Image: iStock
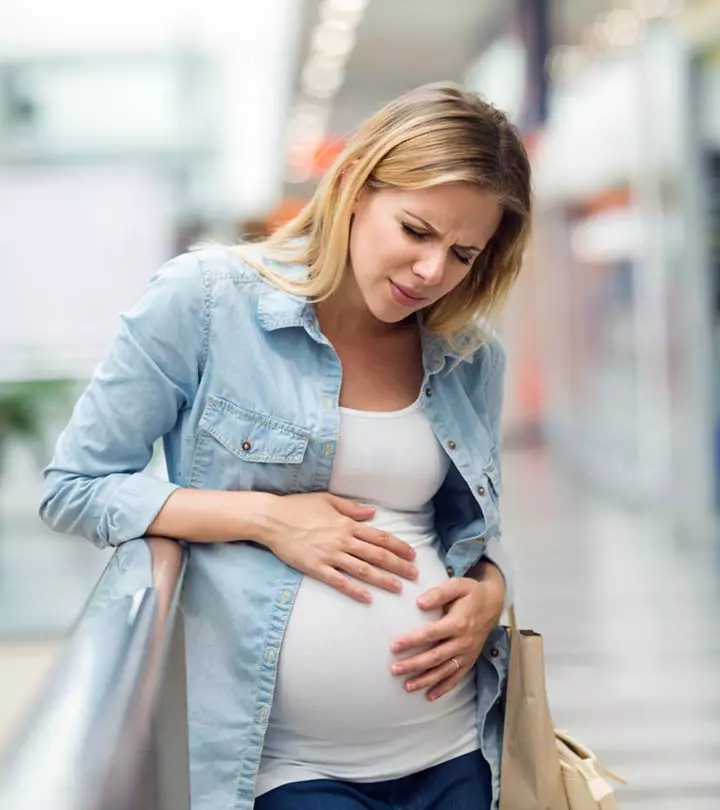
Abdominal pain during pregnancy may indicate labor if it happens towards the end of the third trimester.
But what if it occurs during any other time? Stomach pain during pregnancy could be due to benign causes and resolve on its own. However, there are also a few serious causes behind it that may affect pregnancy.
This post elaborates on the common and serious causes of abdominal pain during pregnancy. We have also included a few home remedies that may help relieve this discomfort.
Key Pointers
- Mild stomach pain or cramps are common during pregnancy.
- Common causes of stomach pain while pregnant involve expanding uterus, constipation, Braxton-Hicks contractions, and GERD.
- Some severe causes for pregnancy-related stomach pain may include placental abruption, miscarriage, preterm labor, and ectopic pregnancy.
- Relaxation, ample hydration, and a balanced, fiber-rich diet are home remedies that can help reduce pain caused by benign causes.
- Pregnant women should seek medical attention if their stomach pain is severe or persistent.
Are Stomach Pains Normal During Pregnancy?
Slight abdominal pain or cramps are normal during pregnancy (1). This is because a woman’s body tries to make space for the expanding uterus, resulting in some pain. A few gastrointestinal disturbances also add up to the cause. Harmless abdominal cramps during pregnancy usually fade out after resting or pooping. However, in rare cases, abdominal pain can indicate a serious condition that requires immediate medical care.
What Are The Common Causes of Abdominal Pain During Pregnancy?
A few physical and hormonal changes during pregnancy may result in abdominal pain.
- Constipation: The hormone progesterone affects the functioning of the lower GI tract and causes constipation in pregnant women. The accumulation of stools may lead to abdominal discomfort. Drinking plenty of fluids and consuming a fiber-rich diet can usually relieve constipation (2).
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD): Heartburn is a common sign of GERD. The increased progesterone levels during pregnancy affect the functioning of the esophageal sphincter (muscles that prevent stomach acid from entering the esophagus). As a result, the stomach acids tend to travel upwards, causing acid reflux, which may also manifest as chest pain during pregnancy. This is a usual pregnancy-related discomfort and usually resolves with dietary changes, eating habits, and medication (3).
