Image: Shutterstock
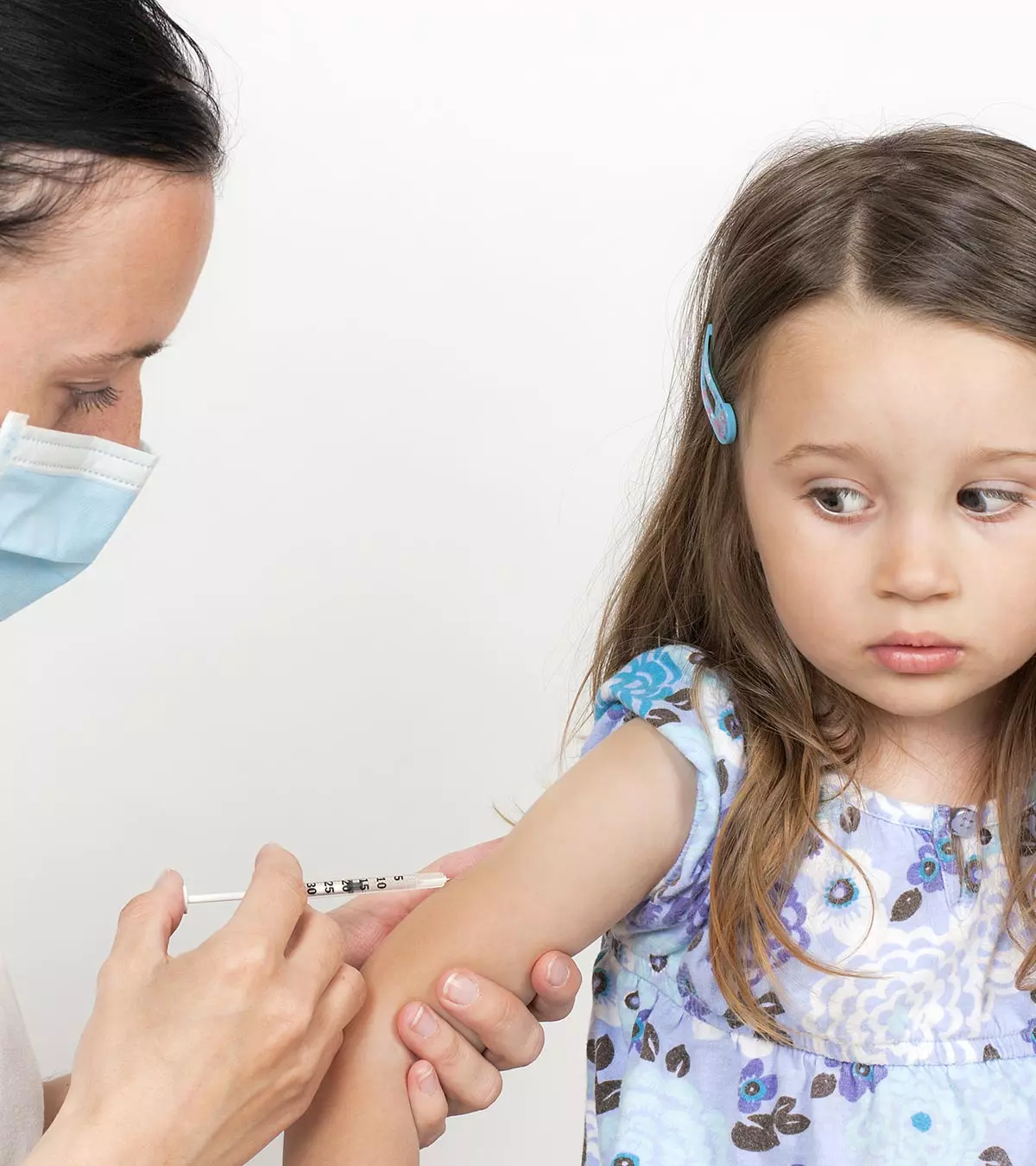
Typhoid fever can be prevented with vaccines. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends the typhoid vaccine for kids who live in high-risk areas. You may ask the pediatrician to know the requirement of the typhoid vaccine for your child since it may not be included in the child’s routine immunization schedule. The type of vaccine may vary depending on the child’s age. However, children older than two years can get typhoid vaccination.
