Image: ShutterStock
Your doctor may have prescribed you to receive an Rh sensitization injection, or RhoGAM shot during pregnancy if you have an Rh-negative blood type
. It’s an intramuscular injection prescribed to prevent Rh immunization in pregnant women (1). Continue reading to know about this injection and why a pregnant woman may require it. This post also discusses Rh sensitization and the key features of RhoGAM.
Key Pointers
- RhoGAM is an intramuscular injection that prevents Rh immunization in pregnant women to reduce the risk of fetal anemia, miscarriage, and stillbirth caused by Rh incompatibility.
- The injection usually doesn’t cause any harm during pregnancy, and the risk of miscarriage due to Rh incompatibility is higher than the injection’s risk.
- RhoGAM needs to be taken during every pregnancy, and if missed, doctors check for Rh sensitivity in mothers and closely monitor the baby to avoid poor outcomes.
- An Rh-negative mother receives a RhoGAM shot after pregnancy loss to prevent incompatibility in future pregnancies.
- Hypersensitive mothers and mothers with hemolytic anemia may experience adverse effects from the RhoGAM shot.
- It’s essential to consult with a doctor before taking RhoGAM and discuss any concerns regarding its effects.
Why Does A Pregnant Woman Need RhoGAM?

Image: Shutterstock
If a mother (pregnant woman) is Rh-negative (the red blood cells lack the Rh factor protein) and the father is Rh-positive, then there are chances that the baby could be Rh-positive. In such a case, the mother, who is Rh-negative, will have to carry an Rh-positive baby.
During pregnancy or delivery, small amounts of Rh-positive blood cells can enter the mother’s bloodstream. Since the mother’s body does not have the Rh proteiniAlso known as Rh factor, a protein found on the surface of red blood cells used in blood typing to determine blood compatibility. , it will treat the Rh-positive blood as a foreign body and cause the body to produce antibodies to attack the red blood cells containing the Rh protein.
If it is the mother’s first delivery, the produced Rh antibodies can cross the placenta and attack the Rh-positive red blood cells of the baby, increasing the risk of fetal anemia, miscarriage, stillbirth, or hemolytic diseaseiA condition in which red blood cells are destroyed, leading to anemia and other complications. (2).
So, if your healthcare provider finds such an Rh incompatibility during your pregnancy, then they might prescribe a RhoGAM injection during prenatal care check-up, which stops the mother’s body from producing antibodies to Rh-positive blood cells.
 Quick fact
Quick factWhen Is RhoGAM Given During Pregnancy?
Image: Shutterstock
An Rh-negative blood type mother may need a RhoGAM injection during her obstetric visit under the following conditions.
- Within 72 hours of delivering an Rh-positive baby or for prevention of Rh immunization at 26 to 28 weeks of pregnancy.
- Bleeding during pregnancy due to certain conditions.
- Trauma to the abdomen during pregnancy.
- After invasive procedures such as amniocentesisiA medical procedure that involves taking an amniotic fluid sample from the uterus to check for chromosomal or genetic disorders. , CVS, fetal blood sampling, or fetal surgery.
- Rh-negative women who could experience pregnancy loss at or up to 12 weeks of pregnancy. The dose is less.
- Ectopic pregnancy (implantation occurring outside the uterus)
- During attempts to manually turn a breech fetal position (3)
Can The RhoGAM Shot Cause A Miscarriage?
As per FDA, the RhoGAM injection belongs to pregnancy category C. There are no animal studies but the available human studies say that this injection does not harm the fetus or affect the pregnancy (2).
RhoGAM injection generally does not cause miscarriage; it is important to note that the risk of miscarriage is higher due to the Rh incompatibility than the injection. Once the mother’s body starts producing antibodies, all future pregnancies will be at risk (2).
Do You Have To Get The RhoGAM Shot In Every Pregnancy?