- Expanding uterus: The muscular changes brought by the expansion of the uterus may result in abdominal pain, mostly near the pelvic region. This is common among most women. Ample rest and a safe exercise routine may relieve pelvic pain (4).
- Round ligament pain: Sharp pain in the abdomen or the hip area is common during the second trimester. This pain is due to the large ligaments that run from the uterus to the groin. A sudden twist or movement may accelerate the pain. The pain usually lasts a few seconds and goes away after some rest. Consult your doctor if the pain is frequent (5).
- Round ligament pain: Sharp pain in the abdomen or the hip area is common during the second trimester. This pain is due to the large ligaments that run from the uterus to the groin. A sudden twist or movement may accelerate the pain. The pain usually lasts a few seconds and goes away after some rest. Consult your doctor if the pain is frequent (5).

- Braxton-Hicks contractions: These are also known as false labor pains and occur during the second and third trimesters. These mild contractions last a few minutes and are characterized by stomach tightening. But, unlike true labor contractions, these false pains subside with any change in the movement or position. Also, these pains let you continue with your daily chores. If the pains last longer and feel unbearable, they may indicate labor (6).
Beth Barnes, a mother, describes how her stomach felt during Braxton Hicks contractions. She explains, “If you can take a hand off of the wall you fell against when the contraction first knocked the wind out of you, yes, you can definitely feel how hard your belly has become. The weirdest part is sometimes it’s only one side of the belly, so you’ll look down, and the left side will be bulging out like a rock, and the right will be round and smooth and smooshy.
“As for saying they ‘probably’ won’t cause discomfort, I don’t know about that. I only know my own experiences with them, and I can honestly say that almost every single one I can recall caused me discomfort. Once, when I was pregnant with Bee (her daughter), they came on so fast and so hard that I had to lean against a lamppost, slumped over, hands on my knees, and just had to breathe it out until it passed. I felt like I was going to pass out (i).”
- Painful orgasm: Orgasms during the later stages of pregnancy may result in contractions in the abdomen. This pain may also be classified under Braxton-Hicks Contractions and is mostly normal. You need not worry about this pain as orgasm during pregnancy is safe. But, if there are any complications, it is better to avoid sex (7).
The pain caused by the above factors seldom poses a threat and subsides on its own. However, do not hesitate to contact your obstetrician if pain due to any of these causes stays for long or causes severe discomfort, is accompanied by bleeding, or if you notice abrupt changes in fetal movements.
 Be watchful
Be watchfulWhat Are The Serious Causes Of Abdominal Pain During Pregnancy?
Sometimes, abdominal pain could be serious and requires medical care. The maternal pain in such cases could be due to the following reasons.
- Ectopic pregnancy: During a tubal or ectopic pregnancy, the egg implants itself in a place other than the uterus, mostly in the fallopian tubes. It may present as shooting pain in the shoulders, abdomen, dizziness, and vaginal bleeding. This pregnancy resembles a normal pregnancy and tends to go unrecognized initially. The risk of ectopic pregnancy could be higher in women with a previous history of infertility, ectopic pregnancies, or endometriosis. The risk may also be higher in women with age above 35, previous fallopian tubes or abdominal surgery, pelvic infertility, or those who conceived after using an intrauterine device (8).
- Placental abruption: It is an uncommon condition where the placenta detaches itself from the uterus, interrupting the fetus’ supply of nutrients and blood flow. The condition may usually occur in the second or third trimester and presents itself through vaginal bleeding, back or abdominal pain, progressive contractions, and a tender uterus.
A few risk factors are pregnancy above the age of 35, previous history of placental abruption, trauma to the abdomen, smoking, and drug abuse (9).
- Urinary tract infection: If not treated on time, the infection may spread to the uterus. The primary symptom of a UTI is pain during urination, foul-smelling urine, incontinence (leaking of urine), or fever. Most UTIs are treated with antibiotics (10).

