Image: Shutterstock
Vomiting in children can be due to various reasons, such as stomach flu or indigestion. Occasional vomiting may not be a major cause of concern, and most children can be treated at home. However, it is recommended to seek medical care for frequent episodes of vomiting or if it is accompanied by other symptoms such as diarrhea or fever.
Read on to understand the causes, symptoms, signs, treatments, and home remedies for vomiting in children. Knowing the causes of vomiting can help you better manage your child’s symptoms. You should also be able to distinguish between occasional vomiting and cases that happen frequently to ensure your child gets medical attention.
Refrain from using vomiting medicine for kids without a prescription. You may also pay attention to the hydration status and
seek rehydration therapyiOral or intravenous fluid therapy used to treat fluid loss in the body. if the child cannot drink enough water or have signs of dehydration.
Key Pointers
- Vomiting in kids may or may not be due to a serious medical condition.
- Some common reasons for vomiting in children include food allergy, food poisoning, infections, head injury, or motion sickness.
- It’s essential to keep the child hydrated after vomiting to prevent dehydration and weakness.
- In severe cases, a doctor may prescribe over-the-counter medications such as antiemetics or anti-nausea medications.
- Home remedies such as ginger, mint, or lemon may help alleviate the symptoms of vomiting in mild cases.
- Seeking medical advice is advisable if vomiting is persistent and accompanied by fever, heartburn, or blood.
Causes Of Vomiting In Children
Some of the common causes for vomiting in children include:
- Gastroenteritis: Also called the stomach flu or stomach infection, it is caused by a virus (commonly norovirusiA virus causing contagious diseases in children leading to diarrhea and vomiting. , astrovirusiA virus typically infecting babies and young children and transmitted through the oral or fecal route. , and enterovirusiA virus that causes mild to severe infections in children presenting with a range of symptoms. ). In addition to vomiting, symptoms of gastroenteritis include nausea, diarrhea, and sometimes fever. In most cases, mild gastroenteritis subsides in a couple of days (1). Severe gastroenteritis that could lead to dehydration and other complications would need medical attention.
- Food allergy: When the child’s immune system reacts differently to a substance or food, it is termed as a food allergy. According to a US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) 2021 report, nearly 5.8% of children in the United States had a food allergy. Some children may be allergic to peanuts, tree nuts, fish, wheat, eggs, milk, and soy. Food allergy symptoms may include vomiting, stomach pain, diarrhea, and breathing problems (2).
 Did you know?
Did you know?- Food poisoning: Stale food or germs in fruits and vegetables may be a reason for food poisoning. Vomiting, nausea, fever, fatigue, and abdominal cramps could be a few symptoms of food poisoning in children and may either disappear in a few hours or take a couple of days to subside (3).
- Appendicitis: The painful condition causes swelling of the appendix. In some cases, the appendix (a thin tube connected to the large intestine) may burst, causing severe infection – this is a medical emergency and has to be treated immediately. Vomiting is one of the symptoms of appendicitis, which could be fatal if left untreated (4).

- Infections: Although viral gastroenteritis (stomach flu) in children is common, some may be affected by non-gastrointestinal infections such as meningitis (bacterial infection causing inflammation in spinal cord and brain), septicemia (bacterial infection in the bloodstream), and urinary tract infectionsiCommon infections of the urinary system characterized by pain and burning sensation in the pelvic region. . Vomiting and abdominal pain may be one of the symptoms of these conditions (5).
- Others: Headache, stomachache, head injury, and motion motion sicknessiA pronounced feeling of illness triggered by any movement. may be a few other reasons for vomiting in children (6).
In most cases, when the condition is not severe, using certain home remedies for vomiting children may help alleviate the discomfort.
Home Remedies For Vomiting In Children
A few common home remedies that people find helpful for curbing vomiting in children are mentioned below.
- Liquids: Make your child sip water once every five to ten minutes. If they are unable to have fluids, then sucking on ice chips or frozen juice bars could be a good idea (7). Chamomile tea, alongside regular water in small, frequent amounts is recommended for rehydration in older children. Chamomile’s calming properties can benefit the stomach (8).

