedic/Pages/Flat-Feet-Fallen-Arches.aspx#:~:text=Normally%2C%20flat%20feet%20disappear%20by,foot%20is%20stiff%20or%20painful. - Dr. David Scher’ The Effects of Flat Feet in Children HSS The Playbook (2016)
https://www.hss.edu/movebetter.htm - C Turner et al.; A Guide to the Management of Paediatric PesPlanus; Australian Journal of General Practise (2020)
https://www1.racgp.org.au/ajgp/2020/may/paediatric-pes-planus - Marc A. Raj et al.; Pes Planus; NCBI (2022)
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430802/ - Flat Feet; Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia
https://www.chop.edu/conditions-diseases/flat-feet-in-children - Pediatric Flatfoot; Foot Health Facts
https://www.foothealthfacts.org/conditions/pediatric-flatfoot - My Child has Flat Feet. What can I Do?
https://www.mountelizabeth.com.sg/health-plus/article/flat-feet-common-children - FLAT FOOT.
https://www.ouh.nhs.uk/paediatricorthopaedics/information/conditions/flat-foot.aspx#:~:text=We%20now%20know%20that%20thewill%20ever%20have%20a%20problem - Does Arch Height Affect A Woman’s Actual Height?
https://www.kon.org/urc/highschool/thakur.html - Flat feet in children.
https://www.rch.org.au/uploadedFiles/Main/Content/rheumatology/Flat_feet_in_children.pdf - Flat feet in children.
https://rhc.nhsggc.org.uk/home/about-your-childs-health-information-resources/patient-information-leaflets/physiotherapy/apcp/flat-feet-in-children-information-for-parents-and-carers/
Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our nurturing community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with fellow parents.
Read full bio of Dr. Dur Afshar Agha
Read full bio of Swati Patwal
Read full bio of Rohit Garoo
Read full bio of Shinta Liz Sunny