- Miscarriage: A pregnancy loss before the 20th week results in a miscarriage or spontaneous abortion. In most cases, a miscarriage might occur within the first trimester. Vaginal bleeding is the primary sign of a miscarriage. The other signs may include severe abdominal pain and period-like cramps. There are many causes for a miscarriage, including infections during pregnancy, hormonal imbalance, problems related to the uterus or cervix, and chromosomal abnormalities. In addition, a previous history of miscarriage, smoking, and pregnancy after the age of 35 may also increase the risk (11).
- Gallstones: The fluctuating hormone levels in pregnancy may lead to the formation of gallstones. Most women with gallstones experience intense upper stomach pain during pregnancy. The pain may be magnified after consuming a fatty meal. Although the removal of gallstones may require surgery, it has a good prognosis (12).
- Preeclampsia: The condition during pregnancy is characterized by high blood pressure and higher levels of protein in the urine. This is a fatal condition as high blood pressure restricts the blood flow to the fetus and affects the supply of nutrients. Edema (swelling of hands and face), blurred vision, shortness of breath, and pain in the right side of the abdomen are a few symptoms of preeclampsia (13). According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), preeclampsia is thought to affect 5 to 7 percent of pregnancies.
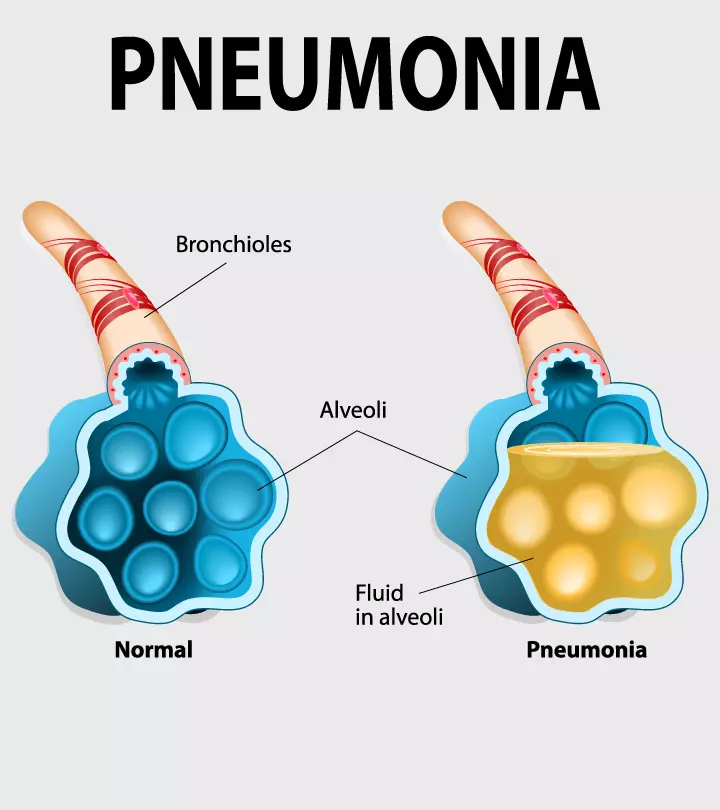
- Appendicitis: It is a condition in which the appendix is infected and inflamed. Since the symptoms resemble that of common pregnancy GI discomfort, the diagnosis of appendicitis may be challenging. Its symptoms may include severe lower abdominal pain and tenderness, nausea, vomiting, and fever (14).
