Image Shutterstock
Our body is home to many microorganisms, and not all are harmful to us. A few microorganisms, called probiotics, live in symbiosis with us and can be found lining our digestive tract, urogenital tracts, and mouth (1). This post talks about the benefits of probiotics for children you should know.
Probiotics can be obtained from fermented foods or supplemented by the body. These live and beneficial bacteria or yeast are helpful when given in the right amounts. They help ward off the harmful microbes that enter one’s body during an infection. They also help digest food and absorb nutrients (2).
Key Pointers
- Probiotics are typically safe for children and beneficial for digestive and immunological health.
- Lactobacillus, Bifidobacteria, and Saccharomyces boulardii are microbe genera commonly used as probiotics.
- A daily probiotic dose of five to ten billion colony-forming units (CFUs) is appropriate for children.
- Common natural sources of probiotics are yogurt, buttermilk, and pickles.
Are Probiotics Good For Children?
Probiotics are generally safe for children and beneficial for the gut. They may help in the prevention of upper respiratory tract infections and diarrhea. Probiotics release metabolic by-products that act as immune health modulators and help maintain a healthy gut environment (3).
However, probiotics may not be safe for premature infants or children with reduced immune system function or cancer as they may increase the risk of infections (4).
 Did you know?
Did you know?What Are The Benefits Of Probiotics For Children?
The right probiotics given at the right dosage are beneficial for children. Each strain of bacteria or yeast offers different health benefits, such as the following (4):
- The by-products released by probiotics boost the immune system.

Image: Shutterstock
- Probiotics are good for the digestive system, as they aid digestion and proper absorption of certain nutrients.
- The right strain of probiotics can shorten infectious diarrhea and reduce antibiotic-associated diarrhea.
- A few studies have indicated that probiotics can reduce constipation among children (5).
- Certain studies state that probiotics reduce the incidence of irritable bowel syndromeiA chronic intestinal and stomach disorder characterized by cramping and constipation , Crohn’s diseaseiA chronic inflammatory condition that affects the digestive system, causing abdominal pain, diarrhea, and weight loss , and pouchitis (a complication following the surgical removal of ulcerative colitisiAn autoimmune disorder that causes sores, bleeding, and diarrhea in the colon and rectum ) (3) (6).
- When used with antibiotics, probiotics may help prevent urinary tract infections (7).
- A few studies suggest that probiotics could help prevent allergies in children such as allergic allergic rhinitisiInflammation of the nasal passage caused by an allergen leading to itching, sneezing, and watery eyes (8).
What Are The Types Of Probiotics For Children?
Three genera of microbes are mainly consumed as probiotics:
- Lactobacillus: The probiotic bacteria Lactobacillus produces lactic acid from milk, protecting the gut from bad bacteria. Lactobacilli are commonly used as probiotic supplements following antibiotic treatment to restore the gut microbiome balance after diarrheal episodes. These friendly bacteria line the gut and vagina (9).
- Bifidobacteria: This species of healthy bacteria also lines the intestine and assists in breaking down the food in the gut and absorbing nutrients (10).
- Saccharomyces boulardii: This yeast is available in supplement form and is used with medications to treat inflammatory bowel diseases, such as Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis (11).
There are many strains of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium. Each subtype of species is mentioned after the abbreviated version of Lactobacillus (L.) and Bifidobacteria (B.).
In addition to the aforementioned three strains, several other bacterial variants may be employed as probiotics. These include:
- Clostridium butyricum: This bacteria is beneficial for promoting regulatory T-cell production, preventing colitis, enhancing liver well-being, and fighting infections. It fortifies gut flora amid antibiotic treatment, with its bacteriocin inhibiting harmful bacteria (12).
- Streptococcus thermophilus: It acts as a probiotic, helping digestion, reducing antibiotic-related diarrhea, easing ulcerative colitis and leaky gut symptoms, improving lactose digestion, and decreasing IBS symptoms. It aids in infant probiotic flora, reduces atopic dermatitis symptoms, prevents bacterial vaginosis, lowers kidney stone risk, boosts good cholesterol, and shows anti-tumor activity while decreasing baby colic (13).
