Image: Shutterstock
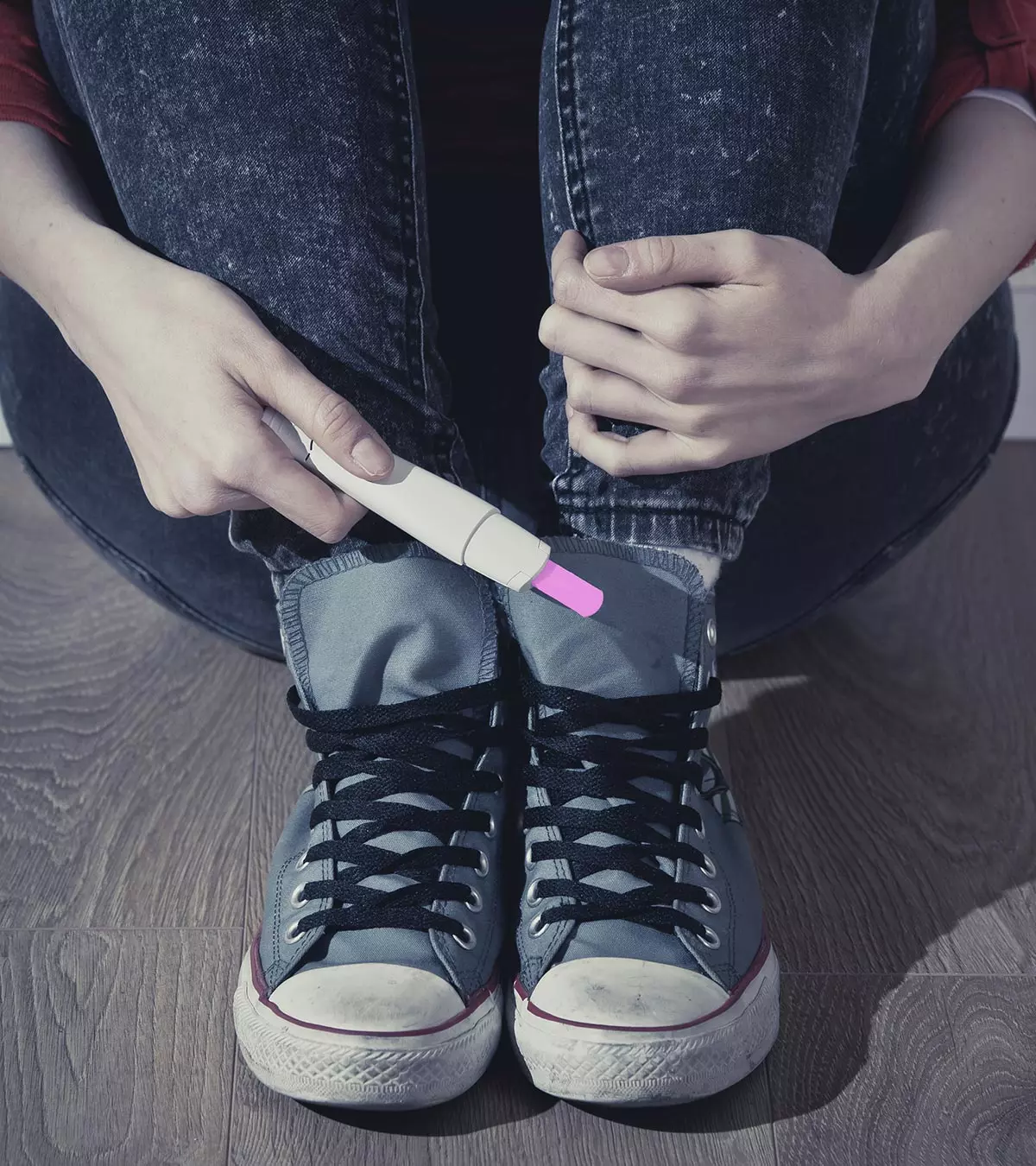
When a woman under 19 years of age gets pregnant, it is an adolescent or teenage pregnancy. Nearly 21 million girls between the ages of 15 and 19 get pregnant, and approximately 12 million of them give birth each year in developing countries. In this, approximately 10 million teenage girls may have an unintended pregnancy, and nearly 777,000 pregnancies occur in girls below age 15 (1).
Teenage pregnancy is concerning since it can be associated with a higher risk of complications during pregnancy and childbirth. High blood pressure, anemia, and infections are common in teen mothers. In many cases, babies can also be prematurely born or have low weight (1). Read on to know the pregnancy symptoms, health risks, and other challenges of teen pregnancy and ways to cope with it.
Key Pointers
- Teenage pregnancy symptoms may include missed period, light vaginal bleeding, tender breasts, morning sickness, and fatigue.
- Anemia, depression, improper nutrition, and improper weight gain commonly occur in teenage pregnancies.
- Babies born to teenage mothers are at a higher risk of low birth weight, congenital malformations, and improper brain development.
- Due to financial constraints and unintended pregnancies, teenage mothers may face problems seeking correct medical guidance and raising their babies in the future.
- Parents should educate their children on reproductive health and safe sex practices to minimize the risk of teenage pregnancies.
Signs And Symptoms Of Teenage Pregnancy