Image: Shutterstock
You need to get these shots in every pregnancy since they work for only a short while. Your doctor might give you one or more shots of Rh immunoglobuliniAlso known as antibodies, proteins produced by the immune system for protection against foreign bodies. during tests, such as an amniocentesis test around the end of your second trimester (28 weeks of your pregnancy), and after delivering your first Rh-positive newborn (5). Your doctor is the best person to determine the treatment.
Do You Need RhoGAM Shot After An Early Miscarriage/Abortion?
As per The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, an Rh-negative mother can make antibodies even if her first pregnancy was not full-term (3)
. So, to prevent Rh incompatibility issues in future pregnancies, Rh immunoglobulin is given to an Rh-negative mother who has had a miscarriage, abortion, or an ectopic pregnancy (5).
Where Do You Inject RhoGAM?
The RhoGAM injection must only be administered intramuscularly (1).
Who Should Not Take RhoGAM Injections?
In the following cases, RhoGAM injections are contradicted (4).
- Mothers who have a serious hypersensitivity reaction to human immunoglobulin products.
- Mothers with a history of hypersensitivity reaction to RhoGAM and its components
- IgA-deficient individuals since RhoGAM may trigger an allergic reaction.
What Are The Side Effects Of RhoGAM Injection?
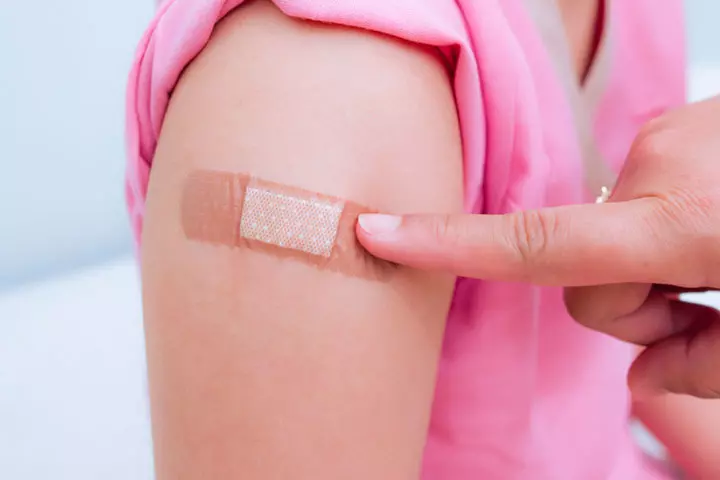
Image: Shutterstock
The RhoGAM injection is usually safe for maternal health, but it may have some minor side effects such as:
- Swelling, induration, redness, mild pain, or warmth around the injection site.
- Sometimes, women may also develop skin rashes, body aches, or slight elevation in body temperature.
Your doctor will keep you in observation for 20 minutes after the administration to check if the injection has triggered any side effects (4).
 Point to consider
Point to considerWhat Happens If You Do Not Get RhoGam Shot When Pregnant?
If you do not take RhoGAM injection during pregnancy, then your body will start preparing antibodies for the Rh protein, which cannot be reversed
. The antibodies might or might not affect your first pregnancy, but it will definitely cause adverse reactions for your subsequent pregnancies.
In the absence of RhoGAM injection, your doctor may perform regular blood tests in the last trimester gynecology visits to see if you have become Rh sensitized, and if you have, then your baby will be monitored for adverse effects. If there is a serious problem, then you might have to deliver preterm (2).
If the immune system of an Rh-sensitized mother destroys fetal red blood cells, a blood transfusion is administered to replace them. The likelihood of the survival of the fetus following a transfusion is influenced by various factors such as the severity of the fetal illness, the transfusion technique used, and the expertise of the performing physician (7).

Image: Shutterstock
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the difference between Rh-positive and Rh-negative blood?
The difference between Rh-positive and Rh-negative blood lies in the existence or nonexistence of a protein named the Rh factor on the exterior of red blood cells. When the protein is present, the blood is categorized as Rh-positive, and if it is not present, the blood is classified as Rh-negative. The terms “positive” or “negative” used in blood typing, such as O positive or A negative, signify the Rh status of the blood (3).
2. Can a woman with Rh-negative blood have a baby with Rh-positive blood?
Yes, it is possible for a woman with Rh-negative blood to conceive a baby with Rh-positive blood if the father is Rh-positive. This is because the baby may inherit the Rh-positive blood gene from the father (8).
3. Are there any natural remedies that can be used instead of a RhoGAM shot?
There are no known natural remedies that can be used as a substitute for a RhoGAM shot.
RhoGAM shot during pregnancy is given to mothers to help reduce the risks of miscarriage and stillbirth in case of Rh incompatibilities between the parents. However, if you have symptoms of hypersensitivity or anemia, you should avoid getting these shots as the results might be contradictory. Consult your doctor and talk to them thoroughly about the benefits and possible side effects of these shots and whether or not you are suitable for receiving them. Ensure that you get a shot of RhoGAM for each of your pregnancies, as their effects do not last for long.
Infographic: Other Uses Of Rho(D) immune globulin
Rho(D) immune globulin is indicated for conditions other than an Rh incompatibility during pregnancy. Refer to the infographic below to know which conditions may require this intervention. Illustration: Momjunction Design Team
This post is for informational purposes only and is not a replacement for a doctor’s consultation. Do not use any medication without talking to your doctor.
Illustration: RhoGAM Shot During Pregnancy: Importance Timings & Effects

Image: Dall·E/MomJunction Design Team
A RhoGAM shot is an injection given to pregnant women to prevent Rh incompatibility between mother and baby. Learn more in this video!
References
1. The RhoGAM story never gets old; RhoGAM Ultra-Filtered PLUS
2. Rh-Negative Blood Type and Pregnancy; American College of Nurse- Midwives
3. The Rh factor: How It Can Affect Your Pregnancy; The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists
4. RhoGAM FAQs; RhoGAM Ultra-Filtered PLUS
5. Rh Sensitization During Pregnancy; University of Wisconsin
6. Rh Factor Treatment in Pregnancy; Intermountain Healthcare
6. Rh Incompatibility During Pregnancy (for Parents); Nemours
7. Intrauterine Fetal Blood Transfusion for Rh Disease; Kaiser Foundation Health Plan of Washington
8. Rh Incompatibility During Pregnancy (for Parents); Nemours
Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our nurturing community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with fellow parents.
Read full bio of Dr. Shashwat Jani
Read full bio of shreeja pillai
Read full bio of Rebecca Malachi
Read full bio of Dr. Joyani Das