Read on to know more about the uses, side effects, and when to get the typhoid vaccine for children.
Key Pointers
- The typhoid vaccine protects against fever and comes in three variations.
- The vaccine is generally safe but not recommended if your child had a severe allergic reaction to it previously and in some other cases.
- Some temporary side effects include mild fever, nausea, and stomach pain.
- In case of a serious reaction such as diarrhea or dizziness, consult your doctor immediately.
What Is Typhoid?
Typhoid is a bacterial infection that can lead to acute illness. The infection is caused by the Salmonella typhimurium or Salmonella paratyphi bacteria and spreads through contaminated water and food (1). Sometimes, it can be contracted from an infected person also.
This bacteria enters the body through the mouth and stays in the intestine for a couple of weeks before the symptoms of infection start showing. It can lead to vomiting, high fever, and diarrhea in children, which can sometimes become severe.
According to a report by the World Health Organization (WHO), globally, there were around nine million cases of typhoid in 2019. Hence, they recommend everyone between the ages of six months to 65 years in a typhoid-prone area to be vaccinated (2) (3).
The Typhoid Vaccine And Its Variants
The typhoid vaccination is a shot to prevent typhoid fever. While it ensures protection against the fever, it does not rule out the chances of the infection completely (1).
Typhoid vaccine comes in three variations and must be taken at least one week before the potential exposure.
1. Typbar-TCV: With one dose, this vaccine provides long-term immunity. It can be either integrated with the routine vaccinations or taken separately (4).
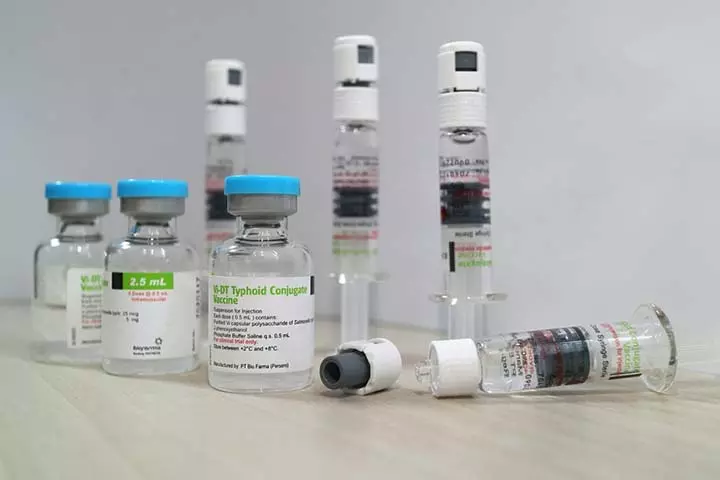
2. Inactivated typhoid vaccine or Typhim Vi: Also known as ViCPS, this vaccine is given in one single injection. A single dose protects for about two years, after which a booster dose would be required at an interval of every three years. It is best suited for adults and children older than two years of age (5).
 Point to consider
Point to consider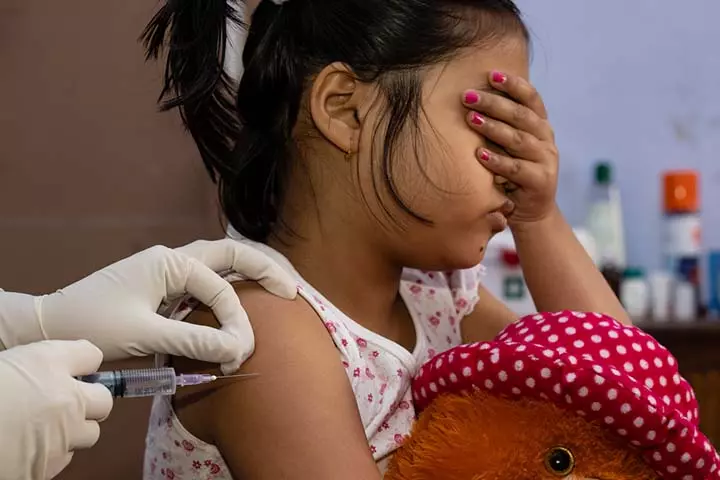
3. Live typhoid vaccine or Ty21a: Taken orally, this vaccine is ideal for adults and children over the age of six years (5). It should be taken in four doses, at an interval of 48 hours each. The capsule must be taken with a drink, before a meal, and should not be chewed.