Since each strain benefits the body differently, probiotic supplements are prescribed based on their effect on the body. L. acidophilus, L. reuteri, B. lactis, B. breve, B. animalis, and B. longum are the commonly available strains of probiotic bacteria.
What Is The Right Dosage For Probiotics?
Each individual has a unique requirement of beneficial bacteria or yeasts. Approximately five to ten billion CFUs (colony-forming units) per day is considered an adequate probiotics dosage. Most probiotic supplements provide around one to ten billion CFU per dose (14) (15).
 Quick fact
Quick factWhat Are The Side Effects Of Probiotics For Children?
The intake of probiotics has a few side effects (1) (2) (16)
• Their consumption may be unhealthy for immunocompromised individuals as they may trigger the immune system and worsen the health condition.
• Probiotics may transfer their antibiotic-resistant gene to the harmful bacteria in the gut.
• A Few probiotic products may not specify the strain used in the supplement. Therefore, the consumption of mixed probiotic products may result in other diseases.
• Probiotics may also cause minor digestive issues such as stomach issues, diarrhea (especially in lactose intolerant children), bloating, or flatulence.

Image: IStock
• The release of D-lactic acid may cause acidosis in patients with short bowel syndrome (17).
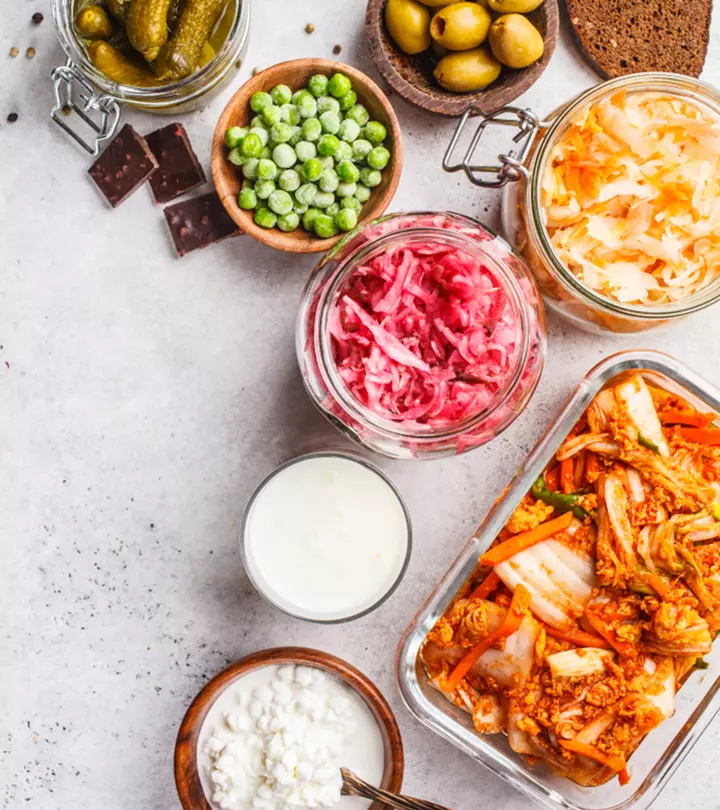
What Are Some Natural Sources Of Probiotics?
Introducing probiotics through natural sources is safer since supplements may not be regulated. However, natural sources of probiotics may contain allergens; hence, always check the ingredient lists of products. Here are a few food sources of probiotics (18):
- Yogurt: This ubiquitous milk product is known for its beneficial microbial colonies. Yogurt contains the strains of Lactobacillus acidophilus or Lactobacillus bulgaricus, which convert the lactose in milk to lactic acid.
Due to its bland flavor, yogurt is versatile and can be combined with fruits as a healthy snack. However, plain yogurt is recommended over the artificial flavors available in the market.