- Solids: It’s best to let the stomach settle before introducing solid foods. When the vomiting decreases, start with bland foods such as toast or crackers, but make sure they eat it slowly. Also, ask them if they are hungry and want to eat. You may also introduce the BRAT diet: bananas, rice, applesauce, and toast. These foods are gentle on the stomach. Noodles, chicken, and yogurt are also well-tolerated (9). Other foods you may give include rice, dry cereal, cooked carrots, bananas, boiled potatoes, or any other fruits and vegetables they want to eat. Do not give any greasy or fried foods as these might make them throw up again (7) (8).
- Oral rehydration solution (ORS): Ask your doctor if you can give the ORS to the child. ORS, such as Infalyte or Pedialyte, has minerals, sugar, and salt, which may help the kid feel better (10).
- Peppermint: Some people give candies or sugar-free sticks containing peppermint to children, to make them feel better after vomiting (11).
- Ginger: Ginger is considered to be effective in controlling gastroenteritis-related vomiting and acid reflux. You can make light herbal tea with ginger essence (11).
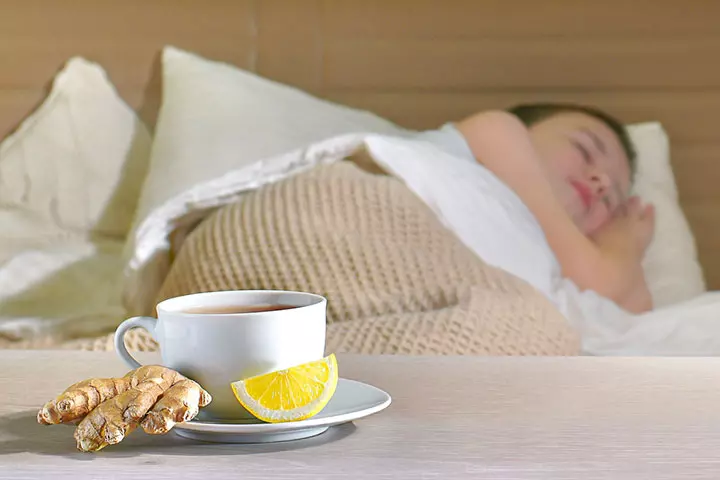

- Lemon juice: You may give your child some sips of lime or lemon water or soda, as it helps in relieving the symptoms of vomiting (12).
- Acupuncture: Stomach 36 (Zu San Li) is an acupuncture point located four finger-widths below the kneecap and one finger-width towards the outside of the shinbone. It aids in treating vomiting while enhancing immune function and overall body strength (13).
 Quick tip
Quick tipWhen To Consult A Doctor?
When it’s been more than three to four days and your child is not feeling comfortable, then consulting a doctor is suggested. Also, medical attention is necessary if there are other symptoms, such as (14):
- Heartburn
- Fever and cough
- Vomiting doesn’t stop and becomes forceful
- Weight loss
- Yellowish green bile or blood in vomit
Based on these symptoms, the doctor will further diagnose the child before suggesting any treatment. They may ask about bowel movements, the appearance of the vomit, any unusual signs that were noticed, frequency and time of vomiting, and any other health problems the child has. If they find something unusual, they would suggest a laboratory test. The treatment plan is recommended based on the results.
Treatment For Vomiting In Children
As vomiting in children is usually a symptom and not a severe condition, there is no significant treatment for it.
If the child is only vomiting and there is no other symptom or underlying condition, then medicines are not recommended. However, if the child has severe vomiting and other signs, such as fever, infection, or diarrhea, then the doctor may prescribe certain medications (15) (16):
- Antiemetics or anti-nausea medicine
- Medicine for an underlying medical condition
- Intravenous fluids for children with vomiting and dehydration
Following these patterns can help doctors recognize the possible causes of vomiting in your child and chalk out a treatment plan.
Is It Possible To Prevent Vomiting In Children?
Typically, it is not possible to prevent vomiting once the stomach expels the content. However, some hygienic tips might help in preventing the constant sensation of vomiting or vomiting in children.
- If your child is allergic to some foods that make them vomit, avoid giving them those.
- Make sure they are eating fresh and hygienically prepared food and not stale food.