This will ensure protection against the infection for two years. Revaccination is necessary every five years, and a booster pill should be taken every two years in the case of continuous exposure to the infection.
Who Should Get The Typhoid Vaccine?
The World Health Organization recommends routine typhoid vaccination for children living in high-risk countries such as India, Pakistan, and Bangladesh (6) . People who are traveling to these countries are advised to get the typhoid vaccination too. To ensure safety, anyone coming in contact with an infected person must get the typhoid vaccination.
When Should The Child Get The Typhoid Vaccination?
In countries where typhoid vaccination is not a part of the routine inoculation schedule for kids, these standard guidelines apply:
- Inactivated typhoid vaccine or Typhim Vi: For kids older than two years but less than six, a Typhim Vi shot shall be given at least two weeks before the travel date or expected exposure.
- Live typhoid vaccine or Ty21a: Children who are six years and older may be given a Ty21a capsule at least one week before traveling to risk-prone countries or possible exposure.
What is the typhoid vaccination schedule?
The typhoid vaccination schedule varies from one country to another. If you live in a country where typhoid vaccination is not a part of the routine vaccinations for children, then the following schedule is to be followed, at least one week before possible exposure (7).
| Age | Vaccine | Dose | Booster |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 to 6 years | Typhim Vi | Single | After 2 years |
| > 6 years | Ty21a | Four (one every 48 hours) | After 2 years |
In countries where typhoid fever is listed among the most common diseases in children, the vaccination schedule is as follows (8) (9):
| Age | Vaccine | Dose | Booster |
|---|---|---|---|
| 9 to 12 months | Typhoid conjugate vaccine | Single | After 2 years |
| 18 months to 2 years | Typhoid conjugate vaccine – booster | Single | After 2 years |
| 4 to 6 years | Typhoid conjugate vaccine – booster | Single | – |
Who Should Not Get The Typhoid Vaccine?
The only absolute contraindication of the typhoid vaccine is a history of severe allergic reactions to the previous dose (10). Otherwise, it is a safe vaccine to opt for.
Check with a pediatrician about the suitability and possible risks of the vaccine for your children.
- Ideally, for children aged nine months or less. Some typhoid vaccines for babies older than six months may be given, especially in typhoid-endemic countries (4).
- Anyone allergic to a particular component of the vaccine must avoid typhoid vaccination.
- Children who’ve had a mild or severe reaction to the previous dose of this vaccine must not get the subsequent or booster dose.
- Children who are not in perfect health and have any minor illnesses should wait until they recover before getting the typhoid vaccination.

- If the child is on antibiotics, you must wait for 72 hours after the last dose before getting typhoid vaccination.
- Most importantly, anyone who has a weak immune system or is undergoing treatment for life-threatening diseases such as HIV/AIDS or cancer must not get the typhoid vaccine.
Check with a pediatrician about the suitability and possible risks of the vaccine for your kids.
What Are The Risks And Side Effects Of Typhoid Vaccine?
