Image: Shutterstock
Although eggs are considered one of the richest sources of protein, you may want to know if it is safe to eat eggs during pregnancy. Eggs are a must-have in a balanced diet as they provide all the required nutrients such as minerals and fats. However, there are certain restrictions and rules to follow regarding food during pregnancy.
Although eggs may be a healthy option for pregnancy, they may have certain side effects on maternal health and fetal development if taken in excess. Knowing how to safely include eggs in your diet can help address these concerns. Read on to know more about the benefits and risks of eating eggs during pregnancy and the precautions to take.
Key Pointers
- Cooked entirely or pasteurized eggs are safe to eat during pregnancy.
- Raw or unpasteurized eggs may contain salmonella and cause food poisoning.
- Eggs are rich in proteins, vitamins, and minerals, and help manage cholesterol levels.
- Choline in eggs is crucial for fetal brain development.
- If cholesterol levels are normal, consuming 3-4 eggs per week is safe.
Is It Safe To Eat Eggs While Pregnant?
Yes, it is safe to eat eggs during pregnancy, provided they are completely cooked or pasteurized. Raw or undercooked eggs contain harmful bacteria such as salmonella that is likely to cause food poisoning. Cooking and pasteurizing the eggs will kill the bacteria, and it will reduce the risk of salmonella poisoning (1).
Nutritional Value Of An Egg
Find below the nutrition table that shows the nutrients present per 100g of a hard-boiled egg (2):
| NUTRIENT | AMOUNT |
|---|---|
| Energy | 155kcal |
| Protein | 12.6g |
| Total lipid (fat) | 10.6g |
| Carbohydrates | 1.12g |
| Cholesterol | 373mg |
| Calcium, Ca | 50mg |
| Iron, Fe | 1.19mg |
| Magnesium, Mg | 10mg |
| Phosphorus, P | 172mg |
| Potassium, K | 126mg |
| Sodium, Na | 124mg |
| Selenium, Se | 130mg |
| Zinc | 1.05mg |
| Iron | 1.19mg |
| Copper | 0.013mg |
| Folate | 44μg |
| Choline | 294mg |
| Vitamin B12 | 1.11μg |
| Vitamin D | 87IU |
What Are The Benefits Of Eating Eggs During Pregnancy?
Eggs are nutrient-rich foods good for both the mother and the developing baby. The benefits of including them in your maternal diet are mentioned next:
- Rich protein sources: Protein is essential for the healthy development of the baby as every fetal cell is made of protein. Eating eggs in sufficient quantities can be helpful for the growing fetus (3). Eggs are a source of complete protein, meaning they contain all nine essential amino acids that the body cannot synthesize (22).
Image: Shutterstock
- Rich sources of essential nutrients: Eggs contain prenatal vitamins B2, B6, B12, vitamin D, and minerals such as selenium, zinc, iron, folic acid, and copper.
- Fetal brain development: Eggs contain good levels of choline which is good for the growth and development of the fetal brain. It will, therefore, protect the baby from neural tube defects (4) (5).
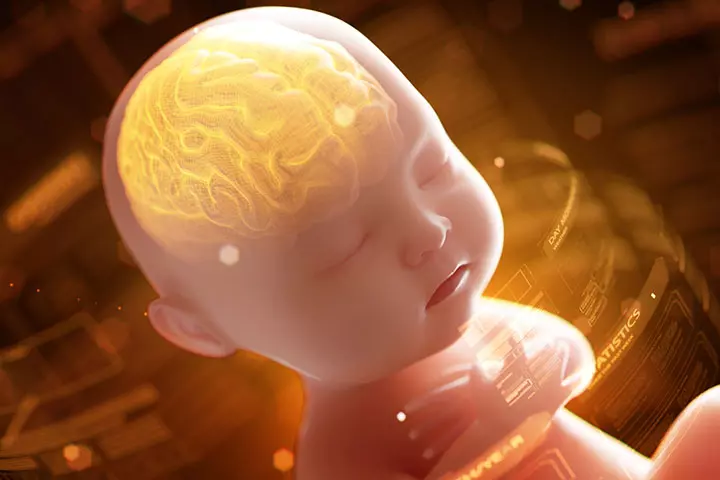
Image: IStock
- Provides calories: You will require about 200 to 300 extra calories in a day during pregnancy (6). An average-sized egg gives around 70 calories, thus helping meet the calorie requirement of both the mother and the baby (7).
