Image: Shutterstock
Teens and social media have a close association since it is not uncommon to find teenagers spend several hours on social media websites. Teenage social media addiction is not classified as a medical condition. Still, it has become a rising concern due to its potential effect on mental and physical health. Social isolation in the real world is often a paramount concern. Thus, understanding this addiction is crucial for parents and educators alike.
According to a Pew Research Center report, 95% of teens have access to smartphones, and 45% stay online almost constantly (1). Due to this, several teens spend less time engaging in in-person activities, such as going outdoors or socializing with friends and family, raising their risk of developing sadness, loneliness, distress, and other related issues (2) (3). Thus, parents should proactively guide their teens to have responsible and regulated social media use.
Keep reading as we share the signs of social media addiction in teens, its causes, effects, and practical tips to help teens regulate their social media use.
Key Pointers
- Signs of social media addiction in teens include constant use of phones, inadequate sleep, poor academic performance, and social withdrawal.
- Social media can help teens build social connections, explore self-expression, and enhance personal and academic development.
- Negative consequences of social media overuse include increased anxiety, depression, poor self-esteem, cyberbullying, isolation, and sleep deprivation.
- Encouraging teens to engage in offline activities and socialize with people in person is a helpful strategy for parents.
Signs Of Social Media Addiction In Teens
When a child or teen first joins a social site, it is normal for them to stay hooked to it most of the time. It usually happens due to the thrill of experimentation that is mostly transient. But if this use continues for longer, a teenager can develop a dependency, affecting other aspects of their life, such as hobbies and studies (4).
According to the American Addiction Center, only a medical or mental health professional can diagnose social media addiction. However, there are a few warning signs that parents and educators can monitor (4) (5).
- Distracted eating or skipping meals to be on the phone
- Missing sleep for social networking or gaming on social media apps
- Taking the phone to the washroom

- Feeling sad when not getting likes, comments, retweets, or views
- Lessor no “in-person” social interaction (social withdrawal)
- No or little interest in activities and hobbies that the teen earlier used to like
- Poor academic performance due to constant distraction
- Inability to reduce or cease social media use even after experiencing its negative consequences
- Behaving unsettled when the internet is down, or the social site or app isn’t working properly
- Being anxious, irritable, and argumentative when confronted about excessive social media use
- They reach for their phone the first thing in the morning.
If you notice any of these signs in your teen, talk to them calmly and try to understand the reason for their addiction. In several cases, teens get addicted to social media due to certain events or factors in life, such as dissatisfaction, unhappiness, and loneliness.
Causes Of Social Media Addiction In Teens
The two main reasons why teens can get addicted to social media are:
1. Easy accessibility

Most social media sites, such as Instagram, TikTok, Facebook, and Twitter, let the user make a profile for free. These platforms also do not charge any money for usage, letting the user use them indefinitely. A teenager can access their apps on phones or tablets or visit their websites and use them for as long as they desire.
2. Psychological reward and gratification
Social media platforms are designed to hold users’ attention longer by tapping into their psychological biases, need for validation, and fear of rejection (6). So, when a teen gets a like or a positive comment on their picture or post:
- It can trigger dopamine release in the brain. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that gives feelings of pleasure or reward. The more favorable responses a teen gets, the more rewarded they will feel, forming “addiction pathways” in the brain (7).
- Regular use of social media gradually forms tolerance, which means teens now need more time on social media than before to get the same dopamine release.
- Excessive technology use can eventually lead to dependence, where a teen needs to use social media to feel normal. A 2022 study by Pew Research Center showed that 54% of adolescents revealed that it would be hard to stop using social media. Among this population, the rate was higher among girls (58%) than boys (49%). If it goes unchecked, this dependence can lead to social media addiction.
FOMO (fear of missing out), nomophobia (fear of not having a working cellphone), smartphone addiction, and pre-existing mental health issues, such as stress, anxiety, and depression, are additional factors that could contribute to social media addiction
(8).
Effects Of Social Media On Teens
Positive Effects Of Social Media
When used in a regulated and responsible way, social media use can help tweens and teens (7):
- Make new friends and strengthen their social and communication skills.
- Build social connections that could provide valuable support, especially if the teenager has affected abilities or chronic illness.