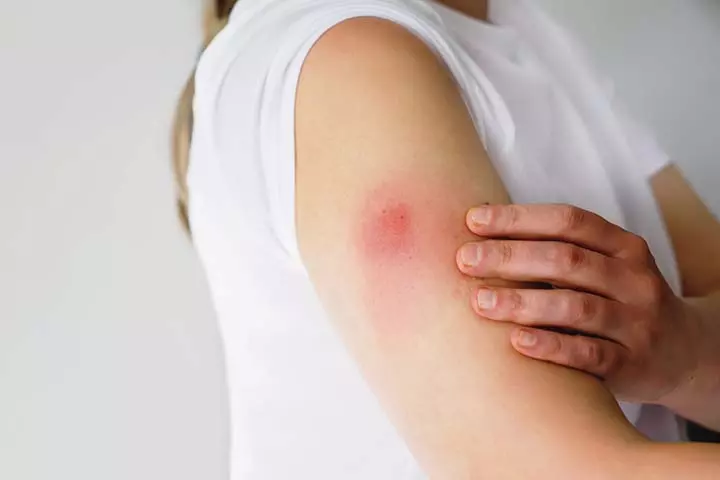
As with any other vaccination or medicine, the typhoid vaccination may also have a few side-effects. The probable risks of a typhoid vaccination are:
- Mild fever or headache after taking either the injection or oral vaccine.
- Swelling or redness around the site of injection.

- Nausea, stomach pain or vomiting.
What If There Is A Serious Reaction?
Some severe reactions may include diarrhea, behavioral changes, dizziness, swelling in the throat, high temperature or fever. For one or more of these side effects, visit the doctor for medical aid (11).
Precautions After The Typhoid Vaccination
A typhoid vaccination does not guarantee complete immunity against the infection. Therefore, it is advisable to adopt the following prevention measures after immunization to minimize the risk further:
- Drink only bottled water.

- Do not consume any fruit or vegetable without washing and disinfecting thoroughly.
 Caution
Caution- Do not share items of personal hygiene with anyone.
- Avoid any direct or indirect contact with a typhoid carrier or an infected person.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How many mL is the typhoid vaccine?
The dosage of the typhoid vaccine is 0.5mL (12).
2. How many injections are required for the typhoid vaccine for children?
Children require only one shot of the typhoid vaccine. (13).
3. Is it common for children to get a fever after a typhoid vaccine?
Yes. Fever is a common symptom observed after vaccination (11).
The typhoid vaccine for kids helps safeguard them from the signs of typhoid. However, it does not guarantee or rule out any risk of being affected by the virus. Hence, maintaining proper hygiene and sanitation and taking care of your child is essential. Check with your child’s pediatrician before administering the vaccine to ensure they do not have any allergic reactions. Further, follow proper precautionary measures after your child has been administered the vaccine and ensure they are hydrated. Some children may experience temporary side effects such as mild fever and swelling at the injection site.
Infographic: Contraindications To The Typhoid Vaccine
The typhoid vaccine is usually considered safe for children and is usually contraindicated if a child has shown severe allergic reactions to the first dose. However, certain conditions may require clearance from your child’s doctor. The infographic below discusses the incidences under which it is advisable to consult a pediatrician before getting the typhoid vaccine.

Illustration: Momjunction Design Team
Illustration: Typhoid Vaccine For Kids: Age-Wise Schedule Guide

Image: Dall·E/MomJunction Design Team
References
1. Sandhya A. Marathe et al.; Typhoid fever & vaccine development: a partially answered question; Indian Journal of Medical Research (2012)
2. Typhoid; WHO
3. Global Typhoid Fever Vaccination; CDC
4. Typbar-TCV®: Questions and answers; Coalition Against Typhoid
5. Roscoe O. Van Camp & Mahmoud Shorman; Typhoid Vaccine; NCBI (2018)
6. Typhoid Fever; CDC
7. International travel and health; Vaccines
8. Jung-Seok Lee et al.; Geographical distribution of typhoid risk factors in low and middle income countries; BMC Infectious Diseases (2016)
9. Vipin M Vashishtha et al.; Indian Academy of Pediatrics (IAP) Recommended Immunization Schedule for Children Aged 0 through 18 years – India, 2014 and Updates on Immunization; Indian Pediatrics (2014)
10. Who Should NOT Get Vaccinated with these Vaccines?; National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases; (2018)
11. Typhoid VIS; CDC
12. Typhoid Vaccine; National Library Of Medicine
13. Typhoid fever; NHS
Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our nurturing community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with fellow parents.
Read full bio of Dr. Vivek Goswami
Read full bio of Dr Bisny T. Joseph
Read full bio of Swati Patwal
Read full bio of Anindita Ghatak