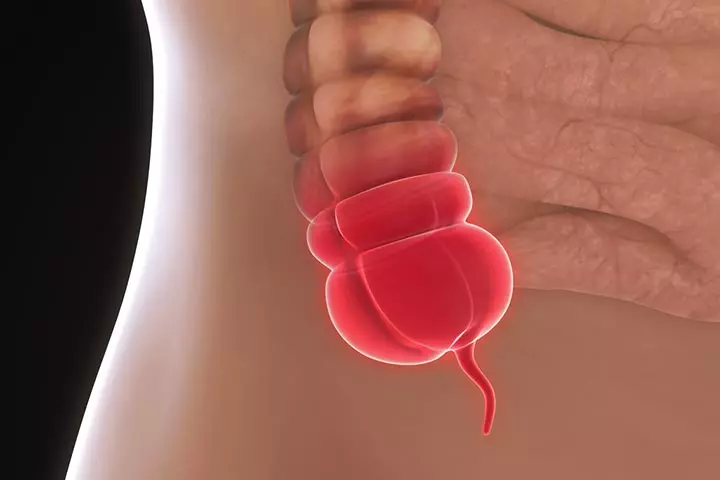
- Preterm labor: If you undergo labor before 37 weeks of pregnancy, it could be preterm labor. The uterus starts to tighten, resulting in shooting pain, back pain, water burst, vaginal discharge, and sometimes diarrhea (15).
If you notice any of the above symptoms, reach out to your medical professional.
How To Ease Abdominal Pain During Pregnancy?
You may try the following tips for relief from abdominal pain caused by common causes.
- Consume small and frequent meals.
- Drink plenty of fluids. Avoid taking alcohol, caffeinated drinks, carbonated, and high-sugar beverages (16).

- Consume a diet rich in fiber.
- Rest well and avoid doing tedious tasks
- Exercise regularly as it may help release gas and prevent soreness and cramping. Perform only pregnancy-safe exercises.
When To Call A Doctor?

Abdominal pain during pregnancy warrants a call to the doctor if the following signs appear.
- Any ache or bleeding during the first and third trimester
- Accumulation of water or swelling of hands, face, or feet (edema)
- Severe pain with or without vaginal bleeding
- Vision problems; sensitivity to light, blurred vision
- Fever, chills, headache, nausea, or vomiting
- Pain while urinating or foul-smelling urine
- Recurring and equally timed contractions that seem progressive.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Why does my pregnant belly hurt at night?
Lying on the bed can cause the uterus to exert more pressure on the stomach. It results in the stomach acids moving up the gastrointestinal tract, leading to heartburn and pain (17). You might also experience discomfort or stomach tightening during pregnancy if you overeat or lie down soon after eating.
2. Where are pregnancy cramps usually located?
Cramps during pregnancy are usually felt either on one or both sides of the abdomen (18). Soaking in warm water and practicing relaxation techniques may help relieve cramps and pregnancy-related pain.
3. Is it safe to take painkillers for abdominal pain during pregnancy?
Seeking guidance from a healthcare professional is crucial before consuming painkillers to address abdominal pain during pregnancy. Their personalized advice, considering the cause of the pain, can help identify safe options that align with pregnancy requirements, considering the medication’s potential risks and benefits.
4. Can dehydration cause abdominal pain during pregnancy?
Insufficient fluid intake can lead to cramping and discomfort in the abdominal area. Therefore, it is essential to prioritize adequate hydration throughout pregnancy to mitigate these symptoms (24).
5. Can abdominal pain harm the baby?
Mild or occasional abdominal pain during pregnancy typically does not harm the baby. However, persistent or severe abdominal pain requires prompt medical evaluation, as it may indicate an underlying complication, which could adversely impact the baby’s well-being (1).
All pains during pregnancy may not be a cause for concern. However, it is better to know the multiple factors that may affect the safety of you and your baby. If you are concerned about the pain, it does not harm giving a doctor a call. The chances are that these pregnancy cramps are normal, and you will feel better quickly.
