Image: Shutterstock
Your kids may love to be around nature most of the time. Exploring the plants, trees, and world around them is exciting for kids. So you may begin to teach plant parts for kids from an early age to make them familiar with these most-loved green beings on the earth. This way, your kids may learn more about the foods that plants offer us and the various things we obtain from plants vital for our survival. In this post, we explain in detail the important parts of plants for kids in an exciting yet informative manner to engage and educate them.
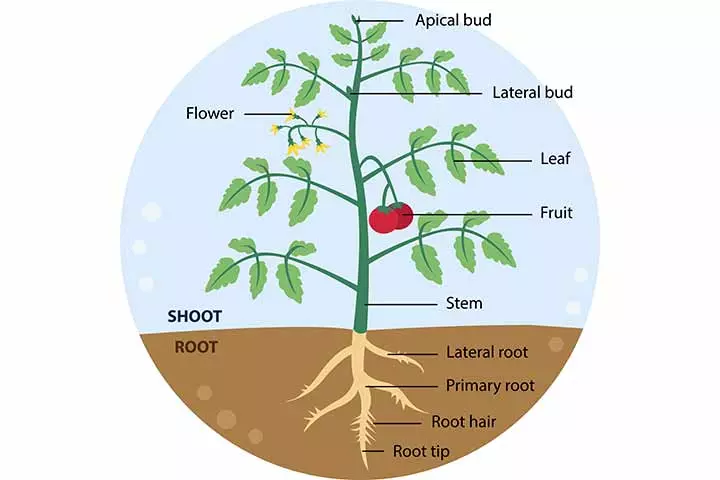
Image: Shutterstock
Key Pointers
- The roots keep the plants steady and supported while helping them absorb water and nutrients from the soil.
- The stem supports the plant body and some store food.
- Leaves produce oxygen and glucose through a process called photosynthesis.
Parts Of A Plant For Kids: A Beginner’s Guide
The two main parts of a plant include the root system and the shoot system. The root system consists of roots, root hair, legumes, rhizomesiA horizontal underground stem, containing nutrients, that sends out roots and shoots, allowing plants to spread and reproduce. , and tubersiA fleshy underground stem that stores food and nutrients for plants and forms the edible part of the plant such as potatoes. . The shoot system is made up of the parts that are above the ground, such as the stem, leaves, flowers, and fruits.
Let us learn about each part in detail.
1. Root

Image: Shutterstock
A vital part of the plant, the root is at the bottom of a plant. It is generally not visible since it is mainly found below the ground. Roots spread out into the soil to absorb nutrients and water, which are then transferred to the other plant parts. Roots also help in keeping the plant steady by securing it firmly to the ground.
Fun fact: In some plants, the roots also store food and nutrients for future use.
2. Stem

Image: Shutterstock
The stem, a vital component of the shoot system in a plant, is an essential link between the root system and the upper parts of the plant. The stem carries nutrients from the roots to the leaves, which then prepare the plant’s food through photosynthesis. Once the leaves prepare the food, it’s distributed by the stem to all the plant parts.
Fun fact: The stem offers support to the plant body and keeps it from wilting. In some plants, such as the cactus, potato, and onion, the stems store food just like the roots!
 Did you know?
Did you know?3. Leaves

Image: Shutterstock
Leaves are flat and of different shapes. Leaves are the ‘chefs’ of a plant since they make food for the entire plant.
They capture energy from the sunlight and carbon dioxide from the air and combine them with the water and nutrients that the stem brings to them. Using these ingredients and a substance called ‘chlorophylliThe green pigment in plants that converts sunlight into energy or food. ,’ which is already present in leaves, they carry out a process called photosynthesis and produce oxygen and glucose. Glucose is distributed by the stem to the other plant parts, and the oxygen is released into the atmosphere.
The ability of plants to trap carbon dioxide and release oxygen into the air makes them immensely beneficial to animals and humans.
Fun fact: Leaves have veins! If you take a close look at a leaf, you’ll notice them. These help with the movement of nutrients and water. Leaves also provide shade to the stems and roots and protect them from excessive sunlight.
4. Flowers
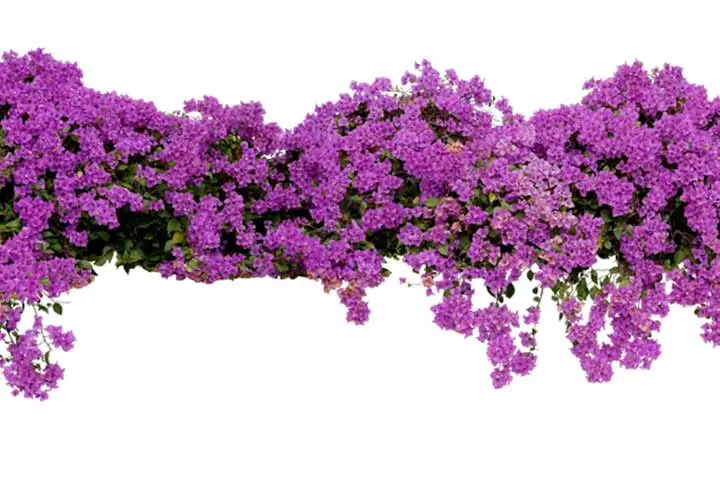

