Image: Shutterstock
Pepto-Bismol is commonly used to treat gastrointestinal ailments such as gastroesophageal reflux, nausea, bloating, stomach upset, belchingiThe process of releasing excess air or gas from the stomach, commonly called burping. , and diarrhea. However, some parents may wonder if it is safe to use Pepto-Bismol while breastfeeding.
If you have diarrhea or acidity while breastfeeding, dietary and lifestyle changes are recommended to resolve the problem. However, if these changes don’t alleviate the issue, you may consider taking Pepto-Bismol after consulting your doctor.
Read this post to learn more about the ingredients of Pepto-Bismol, if it is safe for nursing mothers, possible side effects, and alternative remedies while breastfeeding.
Key Pointers
- Pepto-Bismol is an over-the-counter antacid prescribed for gastrointestinal issues such as heartburn, gas, indigestion, and diarrhea.
- The active component in Pepto-Bismol is bismuth subsalicylate, which may enter the breast milk.
- The CDC suggests nursing mothers to avoid the medication due to its potential side effects.
- Its components are also known to cause undesirable side effects in nursing infants.
- Mothers should discuss its possible effects and alternatives with a doctor before taking Pepto-Bismol while breastfeeding.
What Is Pepto-Bismol?

Pepto-Bismol is an over-the-counter (OTC) antacid used for relief from minor gastrointestinal ailments such as heartburn, nausea, upset stomach, bloated tummy, indigestion, gas, belching, and diarrhea (1). The medicine is available in liquid, capsule, and chewable tablet form.
What Are The Different Types of Pepto-Bismol?
Based on the manufacturer’s information, Pepto-Bismol is available in the following forms (2):
- Oral liquid
- Liquicaps or oral liquid capsules
- Caplets or oral tablets
- Chewable tablets
What Are The Ingredients Of Pepto-Bismol?
The active ingredient of Pepto-Bismol is a compound called bismuth subsalicylate, which plays a significant role in alleviating symptoms of gastrointestinal problems
. It forms a coat (protective layer) on the ulcers and helps in the secretion of prostaglandinsiLipid-derived compounds involved in the regulation of inflammation, blood flow, and blood clots in response to a tissue damage. and mucus that reduce the effects of stomach acid (3).
The concentration of the compound varies based on the form of medicine. The manufacturer recommends no more than eight doses in 24 hours (4).
Is It Safe To Have Pepto-Bismol When Breastfeeding?
If you are a breastfeeding mother wondering ‘Can I take Pepto while breastfeeding?’ It is important to note that the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends lactating mothers avoid bismuth subsalicylate, as it can find its way into breast milk (5).
The Journal of Travel Medicine also recommends lactating mothers avoid medication containing bismuth subsalicylate. Though the effects on the infant are unknown, salicylate was observed to be absorbed significantly (6). Therefore, consult your healthcare provider to learn about its safety aspects before taking this medication while breastfeeding.
What Are The Side Effects Of Pepto-Bismol On Breastfeeding Baby?

The side effects of Pepto-Bismol/Bismuth subsalicylate on the health of the infant are unknown.
But there is some research on the impact of the compound salicylate, which is also called salicylic acid. Salicylate is found in Pepto-Bismol as well as in Aspirin, whose effects on the breastfeeding baby have been widely researched (7).
Studies suggest that less than 1% of maternal salicylic acid dosage passes into breast milk (8). According to the Drug Principles in Lactation published by The American College of Clinical Pharmacy, “Salicylates should be avoided because of the risk of thrombocytopeniaiA condition of low blood platelet count in the body and tinnitusiA condition of hearing sounds such as ringing, wheezing, whistling, or hissing that isn’t present in reality. in a nursing infant (9).”
The compound also holds the potential to cause the following side effects among breastfeeding infants:
- Metabolic acidosis: The American Academy of Pediatrics reports metabolic acidosis as a side effect caused by maternal salicylate dosage. Metabolic acidosis is a condition where the pH of the body fluids, including blood, decreases and causes excessive acidity. Acidosis quite commonly occurs due to a problem in the kidneys, which are responsible for maintaining the normal acidity of the body (10).
Even though there are no studies to prove that the salicylates in Pepto-Bismol have the same side effects as that in Aspirin, it is safe to avoid it during breastfeeding, considering that salicylic acid can pass into breast milk.
What Precautions To Take When Taking Pepto-Bismol?
Whether breastfeeding or not, you should exercise the following precautions before using Pepto-Bismol (1) (11):
- Let your pharmacist know if you are allergic to aspirin, any other medication, or amaranth (a coloring substance used in Pepto Bismol).
- Avoid usage if you have ulcer or bloody or black stools.
- Avoid using the chewable forms of the medicine if you have phenylketonuria, as the chewable tablets contain aspartame.
- Consult your physician if you have a fever, mucus in stools, blood clotting disorder, diabetes, arthritis, or gout.
What Are The Alternatives To Pepto-Bismol?