Infographic: Some More Causes Of Stomach Pain During Pregnancy
Apart from the ones mentioned above, some more causes of abdominal pain might give rise to pregnancy discomfort. These causes are generally not life-threatening and may or may not be linked to pregnancy. Read this infographic to educate yourself on what these causes may be. Illustration: Momjunction Design Team
Illustration: Causes of Abdominal (Stomach) Pain During Pregnancy
_pain_during_pregnancy_illustration.jpg.webp)
Image: Stable Diffusion/MomJunction Design Team
Experiencing discomfort in your lower abdomen during pregnancy? Explore valuable insights into round ligament pain and effective management techniques in this highly informative video.
Personal Experience: Source
MomJunction articles include first-hand experiences to provide you with better insights through real-life narratives. Here are the sources of personal accounts referenced in this article.
i. Braxton hicks contractions.https://iamthemamamantra.wordpress.com/tag/braxton-hicks-contractions/
References
- Stomach Pain In Pregnancy.
https://www.nhs.uk/pregnancy/related-conditions/common-symptoms/stomach-pain/ - 4 Common Pregnancy-Related GI Issues And When To Call The Doctor.
https://utswmed.org/medblog/4-common-pregnancy-related-gi-issues-and-when-call-doctor/ - Pregnancy And Heartburn.
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/12011-heartburn-during-pregnancy#symptoms-and-causes - Uterus Pain.
https://www.medanta.org/patient-education-blog/what-causes-uterus-pain-in-early-pregnancy - Round Ligament Pain.
https://americanpregnancy.org/healthy-pregnancy/pregnancy-complications/round-ligament-pain-during-pregnancy/ - Braxton Hicks Contractions.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470546/ - Sex In Pregnancy.
https://www.nhs.uk/pregnancy/keeping-well/sex/ - Ectopic Pregnancy.
https://www.acog.org/womens-health/faqs/ectopic-pregnancy - Placental Abruption.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482335/ - Urinary Tract Infections (UTI’s) In Pregnancy.
https://www.pregnancybirthbaby.org.au/urinary-tract-infections-utis-during-pregnancy#symptoms - Miscarriage.
https://www.marchofdimes.org/find-support/topics/miscarriage-loss-grief/miscarriage - A Guide To Gallstones During Pregnancy.
https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2781051 - Preeclampsia.
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/17952-preeclampsia - Appendicitis In Pregnancy.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK551642/ - Preterm Labor.
https://www.stanfordchildrens.org/en/topic/default?id=preterm-labor-90-P02497 - Foods To Avoid In Pregnancy.
https://www.tommys.org/pregnancy-information/im-pregnant/nutrition-in-pregnancy/foods-avoid-pregnancy - How can I get better sleep while pregnant?
https://intermountainhealthcare.org/blogs/how-can-i-get-better-sleep-while-pregnant - Pregnancy Cramps
https://americanpregnancy.org/healthy-pregnancy/pregnancy-concerns/cramping-during-pregnancy/ - How can I get better sleep while pregnant?
https://intermountainhealthcare.org/blogs/how-can-i-get-better-sleep-while-pregnant - Pregnancy Cramps
https://americanpregnancy.org/healthy-pregnancy/pregnancy-concerns/cramping-during-pregnancy/ - Stomach (abdominal) pain or cramps in pregnancy.
https://www.tommys.org/pregnancy-information/pregnancy-symptom-checker/stomach-abdominal-pain-or-cramps-pregnancy - Sharp Pain During Pregnancy.
https://americanpregnancy.org/healthy-pregnancy/pregnancy-complications/sharp-pain-pregnancy/ - Best Sleeping Positions During Pregnancy.
https://americanpregnancy.org/healthy-pregnancy/pregnancy-health-wellness/sleeping-positions-while-pregnant/ - Stomach Pain in Pregnancy.
https://americanpregnancy.org/healthy-pregnancy/pregnancy-complications/abdominal-pain-during-pregnancy/
Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our nurturing community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with fellow parents.
Read full bio of Dr. Shashwat Jani
Read full bio of Sindusha MS
Read full bio of Rebecca Malachi
Read full bio of Reshmi Das






 Quick tip
Quick tip