- Regulates cholesterol: Eating eggs regularly will balance the cholesterol levels in the body (8). You should talk to your doctor about your diet if you have a cholesterol issue.
 Quick fact
Quick factHow Many Eggs Can A Pregnant Woman Eat In A Day?
The daily intake of eggs depends on the cholesterol levels in your body. It is advisable to include three to four eggs a week throughout your gestation period, if your cholesterol levels are normal.
How To Select The Best Eggs During Pregnancy?
Though some foods are loaded with high nutrition, they might be harmful if not correctly chosen. Remember the below points while picking eggs from a store:
- Do not forget to check the best-before or sell-by date for packaged eggs.
- Do not buy eggs that have cracked shells as they are susceptible to bacteria and dirt.
- Prefer buying organic eggs as they do not use any antibiotics or hormones in the poultry (9).
- Do a freshness test: Put the eggs in a bowl of water. If they float, they are not fresh, and if they sink to the bottom, they are considered fresh. Another way is to shake the egg near your ear. If it makes a splattering sound, it is not fresh. And if it doesn’t, it is a fresh egg (10).

Image: IStock
- Do not use an egg right out of the refrigerator. Let it sit at room temperature for at least two hours. This is to prevent bacterial contamination of the egg that undergoes perspiration when it is moved to a warmer space from a colder space.
 Did you know?
Did you know?What Is The Correct Way To Store Eggs?
To avoid bacterial contamination, store the eggs in the following manner (11):
- Keep them in egg trays inside the refrigerator to lower the chance of spoilage.
- Keep them in a separate tray, away from other food items.
- Store in the central area of the refrigerator, where the temperature is consistent, rather than on the side of the door.
- Do not store hard-boiled eggs in the fridge for more than three days.
How To Include Eggs In A Pregnancy Diet?
If you are unsure how to incorporate eggs into your diet, you may consult a dietician to use a diet chart for pregnant women that contains eggs. Nevertheless, it is easy to embed eggs within your daily menu easily. Here is how you may cook or prepare eggs to include in your pregnancy diet (12):
- Boil an egg for at least five to seven minutes so that it is properly cooked.
- If you prefer frying eggs, fry them such that the white becomes solid and is no longer translucent.
- If you prefer poached eggs, thoroughly cook for about five minutes or until the whites and the yolk are firm.
- You can add new flavors and texture by using spices and vegetables rather than eating them plain.
 Quick tip
Quick tipWhat Is The Shelf Life Of Eggs?
- An egg should be ideally consumed within 28 days from the time it is laid.
- Consume boiled eggs within two to three days
- Foods containing eggs in any form need to be consumed immediately.
Risks Of Eating Eggs During Pregnancy
Consuming eggs might be risky if you do not choose or cook them correctly.
- Raw or undercooked eggs contain Salmonella bacteria that cause food poisoning (1). It can lead to serious effects including high fever during pregnancy, vomiting or increased morning sickness, diarrhea, dehydration, and abdominal pain. Sometimes, it might also lead to miscarriage or cause complications during childbirth such as preterm labor.
- During pregnancy, it is possible for you to transmit salmonellosis to your baby. If your baby is born with the infection, they may experience symptoms such as diarrhea and fever shortly after birth, and could also be at risk of developing meningitis.

Image: Shutterstock
- Some women are likely to develop allergic reactions such as skin rash, hives, and nasal congestion.
- Egg yolk could cause dangerous cholesterol build-up if you are already suffering from cholesterol issues.
Precautions To Avoid Bacterial Infections With Egg Consumption
- Eggs should be cooked to 160°F (1)
- Handle eggs with thoroughly washed hands
- Use clean utensils that are cleaned with hot water
- Do not splatter raw egg over other food items
- Do not place eggs near other foods
- Clean the platform and utensils with hot water after cooking eggs
- Do not eat items such as mayonnaise or mousse that contain raw egg (12)
- Do not consider eating eggs from outlets you are not sure of the quality or the conditions of preparation.
- Avoid consuming if you get any unusual smell or if the egg is runny (13).
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is consuming boiled eggs good for conceiving?