There are both medicinal and non-medicinal alternatives to Pepto-Bismol.
- Increased fluid intake, avoiding acidic foods, chewing ginger: Try avoiding acidic foods, chewing a piece of ginger or licoriceiA flowering herb known for aiding digestive problems and infections. . But, if your symptoms do not subside in a day, then consult a doctor and take the appropriate medication.
 Quick tip
Quick tip- Sodium bicarbonate and calcium carbonate-based antacids: You can consider antacids made with sodium bicarbonate (baking soda) to relieve acidity. These compounds have a localized effect within the stomach, and maternal dosage is seldom known to cause side effects in a breastfeeding baby (12).
- Simethicone: It provides relief from gastrointestinal discomforts such as gas, fullness, and abdominal discomfort (13).Simethicone is considered relatively safe during breastfeeding as it is said to be unabsorbable from the maternal gastrointestinal tract. Even if it is absorbed, minute amounts are found in the breast milk. But, consult your doctor before taking Simethicone.
- Loperamide: The compound is used for controlling diarrhea, including traveler’s diarrhea (14). Studies found that loperamide is secreted in extremely small amounts in breast milk. Hence, the American Academy of Pediatrics considers loperamide compatible with breastfeeding. However, you should consult a doctor before using the medicine because you may have to monitor the baby for drowsiness, dry mouth, vomiting, and constipation.
- Histamine-based medicines: They are used to suppress acid secretion during GER and provide relief (15). Among the various histamine-based drugs, Famotidine has been found to be least secreted into breast milk (12) but it might alter the taste of the milk.
- Proton pump inhibitors: This class of medicines, including esomeprazole and omeprazole (16) (17), help regulate the production of acid by the stomach to prevent acidity. A low, regulated dosage of these medicines is unlikely to cause any side effects in the breastfeeding baby (18).
 Quick tip
Quick tipFrequently Asked Questions
1. Can Pepto-Bismol interact with other medications while breastfeeding?
Pepto-Bismol may interact with other medicines during breastfeeding, making it unsuitable for lactating mothers. Taking Pepto-Bismol with Methotrexate should be avoided. Aspirin and aspirin-like medications, certain medications used for treating diabetes and gout, as well as medications that treat or prevent blood clots like warfarin, may also interact with Pepto-Bismol (19).
2. Can Pepto-Bismol cause allergic reactions while breastfeeding?
Pepto-Bismol can cause allergic reactions in some people, especially those who are allergic to aspirin or salicylates. The symptoms include skin rash, itching, hives, and swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat (19). After taking Pepto-Bismol, watch for unusual signs in your baby, such as fussiness or feeding changes, and seek medical advice if needed. You should also consult a doctor before having Pepto-Bismol if having painkillers when breastfeeding.
Pepto-Bismol, while breastfeeding, is usually not recommended as the bismuth salicylate contained in it may be secreted in breast milk and reach the baby. It is a medication for treating mild gastrointestinal disturbances whose effects on breastfeeding infants are not clearly known. However, the medication holds a theoretical risk of causing conditions such as thrombocytopenia, tinnitus, or metabolic acidosis in them. Try addressing minor digestive issues with home remedies first, and in case the condition is not relieved, check with your doctor for safer alternatives when lactating.
