Image: iStock
It is advisable not to indulge in activities or quick ways to lose weight while pregnant and also not gain excess weight if you are obese or overweight (1) . The American College of Obstetrics and Gynecology suggests that women need to gain weight during pregnancy irrespective of their body mass index (BMI) (2). However, the amount of weight gain recommended depends on whether you have the ideal weight as per your body type or are overweight or obese.
You may keep your weight gain under control by eating a healthy and balanced diet and indulging in pregnancy-safe physical activities for prenatal care, in case you are overweight. You should also avoid reading misleading articles or watching misleading videos about weight gain or loss during pregnancy. Instead, discuss your concerns with your doctor and act as advised for the health and wellbeing of you and your growing baby. Read this post as we tell you about how to lose weight while pregnant and some safe weight management methods.
Key Pointers
- It is not advised to engage in rapid weight loss programs during pregnancy.
- Managing calorie intake, consuming healthy food, and engaging in light exercises can help maintain a healthy weight while pregnant.
- Yoga, cycling, and swimming are pregnancy-safe exercises that can help prevent unhealthy weight gain.
- Accepting the changes that come with pregnancy and enjoying the journey without stressing too much is crucial for pregnant women.
Why Do Overweight Women Need To Manage Weight During Pregnancy?

According to the UK’s National Health Services (NHS), being overweight increases the risk of a miscarriage, gestational diabetes, preeclampsia (high blood pressure), blood clots, postpartum hemorrhage, and heavy babies in the mother.
In babies, there could be risk of stillbirth or early birth (before 37 weeks). However, these risks are not unique to women who are overweight because they could happen in any pregnant woman (3).
The NHS recommends women not to try losing weight during pregnancy even if they are “very overweight”.
The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s (US CDC) National Vital Statistics System birth data (2015) highlighted an association between gestational and pre-pregnancy weight. As depicted in the graph below, gestational weight gain was deemed appropriate for 32% of women delivering full-term singleton infants, while 48% gained more weight and 21% gained less weight than recommended.
Among women who were underweight before pregnancy, roughly 44% gained weight within the recommended range. Conversely, only 39% of women with a normal weight, 26% of overweight women, and 24% of women with obesity before pregnancy followed the recommended weight gain. Women who were overweight or had obesity before pregnancy had the highest incidence of weight gain above the recommended range.

Comparison of weight gain in women with full-term, singleton births to recommended levels
Source: Gestational Weight Gain* Among Women with Full-Term, Singleton Births, Compared with RecommendationsThe best way to avoid weight issues during pregnancy is to reduce weight before conception. But if you have conceived even as you were trying to lose weight, make sure you are having a controlled weight gain so that you are not crossing the threshold of the recommended weight gain (see the next section).
 Quick fact
Quick factWhat Will Happen If You Lose Weight In Early Pregnancy
Morning sickness causing nausea and vomiting in early pregnancy may affect appetite and regular food intake and cause slight weight loss. This is not uncommon and is not harmful to your baby. However, you need to inform your doctor if you are not able to keep anything down and have lost significant weight. It may be hyperemesis gravidarum, which is a severe form of morning sickness. It may cause dehydration and may not be good for the developing fetus as the baby may be deprived of the required nutrients (4). Pressure-point wristbands, eating ginger (as chews or tea), having small, frequent meals (every two hours), avoiding oily and spicy food, and taking prescription anti-nausea medications may help reduce the symptoms (5).
Safe Ways To Manage Weight When Pregnant
The best approach to deal with excess weight gain is to have a concrete plan and focus on having a healthy lifestyle.
If you are overweight or obese and your doctor recommends weight management, you may follow the below ways:
1. Know your weight needs
The amount of weight that you should gain during pregnancy depends on your pre-pregnancy BMI (body mass index). Before you decide to lose weight during pregnancy, it is good to know your threshold for pregnancy weight gain. The below chart helps you know how much weight you can gain (2):
| Pregnancy weight category | Body mass index | Recommended range of total weight gain |
|---|---|---|
| Underweight | Less than 18.5 | 28-40lb (13-18kg) |
| Normal | 18.5-24.9 | 25-35lb (11-15kg) |
| Overweight | 25-29.9 | 15-25lb (6.8-11kg) |
| Obese | 30 and above | 11-20lb (5-9kg) |
Source: Institute of Medicine/ ACOG
According to ACOG, women who are overweight or obese can gain less weight than recommended as long as the baby is growing fine.
 Did you know?
Did you know?2. Understand your calorie requirement

