Gastroenteritis, also known as the stomach flu, is caused due to an infection in the intestines
. It may affect babies and toddlers, resulting in serious health problems. Stomach flu in toddlers may have several causative factors, but the common flu virus is not responsible for the infection (1).
Read this post as we discuss stomach flu in toddlers, its causes, treatment, and ways to manage the infection with some home remedies.
Key Pointers
- Gastroenteritis is an infection in the digestive system caused by viruses, bacteria, and protozoa.
- The symptoms include diarrhea, vomiting, loss of appetite, stomach cramps, and fever.
- The diagnosis is made by examining symptoms and stool or blood tests.
- Treatment options include rehydration, antibiotics, and pain medication. Rest and fluids can also help.
- Complications of gastroenteritis in toddlers may include dehydration, malnutrition, and secondary infections.
What Is Stomach Flu In Toddlers?
Stomach flu is an infection that affects parts of the gastrointestinal tract (2). Commonly referred to as the ‘stomach bug,’ the infection develops when pathogens attack the gastrointestinal tract and cause widespread inflammation of the digestive system, making it dysfunctional.
The infection can affect any part of the digestive system –from the stomach to the large intestine. A slew of bacteria and viruses cause this infection in babies.
What Causes Stomach Flu In Toddlers?
The following are the most common pathogens to cause gastroenteritis in toddlers (3):
1. Viruses
- Rotavirus
- Norovirus
- Sapovirus
- Adenovirus
- Astrovirus
- Enterovirus
2. Bacteria
- Salmonella
- Staphylococcus
- Campylobacter jejuni
- Escherichia coli
- Shigella
- Yersinia enterocolitica
- Vibrio cholerae
3. Protozoans and parasites
- Giardia lamblia
- Entamoeba histolytica
- Cryptosporidium
- Strongyloides stercoralis
Viruses alone contribute to about 75-90% of stomach flu cases among toddlers (4). Rotavirus is the leading cause of gastroenteritis in the world while norovirus is the most common reason for gastroenteritis in the US (5). According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the global incidence of acute gastroenteritis cases associated with norovirus is estimated to be approximately 18%, potentially resulting in an annual mortality count of around 200,000. Conversely, parasites are accountable for less than 5% of the documented cases.
 Be watchful
Be watchfulHow Do Toddlers Catch The Stomach Flu?

The primary source of the stomach flu pathogens is contaminated food and water. Since toddlers eat a variety of food, they can be more at risk of infection than infants who are exclusively breastfed. Pathogens usually take the fecal-oral route when food and water come in contact with infected feces.
Contaminated objects such as the baby’s toys, toilet seat or potty chair can carry the flu-causing viruses that thrive easily on the surfaces for days together. If someone in the family has gastroenteritis, then they can transmit the disease to the baby by touching the baby’s things without washing their hands properly.
Babies who contract the virus or pathogen will start showing symptoms of the condition soon.
What Are The Symptoms Of Stomach Flu In Toddlers?

The symptoms of stomach flu can take a day or two to develop (6). A toddler with stomach flu will display the following symptoms of the condition (7):
- Diarrhea
- Vomiting
- Nausea
- Stomach cramps or persistent tummy ache
- Poor appetite
- Fever or lethargy
- Irritability and fussiness with a headache
- General malaise
Diarrhea and vomiting are among the first symptoms to suggest something is wrong with the toddler’s gastrointestinal tract
. Stomach flu can be risky, and for this reason, you must take the toddler to the doctor for a diagnosis and treatment.
Julia, a mother of four from Wisconsin, recounts an incident in which her son contracted the stomach flu upon their return from a family vacation. She says, “More panic from me—about work, about the rest of us catching this bug, and about my baby boy being really freaking sick. It could have been worse. At least he was able to play with his trains a bit this day. But it’s just so concerning to have so many trips to the bathroom. By the end of the night I’m sure he had gone more than 10 times, the final three times being in the last hour before bed.”