- If motion sickness is the cause for your child’s vomiting, then giving them ginger or peppermint candy may help in preventing nausea and vomiting. If not, talk to your doctor and get a medicine prescribed, if necessary.
- If dehydration is the cause, see that they are having adequate amounts of water and resting well.
 Point to consider
Point to consider
Frequently Asked Questions
1. My child is vomiting but has no fever. What could be the reason?
Vomiting in children is not always accompanied by fever or its related symptoms. Fever may not usually accompany vomiting caused due to motion sickness, allergies, or food poisoning.
2. What to feed my child after vomiting?
Do not give them any fried or greasy stuff after the child has vomited. You may give them water, candies, herbal tea, or bland foods such as rice cereals or crackers.
3. What forms of vomiting do kids often experience?
Possetting (throwing up in small amounts after feeding), reflux (contents of stomach that travel up the food pipe), and projectile vomiting (forceful vomiting) are some of the kinds of vomiting your child may experience (14).
Stomach flu, indigestion, food allergies, food poisoning, and appendicitis are common causes of vomiting in children. Severe vomiting may lead to dehydration, which may need medical attention. The doctor may prescribe antiemetic medications to treat the underlying cause and intravenous fluids in more severe cases. You may even try some home remedies to manage the condition. Preventing stale food, avoiding allergens, and maintaining a safe distance from other sick children can help prevent illness and vomiting.
Infographic: Cyclic Vomiting Syndrome In Children
Cyclic vomiting syndrome (CVS) is a rare pediatric condition characterized by repeated vomiting and nausea. This infographic details the possible causes and treatment interventions for this disorder in children. Illustration: Momjunction Design Team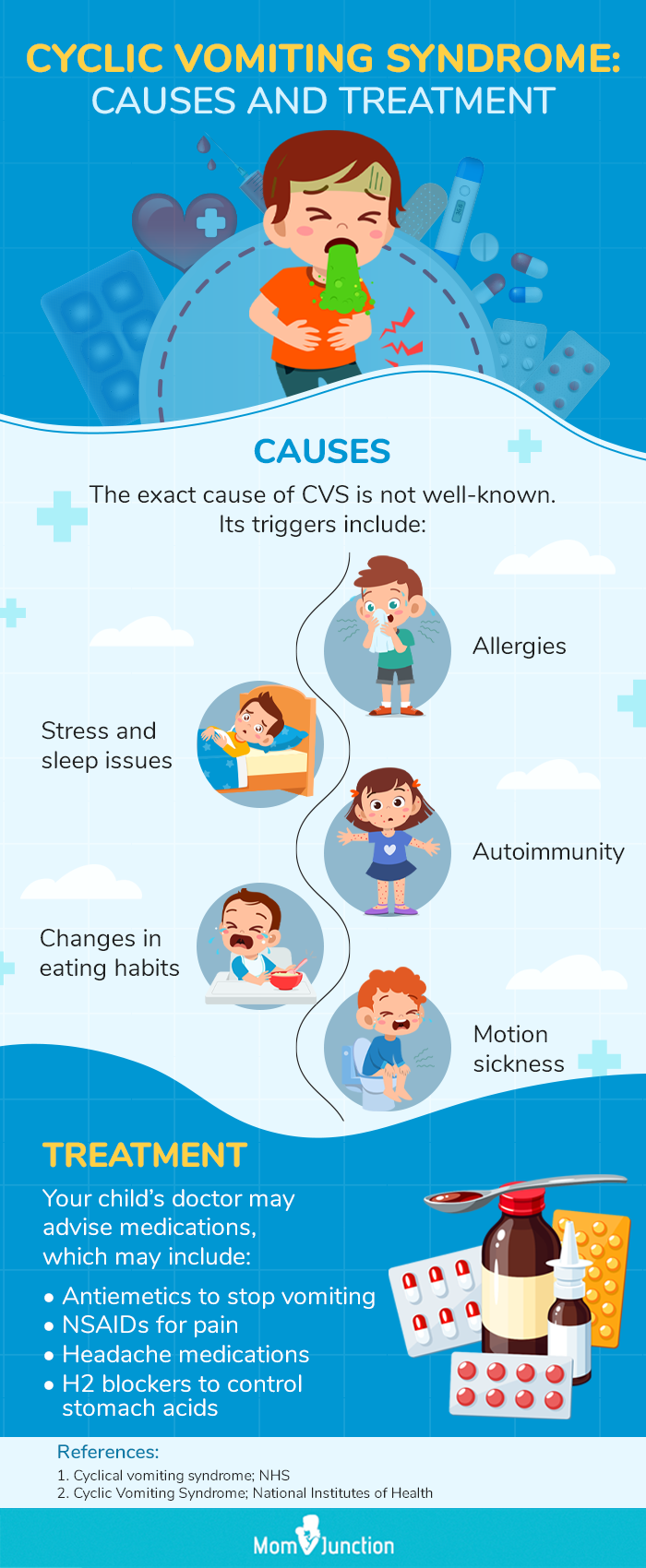
Illustration: Causes Of Vomiting In Children Treatment & Home Remedies

Image: Stable Diffusion/MomJunction Design Team
Vomiting in children can alarm the parents and cause distress in the children. Explore the possible causes of vomiting in children and learn how to assess and manage this condition in this informative video.
References
1. Gastroenteritis In Children; Harvard Health Publishing
2. Food Allergies in Children; Rochester medical Center
3. Food Poisoning in Children; Nicklaus Children’s Hospital
4. Appendicitis in Children; University of Rochester Medical Center
5. K. Allen; The vomiting child; College of Medicine University of Florida
6. C. McCarthy; 8 things to watch for when your child has a headache; Harvard Health Publishing (2017)
7. What To Do When Your Child Is Vomiting; Fairview.org
8. Treatments for Nausea and Vomiting; Stanford Children’s Medicine
9. Diarrhea Nutrition Tips; Stanford Cancer Nutrition Services
10. Nausea and Vomiting in Children: Care Instructions; Kaiser Permanente
11. New study finds ginger proven to treat vomiting in children with acute gastroenteritis; the American Association for the Advancement of Science (2018)
12. How to Handle Vomiting; Nemour’s Children’s Health
13. Acupressure for Kids; Intermountain Health
14. Children and vomiting; Victoria State Government
15. Vomiting; Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia
16. Food Allergy vs. Intolerance: Know the Difference; Canadian Society of Intestinal Research
17. Shamkant B. Badgujar et al.; Foeniculum vulgare Mill: A Review of Its Botany, Phytochemistry, Pharmacology, Contemporary Application, and Toxicology; NCBI (2014)
18. Treating Vomiting; healthy children.org, American Academy of Pediatrics
Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our nurturing community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with fellow parents.
Read full bio of Dr. Kondekar Santosh
Read full bio of Dr Bisny T. Joseph
Read full bio of Swati Patwal
Read full bio of Anindita Ghatak