Signs and symptoms of teenage pregnancy can be similar to pregnancy symptoms in women of other age groups. Missing the menstrual period can be the initial sign of pregnancy. However, missed periods or irregular periods in teens can be due to different reasons.
You may have to confirm pregnancy with a urine pregnancy test or visit a gynecologist for the exact cause of missed menstruation.
The other signs and symptoms of pregnancy may include (2):
- Light vaginal bleeding from implantation of a fertilized ovum (egg) into the uterine wall
- Swollen and tender breasts and nipples due to hormonal changes
- Fatigue caused by increased progesterone hormone
- Headaches due to rising hormone levels
- Morning sickness, namely nausea and vomiting. Although it is called morning sickness, it may occur at any time
- Frequent urination due to the increase in the human chorionic gonadotrophins (hCG) hormones, which leads to increased blood flow to the pelvic regions in the initial weeks of pregnancy and due to the pressure on the urinary bladder from the growing womb during the later trimesters.
- Food aversions and cravings
- Mood swings
These symptoms may vary among girls, as can be seen in the case of Brooke Lehman, a vlogger, who describes the symptoms she experienced when she became pregnant at the age of 17. She recalls, “I started to get sick; I didn’t throw up or anything, but I was just feeling really, really tired, and obviously, my stomach hurt a lot. We got a test, and I took the test, and obviously, that tested positive (i).”
If you experience any of the above symptoms, you may seek the help of healthcare providers for diagnosis.
Why Can Teenage Pregnancy Be A Problem?
Teenage childbearing is associated with a higher risk of pregnancy and childbirth-related complications.
Most teen girls may not be mature enough for childbearing and childcare.
Babies born to teenage girls may have health problems due to inadequate prenatal care. Lack of prenatal vitamins, minerals, and other forms of care may increase the risk of health issues in both mothers and babies.
Most teen pregnancies are unintended and may have severe consequences for a teen’s mental and physical health. Social issues and lack of financial support could affect the psychological well-being of young women, and they may often develop depression and ignorance towards infants.
Along with the maternal health risks, it can be difficult for teen mothers to seek proper prenatal care if they do not have financial resources. It will be hard for them to take care of themselves and their education along with the baby.
Lack or delay in prenatal care can be the primary reason for most of the health risks of adolescent pregnancy. If you are wondering what are the 5 consequences of teenage pregnancy, this post will give you the answer. A pregnant teen may be vulnerable to developing the following health problems (3).
- Anemia
- Depression
- Excess or poor weight gain

- Undernutrition or malnutrition
- Eclampsia (seizures in pregnant women with preeclampsia, that is, organ failure due to high blood pressure)
Babies born to teen mothers may also have certain health risks, including (3):
- Low birth weight
- Premature birth
- Congenital malformations
- High risk of sudden infant death syndrome
- Risk of mental retardation, brain damage and birth injuries
The absence of a family support system and a lack of income sources can further make teen pregnancy challenging
. Unintended pregnancy may cause postpartum depression and postpartum blues in some teenage mothers.
Being a mother of more than a child can be extremely difficult for teen parents, especially for single mothers without support.
 Quick fact
Quick factWhat Are The Probable Consequences Of Teenage Pregnancy?
The significant consequences of teenage pregnancy on the parents and individual may include (4).
- Unintended and unplanned pregnancies could result in less interest and chances for the mother to seek prenatal care. Some pregnancies are identified in later trimesters, and the mother may not be able to receive early prenatal care. Lack of prenatal care could have adverse outcomes.
- Financial burden and poverty can cause extreme hardship for teen parents who lack family support, proper education & employment.

- Teen mothers may have difficulties in balancing newborn care and education. A lack of education can limit future career opportunities and financial independence. Statistics show that only 3% of teenage mothers were able to finish graduate school before the age of 30 years (4).
- Childcare can be stressful for young people due to a lack of knowledge and family support.
- Single mothers may have additional emotional problems and relationship troubles, along with other struggles.
- Financial difficulties and emotional issues may also cause a lack or delay in postpartum care and newborn care.
- Mothers who are under 15 years of age may have a more challenging time coping with childbirth especially if they lack the parenting skills required to fulfill their parental responsibilities.
- Unintended pregnancies may result from sexual assault or child marriage. These cases require additional medical care.
Altogether, it is not easy for a child to take care of another child. Many teen parents may not be able to ensure the well-being of the newborn since they lack parental responsibility, resources, and knowledge.
 Quick fact
Quick factHow To Reduce The Risks Of Teen Pregnancy?
The best method to reduce the risk of teen pregnancy or teenage pregnancy prevention is to educate children about reproductive health from an early age, including topics such as fertility, sex education, safer sex practices, STD prevention, birth control, and overall sexual health. There are many ways to prevent pregnancy after unprotected intercourse. Thus, seeking timely medical care for appropriate prescriptions can protect a teen as well as contribute to a reduction in the rates of teenage pregnancies around the globe. According to the 2022 Vital Statistics Rapid Release report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, teenage pregnancy birth rates have dropped from 13.9 births per 1,000 females in 2021 to 13.5 births per 1,000 females in 2022.
Parents can adopt the following methods that may help reduce the incidence of teen and adolescent pregnancies (4) (5).
- Reproductive education helps reduce the rate of unintended pregnancies among teenage girls.