Image: Shutterstock
Besides being the most attractive parts of a plant, flowers help in propagation (reproduction of new plants) by producing new seeds and seedlings. They have ‘male’ and ‘female’ parts called the stamen and pistil (carpel) respectively, located in the center of the flower.
Flowers also have petals, which are the colorful leaves, and the sepal, which provides support to the petals.
Fun Fact: Most flowers have a sweet fragrance and bright petals to attract insects and animals, which serve as pollinators. They help spread the pollen, the fine powder seen in flowers, from one flower to another. This leads to fertilization and results in seeds.
 Trivia
Trivia5. Fruit
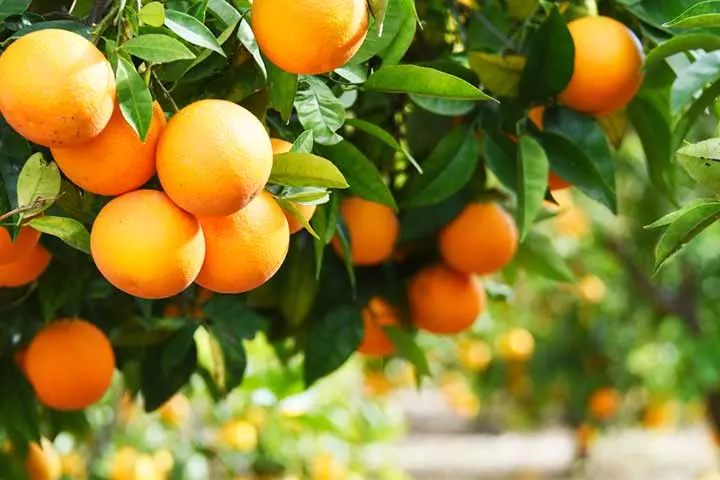

Image: Shutterstock
All flowering plants produce fruits, but not all fruits are edible. Thus, you should educate your child about what they should not eat. The primary function of a fruit is to protect the seed/seeds like pods, from drying or being dispersed.
Some fruits are fleshy, while others are hard. And while some fruits have multiple seeds in them, others have just one seed.
Fun Fact: Most fruits are sweet to taste – this is also one of nature’s tricks to attract animals to the fruit. Once an animal or bird eats the fruit, the seed falls to the ground and grows into a plant!
6. Seed
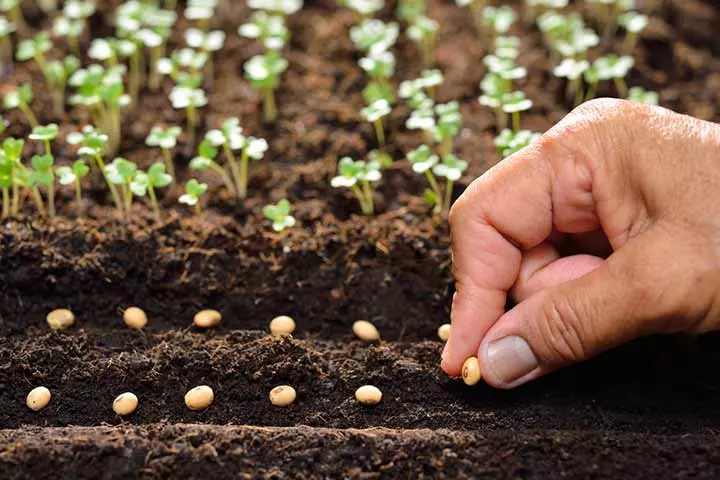

Image: Shutterstock
The seed is a small hard substance found in a fruit or other parts of a non-flowering plant. Seeds need to get transported for them to germinate and grow into a plant. This process of propagation is carried out by the wind, insects, animals, and birds.
Fun Fact: The coconut is all three – a fruit, a nut, and a seed!
Kushi, a mother, shares her experience of teaching her little one about plants. She says, “My three-year-old daughter, whenever she watches a conical tree …shouts..“Mom…… Christmas tree.” She watches a Christmas tree in Jingle Bells rhyme. I showed her a mango tree and a banana tree in our surroundings. Then I told her when a tree is small, it’s called a plant, grows big into a tree, and we get flowers, fruits, and vegetables from plants and trees. I introduced some plant parts like leaves, stem, and root.
“Then I wanted to teach her how a plant grows…So, I made her plant seeds in a cup filled with soil. I made her put the cup in a place where it would get a good amount of sunlight every day. I made her water it daily. Within some days, she watched a small plant come out from the seed in the cup (ⅰ).’’
 Did you know?
Did you know?What Are Vegetables?
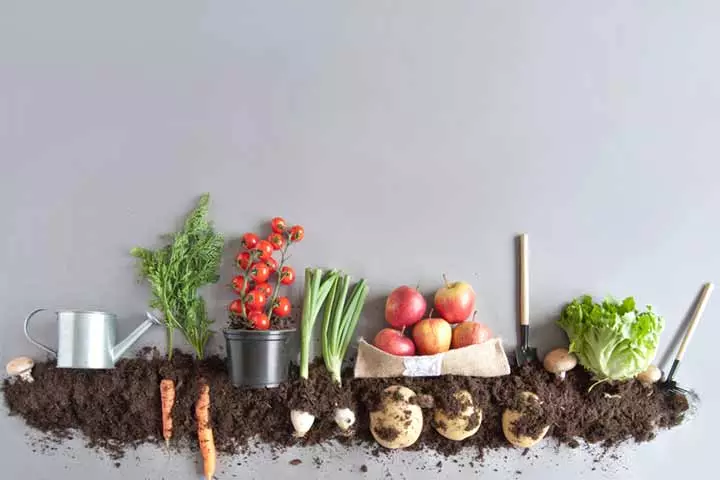