Talking about the possible source of infection, she adds, “All of the families on our trip last weekend have been affected by this horribleness in one way or another. Apparently the internet says that water parks are cesspools for germs. Did not know this. So glad we could find out. So that’s that. Sick little boy over here, for the past three days. The doctor says they don’t think twice about a stomach bug until it lasts 5-7 days (i).”
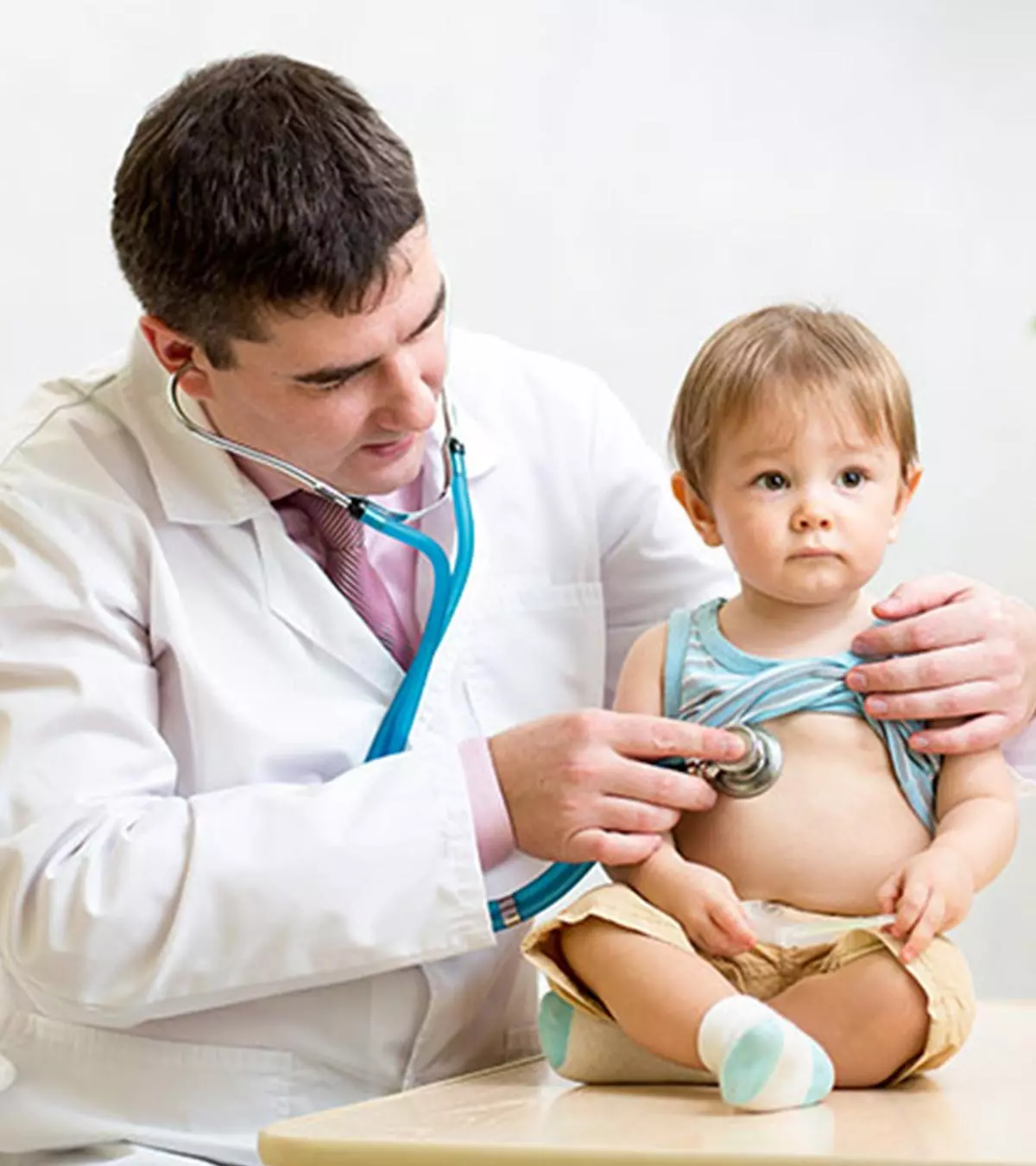
How Is Stomach Flu Diagnosed?