- You can develop strong bonding with your child to make them comfortable to share any incidence of sexual abuse or unprotected sex.
- Have an open, two-way conversation about sex and your teen’s perception of it. Gradually acquaint the teen about the consequences of unprotected sex and teenage pregnancy.
- Teenage years and puberty mark the phase when dating tends to begin for many teenagers. Acquaint the teen with ways of setting boundaries in their relationship.
- It is okay to set rules on dating but do so while considering your teen’s opinion. Have a discussion with the teen to reach a consensus.
 Experts say
Experts sayIf pregnancy is discovered, then act promptly. You may discuss the possible options and resources, including abortion for teenagers, to avoid the continuation of pregnancy as per doctors’ recommendations.
If your teen decides to continue the pregnancy, then the teen should take the following steps to reduce the risks.
- Ensure regular prenatal care as soon as possible to reduce the health risks and complications of teen pregnancy and childbirth
- Take prenatal vitamin and mineral supplements to avoid congenital malformations and other complications
- Avoid alcohol, drugs, or tobacco use
- Follow a healthy diet and stay hydrated

- Do walking or other exercises suggested by the doctor
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) compared teen birth rates for 2018 and 2019. According to the findings presented in the graph below, the teen birth rate among 15 to 19-year-old females has declined in all races and origins. However, the rates remain unchanged for non-Hispanic Asians, non-Hispanic Native Hawaiian, non-Hispanic American Indian/Alaska Natives (AI/AN), and other Pacific Islander teenagers.

Birth rates among US females aged 15-19 by race and origin
Source: About Teen Pregnancy; CDCFrequently Asked Questions
1. What are the reasons for teenage pregnancy?
The causes of teenage pregnancy include (7):
- Less information about reproductive health and rights
- Sexual violence against vulnerable teenagers
- Family or community pressure for early marriage and lack of access to contraceptives
- Lack of proper education due to discontinuation of school
2. Who is more at risk of teenage pregnancy?
Poverty, low maternal education level, having a mother who gave birth in her teens, having a single parent, staying in a household where conflicts are frequent, alcohol and drug abuse, low self-esteem, and a teen’s race and ethnicity are some risk factors of teenage pregnancy (8).
3. Why is it important to spread awareness about teenage pregnancy?
Teenage pregnancy can negatively affect the health, education, and overall life of the young mother and her baby. It can also have social and economic consequences for the young mother and family. Thus, informing teens about the risks and effects of teenage pregnancy is essential. Staying informed will help teens make informed decisions and better care for their sexual, physical, and mental health.
Adolescent or teenage pregnancy is a complex situation that can put the teen and their family under intense social and emotional pressure. Besides, it can pose health risks for the teen and her baby. Thus, families should provide ample support and guidance to pregnant teens. Additionally, parents should educate their children about their reproductive health and underage pregnancies from a young age to help prevent teen pregnancy. Yet, if a teen gets pregnant, seek prompt medical guidance to make an informed decision to continue or discontinue the pregnancy.
Infographic: Possible Health Problems That May Arise In Teenage Pregnancy
In addition to the possibility of financial struggles, lack of family support, societal pressure, and other emotional factors, pregnant teen girls can also face health challenges. These issues could occur due to their young age and ignorance of prenatal care. Look through the infographic below to know more.

Illustration: Momjunction Design Team
Illustration: Teenage Pregnancy: Consequences And Risk Reduction

Image: Stable Diffusion/MomJunction Design Team
Personal Experience: Source
MomJunction articles include first-hand experiences to provide you with better insights through real-life narratives. Here are the sources of personal accounts referenced in this article.
i. 17 & pregnant; Story time;https://www.youtube.com/watch?feature=shared&v=ODRGrCGLSK0
References
1. Adolescent Pregnancy; The World Health Organization
2. What are some common signs of pregnancy?; The Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD)
3. What Are Some of the Complications of Teenage Pregnancy?; Pediatric Education
4. Risks of Teen Pregnancy; Nationwide Children’s Hospital
5. Tips for parents to help their children avoid teen pregnancy; University of Delaware
6. Help Pregnant Teens Know Their Options: AAP Policy Explained; Healthy children; The American Academy of Pediatrics
7. Teenage Pregnancy; Plan International
8. Risk Factors for Teenage Pregnancy; Southeastern Idaho Public Health
9. Teen Childbearing And Child Welfare; The National Campaign
10. Unintended Pregnancy in the United States; Guttmacher Institute.
11. Health Care Providers and Teen Pregnancy Prevention; CDC.
Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our nurturing community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with fellow parents.
Read full bio of Dr. Priya Shukla
Read full bio of Dr Bisny T. Joseph
Read full bio of Swati Patwal
Read full bio of Anindita Ghatak