Vitamins and nutrients such as Vitamin B12 and omega-3 fatty acids (like DHA) promote fertility and improve conception rates (14). Since eggs, cooked or boiled, are a rich source of these nutrients (15), we can conclude that egg consumption is good for conceiving.
2. Is egg yolk good for pregnancy?
Yes, egg yolks are a rich source of protein, calcium, vitamins, omega-3 fatty acids, and essential minerals such as iodine and phosphorus, which are beneficial for pregnant women (16).
3. Which part of the egg is good for pregnancy?
Egg yolks are more nutritious and beneficial for pregnant women (16). Also, it is advised to eat thoroughly cooked or pasteurized eggs while pregnant (17).
4. How long should I boil an egg while pregnant?
It is recommended to eat hard-boiled eggs while pregnant, which requires eggs to be boiled in water for around 10–12 minutes (18).
5. Is there any relationship between egg consumption and gestational diabetes during pregnancy?
Studies indicate that including higher amounts of eggs in the pregnancy diet can reduce the risk of gestational diabetes in women (19).
Eggs are protein-rich food sources that offer a pregnant woman several health benefits. If you are thinking about the safety of consuming eggs during pregnancy, know that you may include them while following certain precautionary measures. When buying, choose eggs that are fresh, uncracked, and organic. Make sure to boil or cook eggs properly before consuming them to avoid the risk of allergies, food poisoning, or other adverse potential outcomes of consuming raw eggs. If you have any concerns about eating eggs while pregnant, you may clear your doubts with your healthcare provider.
Infographic: List Of Foods That Might Contain Raw Eggs
Pregnant women are advised not to eat raw eggs due to the risk of salmonellosis. Our infographic brings you a list of foods that might contain raw eggs. Save this list on your phone or pin it on your pantry door to steer clear of these foods. Illustration: Momjunction Design Team
Illustration: Is It Safe To Eat Eggs During Pregnancy? Benefits And Risks

Image: Stable Diffusion/MomJunction Design Team
Are you expecting and questioning the compatibility of eggs with pregnancy? Your answers await in this video, where the truth about eggs and their relation to pregnancy is unveiled.
References
1. Food Safety for Pregnant Women; U.S. Department of Health & Human Services
2. Egg, whole, cooked, hard-boiled; U.S. Department Of Agriculture
3. Fatemeh Borazjani et al.; Milk and Protein Intake by Pregnant Women Affects Growth of Foetus; J Health Popul Nutr (2013)
4. Kate Girard; Pregnancy & Post-Partum Nutrition; University of Montana
5. Shaw GM et al.; Choline and risk of neural tube defects in a folate-fortified population; Epidemiology (2009)
6. Healthy Eating During Pregnancy; UC Davis Medical Center (2013)
7. Shell Eggs; USDA (2012)
8. Rachel E. Scherr et al.; Nutrition and Health Info Sheet: Cholesterol; Center for Nutrition in Schools Department of Nutrition University of California, Davis (2016)
9. What points should you consider when buying eggs; Egg Safety Center.
10. How to Tell If Eggs Are Good or Bad: The Ultimate Egg Test; Utopia.org (2018)
11. Alice Henneman & Joyce Jensen; Cracking the Date Code on Egg Cartons; University Of Nebraska–Lincoln
12. Dairy and Eggs from Food Safety for Moms to Be; U.S. Food and Drug Administration (2018)
13. Eating Runny Eggs Is Not Safe; Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine Footer Legal (2017)
14. Fertility and diet: Is there a connection? Harvard Medical School
15. Egg, whole, raw, fresh; US Department of Agriculture
16. Comparing egg white and egg yolk; British Lion Eggs
17. Eating Eggs During Pregnancy; Australian eggs
18. 5 Snack Foods to Eat While Pregnant; Hopkins Medicine
19. Alireza Milajerdi et al.; (2018); Associations between higher egg consumption during pregnancy with lowered risks of high blood pressure and gestational diabetes mellitus; NCBI
20. Pregnancy and diet; Better Health
21. Foods to avoid when pregnant; American Pregnancy Association
22. Protein in Eggs; Australian Eggs
Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our nurturing community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with fellow parents.
Read full bio of Dr. Burcu Saygan Karamürsel
Read full bio of Rebecca Malachi
Read full bio of Swati Patwal
Read full bio of Dr. Joyani Das





