Infographic: Who Should Not Take Pepto Bismol?
Pepto Bismol is usually not recommended during breastfeeding due to the risk of the infant being exposed to salicylate. However, other underlying health conditions make Pepto Bismol unsuitable for use, too. The infographic below summarizes who should not take the medication. Illustration: Momjunction Design Team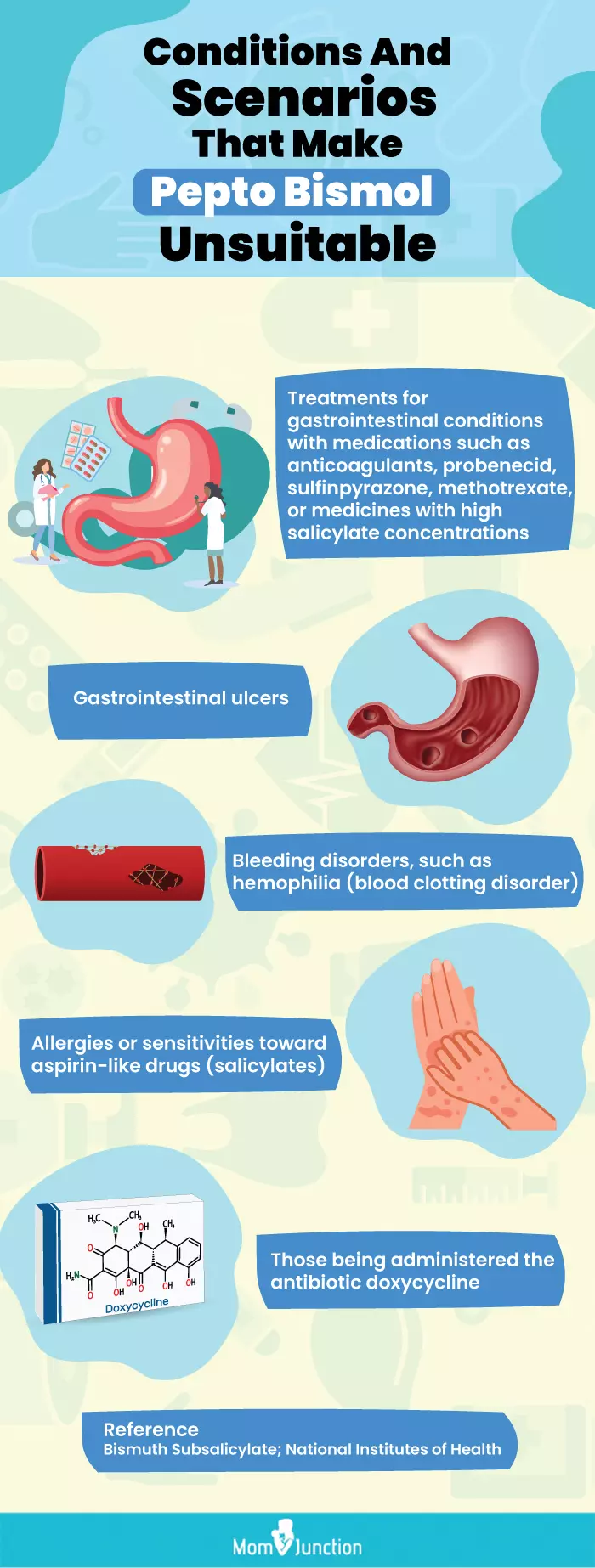
Illustration: Can You Have Pepto Bismol When Breastfeeding?

Image: Dalle E/MomJunction Design Team
Did you have to take Pepto-Bismol while breastfeeding? Tell us about your experience in the comment section below.
This post is for informational purposes only and is not a replacement for a doctor’s consultation. Do not use any medication without talking to your doctor.
References
- PEPTO-BISMOL- bismuth subsalicylate.
https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/fda/fdaDrugXsl.cfm?setid=854c803e-5edb-4e94-bc84-77b35fc69225&type=display - All Pepto Bismol Products.
https://pepto-bismol.com/en-us/products - Bismuth subsalicylate.
https://tmedweb.tulane.edu/pharmwiki/doku.php/bismuth_subsalicylate - Pepto-bismol FAQs.
https://pepto-bismol.com/en-us/faq - Foodborne and Waterborne Illness and Breastfeeding.
https://www.cdc.gov/breastfeeding-special-circumstances/hcp/illnesses-conditions/food-water-borne-illness.html?CDC_AAref_Val=https://www.cdc.gov/breastfeeding/breastfeeding-special-circumstances/maternal-or-infant-illnesses/food-illness.html - Lin H. Chen, et.al.; (2010); Breastfeeding travellers: precautions and recommendations; Journal of Travel Medicine.
https://academic.oup.com/jtm/article/17/1/32/1879801 - Aspirin.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK501196/ - Bismuth subsalicylate.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK501324/ - Julie J. Kelsey; Self-Assessment Program 2016-2018; Drug principles in lactation.
https://www.accp.com/docs/bookstore/psap/p2016b3_sample.pdf - Metabolic acidosis.
https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000335.htm - Who can and cannot take Pepto-Bismol.
https://www.nhs.uk/medicines/pepto-bismol/who-can-and-cannot-take-pepto-bismol/# - Philip O. Anderson; (2018);Treating gastroesophageal reflux and heartburn while breastfeeding.
https://www.liebertpub.com/doi/pdfplus/10.1089/bfm.2018.0124 - A Young Seo, Nayoung Kim, and Dong Hyun Oh; (2013); Abdominal bloating: Pathophysiology and treatment.
https://www.jnmjournal.org/journal/view.html?doi=10.5056/jnm.2013.19.4.433 - Loperamide.
https://medlineplus.gov/druginfo/meds/a682280.html - H2 Blockers.
https://aboutgerd.org/treatment/medications/h2-blockers/ - Esomeprazole.
https://medlineplus.gov/druginfo/meds/a699054.html - Omeprazole.
https://medlineplus.gov/druginfo/meds/a693050.html - Omeprazole | Esomeprazole.
https://mothertobaby.org/fact-sheets/omeprazole-esomeprazole/pdf/ - Bismuth Subsalicylate Tablet.
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/drugs/18631-bismuth-subsalicylate-tablets - BRAT Diet: Recovering From an Upset Stomach.
https://familydoctor.org/brat-diet-recovering-from-an-upset-stomach/ - Nausea and acupressure.
https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/002117.htm
Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our nurturing community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with fellow parents.
Read full bio of Melissa Kotlen
Read full bio of shreeja pillai
Read full bio of Rohit Garoo
Read full bio of Vidya Tadapatri



