Image: Shutterstock
Like fruits, vegetables are also the end product of a plant. They are the edible parts of a plant that humans and animals can consume. A vegetable can be any part of a plant, such as the seed, root, stem, leaf, tuber, or even flower.
Fun Fact: Tomatoes are fruits! Until the late 1800s, they were considered vegetables because of the way they are used in cooking.
Xylem And Phloem
Plants have two different types of tissues called xylem and phloem, which serve different purposes. The xylem is responsible for carrying water and nutrients from the roots to the different parts of a plant, while the phloem carries nutrients from the leaves to all parts of the plant.
Just as humans have different body parts for various functions, plants have different parts that serve specific functions. These work together and help the plants flourish.
 Trivia
TriviaFrequently Asked Questions
1. How do you define a plant for kids?
For kids, plants can be defined as: a living thing that grows on the surface of the earth, has leaves and roots, and produces colorful flowers and fruits.
2. Which part of the plant is a potato?
A potato is the tuber of the potato plant. It is a root vegetable and grows under the soil.
3. What is the most common type of plant?
Phragmites australis, also known as the common reed, is the most common type of plant that can be seen (5).
4. What does a plant need to survive?
Like every other living organism, plants also need air, water, sunlight and minerals from the soil for survival.
5. What are some fun activities to learn about plant parts?
Learning about plants can be made more exciting with hands-on activities. You can take your child on a nature walk or scavenger hunt and create a plant scrapbook with all the findings. Your child may also enjoy conducting a plant growth experiment at home or making a mini garden in the backyard. You may also ask your child to build a 3D plant figure with recycled materials or playdough to help them understand plant parts better.
You may explain plant parts to kids to improve their knowledge and enhance their love for nature. You may use a photograph or a natural plant to explain its parts and functions. Explain how each part aids the plant’s growth and yields flowers or fruits. You might explain to them the value of plants in air purification and how they benefit humans. Understanding plant parts is essential as they play vital roles in our ecosystem. Roots prevent soil erosion, stems support the plant structure, leaves produce oxygen, flowers attract pollinators, fruits provide food, and seeds ensure the continuation of plant life.
Make learning facts about plants for kids even more interesting by involving them in gardening activities or taking them on hikes or treks. And once they have a basic idea about the parts of a plant, you could introduce them to photosynthesis for kids.
Infographic: Plants Activities For Children
Plants are the life of our planet, providing oxygen while keeping the Earth clean and green. Since children are the torchbearers of the Earth’s future, they need to know the importance of plants to protect and nurture them. In this infographic, we bring you some interesting plant activity ideas to engage children in a fun learning process. Illustration: Momjunction Design Team
Illustration: Plant Parts For Kids: Interesting Facts And Functions

Image: Stable Diffusion/MomJunction Design Team
Learn all about plants with this fun video! Discover the different parts of plants and how they work together to help them grow. Explore the fascinating world of plants!
Personal Experience: Source
MomJunction articles include first-hand experiences to provide you with better insights through real-life narratives. Here are the sources of personal accounts referenced in this article.
ⅰ.Need of a plant;https://kushiswayoflearning.wordpress.com/2020/10/24/needs-of-a-plant/
References
- Anthophyta: More on Morphology; University of California Museum of Paleontology
https://ucmp.berkeley.edu/anthophyta/anthophytamm.html - Non-flowering Plants; North Florida Educational Institute
https://www.nfei.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/03/science-packages-6.pdf - Germination; Kids Growing Strong
https://kidsgrowingstrong.org/germination/ - Is a coconut a fruit, nut or seed?; Library of Congress
https://www.loc.gov/everyday-mysteries/agriculture/item/is-a-coconut-a-fruit-nut-or-seed/ - Phragmites australis (common reed); CABI
https://cabidigitallibrary.org/doi/10.1079/cabicompendium.40514
Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our nurturing community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with fellow parents.
Read full bio of Beth Sullivan
Read full bio of Bharathi V
Read full bio of Harshita Makvana
Read full bio of Kavita Kankani