Here’s how a pediatrician will diagnose stomach flu in toddlers:
- Symptomatic diagnosis: In most cases, the doctor can identify the condition by assessing the symptoms. If the details of the symptoms are insufficient or inconclusive, then the doctor will proceed to other diagnostic methods.
- Stool test: Stool test helps determine the precise cause of gastroenteritis. A sample of stool is collected for laboratory analysis to identify the pathogen causing the infection.
- Blood test: Blood tests determine the presence of pathogens in the blood and also the antibodiesiDefensive proteins produced by the immune system in response to foreign invaders such as bacteria and viruses. produced by the immune system.
What Is The Treatment For Stomach Flu In Toddlers?
The treatment depends on the fundamental cause of stomach flu. The following medications help cure the infection:
- Rehydration salts help restore the essential salts lost by the body through diarrhea.
- If bacteria are the cause of the infection, then the doctor will prescribe antibiotics.
- Anti-parasitic medicines work against parasites and protozoansiA large group of single-celled parasites capable of causing severe intestinal diseases in humans. .
- Analgesic medicines help subdue the pain and discomfort caused by gastroenteritis. They also work in reducing the fever.
Usually, rehydration salts are the only remedy suggested for gastroenteritis. Medical experts state that the only treatment your child will probably need is bed rest and plenty of fluids. Read more about how to care for the baby at home.
Home Remedies For Stomach Flu In Toddlers
Homecare plays a significant role in ensuring a speedy recovery of the toddler. Here is what you should do to nurse your baby back to health (8):
Provide plenty of fluids:
- Give your toddler small sips of liquids throughout the day. Do not let the child drink it all at once, as that can make them throw up.

- Babies who only breastfeed can have an extra feed of milk.
- Toddlers can have plain water as well as oral electrolyte solutions, also called oral rehydration salts (ORS), such as Pedialyte. Toddlers can be breastfed too.
- The amount of ORS you need to give your toddler depends on their weight. The World Health Organization (WHO) suggests that you multiply the toddler’s weight in kilograms with 75 to arrive at the volume of ORS you need in milliliters (9). Give the recommended amount of ORS over the first four hours. You can give more later if the child is still dehydrated.
- You can give the baby formula or breast milk, but avoid animal milk since the baby’s tummy can have problems digesting it (10).
Rest is vital:
- Make sure your little one rests a lot. Bed rest gives the body time to fight infection.
- Avoid sending the toddler out to play or indulge in high-intensity games and activities.
- Good sleep is also essential for a speedy recovery.
Home care alone can help your toddler feel better in a few days. Vomiting usually goes away in a couple of days, but diarrhea in toddlers can persist for a couple of weeks (11). The infection is entirely gone by the end of two weeks.
Continue with home care for an extended duration to replenish the fluids and calories lost by the baby. Proper home care also involves giving the right food to the baby.
What To Feed A Toddler With Stomach Flu?
You can safely feed the following food items to your toddler with stomach flu:
- Bananas can help control loose stools and are often recommended for children with stomach flu. Mash the banana and give small bites whenever your little one feels hungry.
- Apples are also light on the stomach and ensure your baby gets nutrition.
- Broth is great since it is mostly liquid. You can prepare a chicken or vegetable broth for your baby to replenish the essential micronutrients that are lost due to diarrhea and vomiting.
- Oats and rice are mild on the stomach and are easier to digest. You can mash boiled rice and give it to the toddler. Oats are rich in fiber and free of gluten. They keep your little one’s tummy full for longer.

- Crackers and toast make an excellent snack for toddlers with gastroenteritis. You can give them between meals.
- Yogurt is a probioticiSubstances containing live microorganisms that provide health benefits to the body. and is often recommended for adults with stomach flu. The good thing about it is that you can give it to your child too. You can introduce yogurt at the age of nine months. Start with small quantities and slowly make it a part of the baby’s meals. Do note you can give cow’s milk to a child only after the age of 12 months (12).