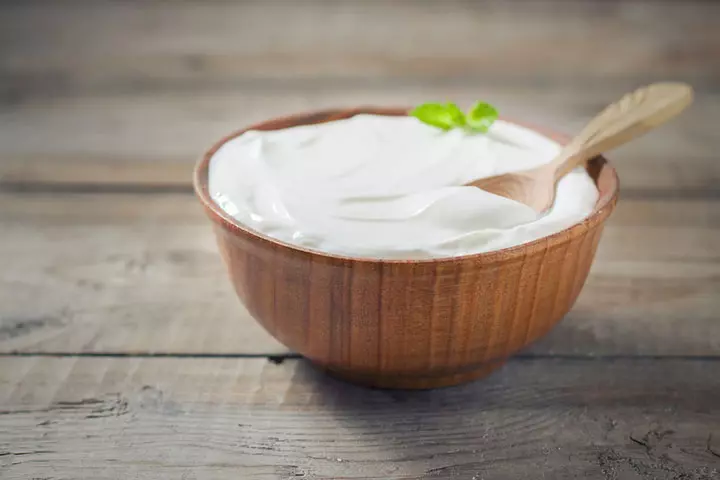

Image: Shutterstock
- Kefir: This milk product is harbored by Lactobacillus kefiri. It can be prepared with animal and plant-based milk. The milk is fermented, thickened, and strained to obtain kefir grains, which can be added to plain milk to increase their probiotic quality.
- Buttermilk: Indian buttermilk, and its varieties, such as lassi and chaas, made from unflavored, diluted yogurt, are good probiotics. Alternatively, the cultured buttermilk available in the US does not offer many probiotic benefits.
- Viili: This Finnish milk product with a ropey consistency is cultured by Lactobacillus.
- Pickles and other fermented dishes: Traditionally prepared brine-cured and salt-cured pickles without preservatives such as sodium benzoate are good sources of probiotics. Kimchi from Asia, curtido from Central America, choucroute from France, and sauerkraut from Germany are good probiotic sources.
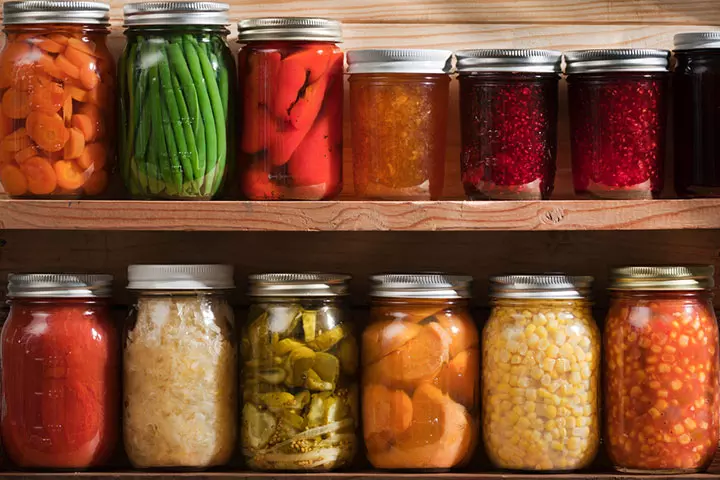

Image: IStock
- Lebne: It is a Middle Eastern cheese made from yogurt and has a thick consistency due to the elimination of whey. It is also known as Greek yogurt or strained yogurt and has an acidic flavor.
What Are The Precautions To Take While Consuming Probiotics?
Probiotics are safer for consumption through food than supplements. According to a study published in the Gastroenterology journal, it was found that one in 20 US adults or children use nonfood pre-, pro-, or synbiotic products, and use has sharply increased in recent years. Here are some precautions you should consider while giving probiotics to a child (2):
- There is no standard regulation for probiotic supplements in the US. You may find them as dietary supplements, food products, or drugs. Since dietary supplements sold as food products may not be FDA approved, they could contain unregulated strains of bacteria, which may have adverse effects.
- Always read the product description and give it at the dose recommended by a medical professional. Although probiotic overdoses do not have known side effects, their consumption may cause minor gastrointestinal disturbances.

Image: Shutterstock
- One dosage doesn’t suit all as the microbiome population varies in each individual.
- Stop offering the probiotic if you notice any side effects.
- Some probiotics may need to be stored in a sterile environment or refrigerated to prevent the death of the organisms.