As mentioned in the above table, all pregnant women don’t need to gain the same amount of weight. So, you need to know your calorie requirements. Your calorie requirement increases in the second and third trimester.
For women with normal weight, the average caloric intake should increase by around 300kcal/ day during pregnancy. However, it varies depending on your BMI among other things. Therefore, talk to your doctor to understand your specific needs (6).
Don’t follow low-calorie diets or rigorous weight loss strategies regimes like intermittent fasting.
3. Eat frequent but small meals
This could help you manage your weight, whether you are pregnant or not. Practice portion control by eating frequent but small healthy meals during pregnancy. This is especially useful during pregnancy when eating a full meal can make you feel sick. Experts advise eating three not-too-big main meals and two to three smaller meals per day (7).
4. Eat healthy food

Losing weight does not mean starving yourself; definitely not when you are pregnant. It means healthy eating. Prioritize foods rich in vitamins, minerals, and other essential nutrients over empty-calorie options. Here are some foods you should eat:
- Fresh fruits and vegetables
- Cereals and bread made with whole grains
- Low-fat milk and dairy products
- Foods rich in folate, such as strawberries, spinach, and beans
- Unsaturated “good” fats such as Omega-3 fatty acids and fats like olive oil, canola oil, and peanut oil
And then you need to avoid some foods, including:
- Food laced with artificial sweeteners
- Food and drinks that contain sugar or corn syrup
- Junk food like chips, candy, cake, cookies, and ice cream. It’s okay to cheat once in a while, just don’t make it a habit
- Salt causes water retention in the body. So, have it in moderation
- Unhealthy fats like margarine, butter, gravy, sauces, mayonnaise, and salad dressings
5. Do not eat for two
Pregnancy does not mean you have to eat for two. In fact you do not have to eat for two but eat healthy food. Besides calories and proteins in the required amounts, the body also needs nutrients such as folic acid, prenatal vitamins such as vitamin B12, and calcium.
Nuts provide protein while milk and cereals supply the extra calories. Eggs and yogurt are a great source of protein, calcium, and vitamin D. Spinach is high in folic acid and should be included in your everyday diet and nutrition. Red meat provides iron.
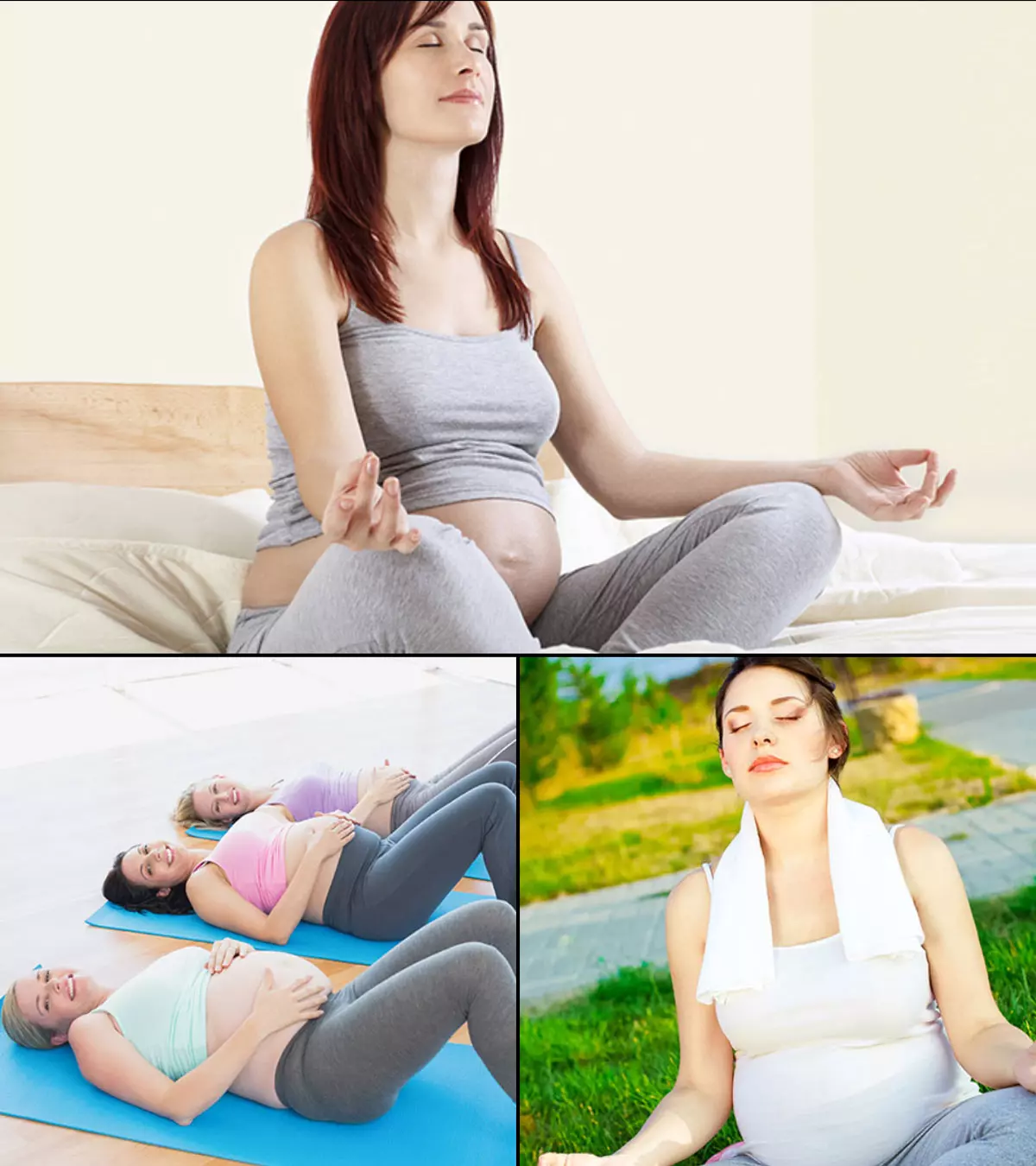
6. Exercise