- Breast milk: Breast milk is the safest food for your baby or toddler since there is no specific time to stop breastfeeding. Breast milk contains fluids and electrolytes that can help the baby feel better and replenish the salts lost through diarrhea (13). Experts also note that there are fewer cases of gastroenteritis among infants who are breastfed than those who are bottle fed.
Feed your baby or toddler only when they are receptive to food. Feed them small portions over a few intervals but do not force-feed them. Excess feeding can induce vomiting and make the condition worse. Treatment, along with home care, is essential to halt the progress of stomach flu and prevent complications.
What Are The Complications Of Stomach Flu Among Toddlers?
Untreated gastroenteritis can lead to the following complications in babies and toddlers:
- Dehydration is the most significant risk of gastroenteritis. Excess loss of fluids from the body can cause severe electrolyte imbalance, which can impact various organs of the body.
- Loose stools and vomiting prevent the toddler from eating as much as they should which can eventually lead to malnutrition. Malnutrition has a direct impact on the baby’s growth and ability to achieve developmental milestones.
- If the stomach flu extends for long, then the baby runs the risk of developing irritable bowel syndrome, which is a permanent condition causing repeated irritation of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Gastroenteritis can damage the internal mucosal liningiThe soft inner lining found in bodily cavities and organs. of the small intestine and impede its ability to produce the lactase hormone (14). It means the baby will have trouble digesting breast milk and dairy products. Such lactose intolerance is called secondary lactose intolerance and is mostly temporary, but may last for a long time.
- Sometimes the pathogen can find its way to other parts of the body and cause secondary infections. For instance, the adenovirus is capable of infecting both the digestive and respiratory systems. The virus can also reach the respiratory tract and cause a widespread infection.
- Certain pathogens such as the E. coli can induce a low platelet count and deplete the body’s iron reserves quickly. Such a condition is called hemolytic uremic syndrome. Although it is rare, there is still a risk of this complication in babies.
Complications of stomach flu seldom happen if you take care of your toddler. With a few precautions, you can even prevent the condition.
How To Prevent Stomach Flu In Toddlers?
Preventing stomach flu in babies and toddlers is easier than you think. Here are the steps to follow:
- Vaccination: Get the baby the rotavirus vaccine, which is available at private and government dispensaries. Speak to your baby’s pediatrician about it. Immunization can significantly minimize the risk of contracting the stomach flu caused by rotavirus (15).
- Provide well-prepared, clean food and clean water: Always give home-cooked meals to your older infants and toddlers. It prevents exposure to pathogens that can cause stomach flu. Also, make sure that the water your toddler drinks is boiled and cooled.
- Maintain personal hygiene: Washing the toddler’s hands before eating and after using the toilet can prevent the infection. Young infants may not use their hands to eat but tend to put their hands or objects in their mouth. So keep their hands clean and disinfect the baby’s things regularly using a baby-safe soap and warm water.
- Good hygiene across the house: Your child may unknowingly catch the infection from another family member. Ensuring that all the members of the house adhere to hygienic practices can protect the baby from the infection. Parents should ideally wear gloves when handling the baby’s potty and then wash hands. You must wash hands every time you change the baby’s diaper to prevent the spreading of the infection accidentally.
 Quick tip
Quick tipFrequently Asked Questions
1. How long does the stomach flu last in toddlers?
Stomach flu may last between one and three days. For most toddlers, the vomiting subsides within 24 hours (16). It is better to get it treated than to wait for the flu to subside.
2. When should I take my child to the doctor for stomach flu?
Dehydration due to diarrhea, vomiting, and loss of appetite is one of the biggest concerns of stomach flu. Contact the healthcare provider immediately if you notice any signs of dehydration, such as fewer wet diapers, lack of tears, increased sleepiness, dry mouth, or a sunken fontanelle (6).