- Read the label for any allergens.
- Probiotics cannot cure diseases and, hence, are not given to replace medications. Watch out for probiotic supplements that offer misstatements about products.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Do probiotics help children with ADHD?
Yes. Several studies have found a link between probiotics and the improvement of ADHD symptoms. A study found that taking the probiotic Lactobacillus orally for the first six months of life reduced the incidence of ADHD or ASD at 13 years of age (19). Similarly, another study found that children with ADHD who received Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (LGG) supplementation had a higher health-related quality of life (20).
2. Can probiotics help children focus?
Probiotics play a role in the gut-brain axis and have been shown to improve the cognitive functioning of the brain in human clinical studies and animal studies. However, the exact role of probiotics in this association is yet to be determined (20) (21).
3. At what age can I give my child foods with probiotics?
Probiotics are safe and well-tolerated in healthy babies and children, premature babies, babies with low birth weight, and children with HIV (22). Hence, you may add food sources with probiotics to your baby’s diet after they start eating solid meals (six months onwards).
Probiotics for children are believed to be safe and help by boosting immunity, relieving constipation, etc. However, you should not give them to children without consulting a doctor as it may cause acidosis, bloating, or other side effects. It is important to know that probiotics from food sources are much safer than supplements. However, be cautious of food allergens that may adversely affect your child’s health. Before using any probiotic supplements, read the product details carefully and determine the correct dosage. In case of any concerns, discontinue the usage and talk to your doctor.
Infographic: Benefits And Dietary Sources Of Probiotics For Children
A healthy gut makes a healthy person, and probiotics foster good digestive health. Let’s read through our infographic to explore different sources of probiotics and what other benefits their consumption can have on children. Knowing these benefits will help you make an informed decision if you’re thinking about including probiotics in your child’s diet.
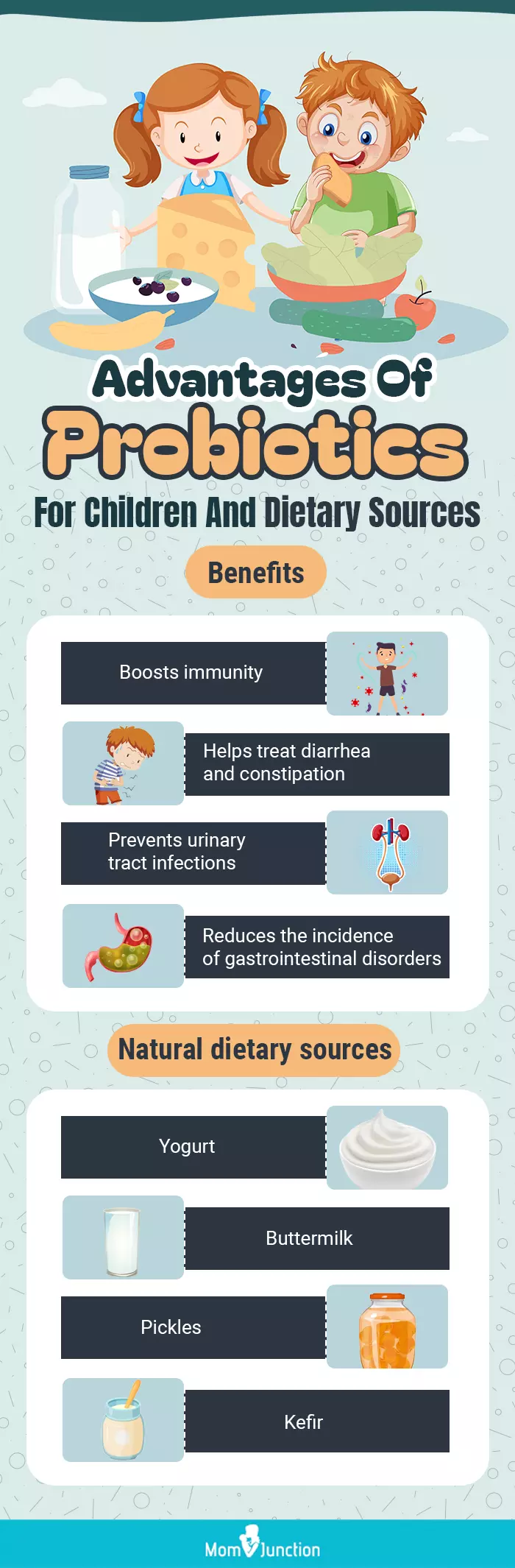
Illustration: Momjunction Design Team
Illustration: Probiotics For Kids: Health Benefits Side Effects & Dosage

Image: Stable Diffusion/MomJunction Design Team
Integrate probiotics seamlessly into your child’s diet to aid digestion. Discover the advantages and the right method to include these beneficial microorganisms in your child’s nutrition through this video.