According to the US CDC, a substantial 42.5% of individuals reported a decline in their physical activity while pregnant (8). You do not have to stop working out because you are pregnant. Working out is important if you want to manage your pregnancy weight (3) and prepare your body for the delivery.
But talk to your doctor or a trainer specialized in exercises for pregnant women, before you plan your workout regimen. You may have around 30 minutes of exercise four to five times a week. You may try low impact exercises such as:
- Yoga
- Walking
- Swimming
- Dancing
- Cycling
Do not take up exercises that are taxing, and avoid exercises if you experience any of the following (9):
- Vaginal bleeding
- Dizziness
- Headache
- Chest pain
- Muscle weakness
- Amniotic fluid leakage
- Have a medical condition (such as threatened miscarriage, incompetent os, placenta previa or high blood pressure) for which the doctor has specifically advised to avoid exercises
 Quick tip
Quick tip7. Carry your lunch to work
This way you can avoid eating outside food or junk food. Also, you can limit the quantity of the food you take. Preparing your lunch gives you the freedom to add all the veggies and fruits you want, and avoid the ingredients that may cause unnecessary weight gain.
8. Accept the Changes

Respecting your body also means accepting what it is. Gaining weight is normal during pregnancy and, in fact, is essential for your baby’s health. Just make sure your weight gain is within the limits set by your doctor. Do not resort to any crash diets or take other unhealthy short-cuts to lose weight during pregnancy because that will have an impact on your baby.
Enjoy the journey to motherhood. Love yourself and remember that after delivery once you are settled with the baby you can get back to your fabulous self with some effort and lots of determination. One can start exercises (especially abdominal) six weeks after a normal delivery and 12 weeks after a cesarean section. Routine walking can be done after delivery whenever you can.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Will walking during pregnancy help lose weight?
Walking at a moderate pace is recommended during pregnancy. An easy rule to check you are not straining yourself is you should be able to walk and talk simultaneously. If you cannot, you should slow down (10). Walking is an excellent exercise during pregnancy, but it is not advisable to use it for losing weight during this time.
2. Why am I gaining weight so fast during pregnancy?
Pregnancy increases food cravings, and consuming high-fat junk food or those with sweeteners may cause rapid weight gain. However, gaining weight during pregnancy as fast as one kilogram per week may indicate health issues such as pre-eclampsia. The condition causes high blood pressure and may cause nausea, dizziness, and headache. Consult a doctor if symptoms arise (7) (11).
3. Can I still exercise if I am considered high-risk during pregnancy?
For women with high-risk or complicated pregnancies, it is better to consult a doctor before engaging in strenuous activities. Nevertheless, it is generally advisable for high-risk pregnancies to participate in gentle activities like walking or stretching. Although intense exercise is discouraged, doctors can design a personalized plan for safe, light activities. Bed rest is no longer recommended as it does not enhance outcomes and may cause additional complications (12).
4. How often should I monitor my weight during pregnancy?
It is advisable to consult your healthcare provider for personalized guidance on monitoring your weight during pregnancy.
5. How can stress management and self-care practices help support healthy weight loss during pregnancy?
Stress management and self-care are vital for promoting healthy weight loss during pregnancy. Prioritize sleep, consume nutritious food, exercise regularly, practice self-care, and seek social support. These strategies aid in stress management, appetite regulation, well-being, and preventing excessive weight gain, benefiting both mother and baby.