3. When should I be concerned about my child’s stomach pain?
If the abdominal pain continues or worsens beyond 24 hours, you should contact your healthcare provider. You should seek medical care immediately if you notice any accompanying symptoms such as bloody stools, troubled breathing, or a rigid abdomen (17).
4. What is the difference between stomach flu and food poisoning in toddlers?
The NIH defines stomach flu as viral gastroenteritis, indicating the condition is primarily related to viral infections in the intestine. Food poisoning is a foodborne illness due to a disease (caused by viruses, bacteria, and parasites) or digestive tract irritation. Both conditions may have overlapping symptoms and are difficult to differentiate. However, the significant difference is their onset time after exposure to the pathogen. The stomach flu may start 24 to 48 hours after entering the human system, while food poisoning occurs quickly (usually after two to six hours of ingesting contaminated food or water. Also, symptoms of food poisoning resolve faster than those of stomach flu (1) (20) (21).
Stomach flu in children is mainly caused due to the consumption of food or water contaminated with the pathogens of the disease. Stomach cramps, fever, and poor appetite are common symptoms of this disease that can be treated with the help of antipyretic and anti analgesic medicines. Ensuring plenty of fluids in their diet and letting them rest enough can help in your child’s recovery from this infection. It is also important to take proper care of them and keep their surroundings clean to prevent the risk of such infections.
Infographic: How To Manage Stomach Flu In Toddlers At Home?
Several viruses, bacteria, and parasites can cause stomach flu in children, resulting in diarrhea, vomiting, poor appetite, and other symptoms. The doctor will treat your child depending on the underlying cause and the responsible pathogen. However, certain homecare tips and dietary choices, as listed in the following infographic, can help in a toddler’s speedy recovery.

Illustration: Momjunction Design Team
Illustration: What Causes Stomach Flu In Toddlers And Remedies You Can Try

Image: Dall·E/MomJunction Design Team
Stomach flu, also known as the stomach bug, can be a real pain. Learn how to prevent and treat it in this video.
Personal Experience: Source
MomJunction articles include first-hand experiences to provide you with better insights through real-life narratives. Here are the sources of personal accounts referenced in this article.
i. Is this a joke? Flu Gods?https://julia-transition.blogspot.com/2013/01/is-this-joke-flu-gods.htmlReferences
1. Symptoms & Causes of Viral Gastroenteritis (“Stomach Flu”); NIH(2008)
2. W. J. Cochran; Gastroenteritis in Children; Merck Manuals
3. E.J.Elliott; Acute gastroenteritis in children; NCBI(2007)
4. C.A.Churgay, Z.Aftab; Gastroenteritis in Children: Part I. Diagnosis; American Academy of Family Physicians(2012)
5. Norovirus; Baylor College of Medicine
6. Kids and the Stomach Flu; CHOC Children’s
7. Dr. C.Tidy; Gastroenteritis in Children; Patient
8. How to Prevent the Stomach Flu; The Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia(2016)
9. Integrated Management of Childhood Illness; WHO (2014)
10. When to take a vomiting child to the doctor;University of Utah
11. What’s normal when your kid has a stomach bug; University of Utah
12. Baby’s food basics; University of Utah
13. Vomiting and Diarrhea; American Academy of Family Physicians
14. D.L.Swagerty, A.D.Walling, R.M.Klein; Lactose Intolerance; American Academy of Family Physicians(2002)
15. Rotavirus Vaccine VIS; U.S. Department of Health & Human Services
16. What to do with the stomach flu: Remedies for kids; Children’s Hospital Association
17. Abdominal pain – children under age 12; National Library of Medicine
18. Stomach Flu; Kids first Pediatric Partners
19. Surviving the Stomach Bug: Truths & Tips for Parents; American Academy of Pediatrics
20. Definition & Facts of Food Poisoning; NIH (2019)
21. Stomach Flu or Food Poisoning? How To Tell; Cleveland Clinic
Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our nurturing community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with fellow parents.
Read full bio of Dr. Richard Mario Lurshay
Read full bio of Rohit Garoo
Read full bio of Dr. Ritika Shah
Read full bio of Anindita Ghatak