References
- Probiotics.
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/14598-probiotics - Probiotics: What You Need To Know.
https://www.nccih.nih.gov/health/probiotics-usefulness-and-safety - Probiotics And Prebiotics In Pediatrics.
https://publications.aap.org/pediatrics/article/126/6/1217/65014/Probiotics-and-Prebiotics-in-Pediatrics?autologincheck=redirected - The Pros And Cons Of Probiotics For Kids.
https://www.geisinger.org/health-and-wellness/wellness-articles/2018/02/09/13/53/the-pros-and-cons-of-probiotics-for-kids - Positive Effect Of Probiotics On Constipation In Children: A Systematic Review And Meta-Analysis Of Six Randomized Controlled Trials
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5408016/ - Probiotics Are A Good Choice In Remission Of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: A Meta Analysis And Systematic Review.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28294322/ - The Efficacy Of Probiotics In Prevention Of Urinary Tract Infection In Children: A Systematic Review And Meta-Analysis.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29102297/ - Various Effects Of Different Probiotic Strains In Allergic Disorders: An Update From Laboratory And Clinical Data
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2883099/ - Lactobacillus Acidophilus.
https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content?contenttypeid=19&contentid=Lactobacillus - Bifidobacteria And Their Role As Members Of The Human Gut Microbiota
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4908950/ - Saccharomyces Boulardii: What Makes It Tick As Successful Probiotic?
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7344949/ - N. Cassir et al.; (2016); Clostridium butyricum: from beneficial to a new emerging pathogen.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1198743X15009143#sec2 - S. thermophilus Probiotics Benefits & Side Effects.
https://probiotics.org/s-thermophilus/ - Probiotics In children.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18061785/ - Probiotics.
https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Probiotics-HealthProfessional/ - Probiotics.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20208051/ - A Case Of D-Lactic Acid Encephalopathy Associated With Use Of Probiotics
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19917522/ - Sources.
https://internationalprobiotics.org/resources/sources/ - Gara Arteaga-Henríquez et al.; (2020); Treating impulsivity with probiotics in adults (PROBIA): study protocol of a multicenter double-blind randomized placebo-controlled trial.
https://trialsjournal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13063-019-4040-x - Hojka Gregoric Kumperscak at al.; (2020); A Pilot Randomized Control Trial With the Probiotic Strain Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (LGG) in ADHD: Children and Adolescents Report Better Health-Related Quality of Life.
https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/psychiatry/articles/10.3389/fpsyt.2020.00181/full - Probiotics may help boost mood and cognitive function.
https://www.health.harvard.edu/mind-and-mood/probiotics-may-help-boost-mood-and-cognitive-function - Fact Sheet: Probiotics for infants and children.
https://www.mcri.edu.au/impact/watch-listen-download/download/fact-sheet-probiotics-for-infants-and-children - Can probiotics help when my child has an infection and needs to take antibiotics?
https://www.healthychildren.org/English/tips-tools/ask-the-pediatrician/Pages/Can-probiotics-help-prevent-tummy-trouble.aspx - How to get more probiotics.
https://www.health.harvard.edu/staying-healthy/how-to-get-more-probiotics
Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our nurturing community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with fellow parents.
Read full bio of Dr. Jessica Madden
Read full bio of Sindusha MS
Read full bio of Dr. Ritika Shah
Read full bio of Dr. Joyani Das