6. How can a woman who is overweight or obese before pregnancy safely and effectively manage her weight during pregnancy?
Research indicates that overweight and obese expectant mothers can safely lower weight gain through dietary and exercise interventions (13). It is advisable for pregnant women to consult healthcare experts to devise a personalized plan that caters to their unique requirements.
7. What role does hydration play in weight management during pregnancy, and how much water should a pregnant woman aim to drink each day?
Pregnant women should consume 10 cups of water every day (14). While staying hydrated aids weight management and offers health benefits, it’s important to recognize that drinking more water won’t lead to substantial weight loss without calorie control and exercise (15). Adopting a holistic and enduring approach to well-being is vital for successful weight management.
The NHS of the UK suggests that gaining too much weight during pregnancy might increase the risks of miscarriage or high birth weight in babies. However, trying to lose weight might compromise the nutritional requirements of you and your baby. Thus, it is advised not to try losing weight while pregnant. Instead, weight monitoring and maintaining your calorie intake, eating healthy food, maintaining proper hydration, and trying light exercises can be more helpful. Moreover, try to avoid junk food and include healthy fats. Following these tips to manage your weight while pregnant could help you have a healthy pregnancy and reduce the risks of complications.
Infographic: Safe Ways To Manage Weight When Pregnant
Weight gain during pregnancy is natural and necessary for the health of both the mother and the baby. However, you must ensure that it is managed in a safe and healthy way, as carrying excess weight can lead to complications during pregnancy and childbirth. So use this infographic as a guide to maintaining a healthy weight. Illustration: Momjunction Design Team
Illustration: Safe Ways To Lose Weight While Pregnant

Image: Stable Diffusion/MomJunction Design Team
While most pregnant women may sleep in their habitual position in the first trimester, it gets progressively uncomfortable. Learn about a few safe and comfortable sleeping positions for pregnancy from this video.
References:
1. Maxine Johnson, et al.; Weight management during pregnancy: A systematic review of qualitative evidence; Midwifery
2. Weight gain during pregnancy; Committee on Obstretrics practice, The American College of Obstetrics and Gynecology
3. Overweight and pregnant; NHS (2017)
4. Morning Sickness; Cleveland Clinic
5. Hyperemesis Gravidarum; Cleveland Clinic
6. Michelle A. Kominiarek and Priya Rajan; Nutrition recommendations in pregnancy and lactation; PubMed Central (PMC), NIH
7. Pregnancy and birth: Weight gain in pregnancy; Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG) (2018)
8. Physical Activity Before and During Pregnancy, Colorado Pregnancy Risk Assessment Monitoring System, 2012–2015; Center for Disease Control and Prevention
9. 3 Myths About Exercise and Pregnancy; Johns Hopkins Medicine
10. Managing your weight gain during pregnancy; MedlinePlus
11. Pregnancy and birth: Weight gain in pregnancy; National Library of Medicine
12. How safe is exercise during pregnancy?; Harvard Health
13. High BMI and Pregnancy Weight Gain with Alan Peaceman, MD; Northwestern University, Feinberg School of Medicine
14. Why it’s important for you to drink water and stay hydrated; UC Davis Health
15. Yes, drinking more water may help you lose weight; Johns Hopkins University.
16. Obesity and Pregnancy; American College of Obstetrics and Gynecology
17. Pregnancy Weight Gain; American Pregnancy Association
18. Exercise During Pregnancy; American College of Obstetrics and Gynecology
Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our nurturing community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with fellow parents.
Read full bio of Dr. Sangeeta Agrawal
Read full bio of Rebecca Malachi
Read full bio of Swati Patwal
Read full bio of Aneesha Amonz