- Learn different ways of self-expression and enjoy some fun time with friends, family, and peers.
- Discover information and learning resources that can promote personal and academic development.
- Find emotional support during tough times and vent out one’s feelings, emotions, and thoughts.
- There are also social media pages and influencers that provide positive influence and edifying information.
 Things to know
Things to knowNegative Effects Of Social Media

The unguided and excessive use of social media can have several adverse effects on teenagers.
- Increased isolation and loneliness due to reduced in-person social interaction.
- Low self-esteem and anxiety due to constant comparison with others on social media.
- Disrupted sleep patterns due to increased blue light exposure at bedtime.
- Decreased physical activity, affecting overall health and leading to health issues, such as obesity.
- Exposure to bullies (cyberbullying), offensive comments, and abuse.
- Exposure to risky teenage behavior, such as sexting, substance abuse, or eating disorders.
- Distorted sense of self due to exposure to increased fakeness and filters often found on social media.
- Spending hours scrolling through feeds or engaging in online interactions often distracts from studies, leading to procrastination and poor time management.
 Did you know?
Did you know?Practical Tips To Deal With Social Media Addiction In Teens
Confiscating your teen’s cellphone/tablet to stop social media overuse is futile as it can backfire by making teens feel dejected. Here are some practical tips that can manage and prevent social media addiction in adolescents and teens(9) (10).
- Talk about social media. Discuss with your child the positive and negative influences of media on teenagers, including the harmful effects of excessive social media use. Help them develop awareness that social media images aren’t always realistic and that they shouldn’t form stereotypes, beliefs, or opinions solely based on what they see on screen. Instead, guide them to talk to people around them and learn from their experiences.
- Set clear boundaries. According to a study, adolescents who spend more than two hours on social media are more likely to experience mental health problems than those who use it for lesser duration (11). So, set a time limit on using social media use and monitor your teen’s accounts to ensure that their social media use is within limits and not interfering with their sleep, meals, homework, or other activities.
Parnika Puri, a teenage blogger contemplates her struggle with social media addiction and how she tried to overcome the same. She says, “I gave myself a time limit of one week, I shut my phone off every morning at 7:00 am and turned it back on every night once I completed my homework (depending on the day, that was around 8:00–9:00 pm). And to no surprise, I opened my phone every night to at least 150 text messages, Snapchats, Facebook notifications, etc. I’d spend around 30 minutes each night responding to those I deemed necessary (i).”
- Adhere to a gadget-free bedtime routine. Encourage your teen to religiously follow a bedtime routine that avoids electronic media use at least an hour before bedtime. Ask them to keep their cellphones and tablets out of their bedrooms and indulge in relaxing activities, such as reading a book, to ensure they sleep peacefully.
- Lead by example. If you stay hooked on your social media handle while eating or talking to others, your teen will likely follow in your footsteps. So use social media responsibly and regulate yourself to model desirable behavior. Additionally, keep your teen informed about specific behaviors, such as cyberbullying and sexting, to prevent misuse of social media and maintain online safety.
- Maintain a balance. Social media use has its pros and cons. Parents should train their teens to strike the right balance and use social media to reap its benefits and avert negative consequences. Since teenagers have limited self-regulation ability and are susceptible to peer pressure, continuous parental monitoring and guidance are a must to ensure teens maintain a balanced approach to social media use.
- Turn off notifications. Constant pings or notification pop-ups trigger the brain’s reward system, making it difficult to resist the urge to check the phone. So turn off automatic notifications on your teen’s phone, or ask them to put their phone on silent while doing important things, such as eating meals, doing homework, or studying. Additionally, you can uninstall unnecessary social media apps from their phone and ask them to use social media only on a computer/laptop.
- Encourage face-to-face conversations. Ask your teen to reduce the number of social media friends and socialize in person. Encourage them to plan a day out with friends and follow a digital detox routine as much as possible. Alternatively, you can take them to a fun event or party where they can meet people of their age and interests and make new friends. Doing so is particularly important if the teen has social anxiety issues. During these conversations, be intentional about reminding your teen to be the master of gadgets, the internet, and platforms, not a slave to them.

- Boost self-confidence and positivity. Social media creates unrealistic images that teens try to follow. In the process, they often lose their self-confidence and self-esteem and feel unworthy. Guide your teen to believe in themselves no matter what. Create an open communication environment where they can share their anxieties and vulnerabilities and learn ways to cope with undue stress caused by social media.
- Use digital well-bring features. Digital well-being features, such as screen time dashboards, tell about the time one spends on their device. Train your teen to use this feature on their phone/tablet to keep track of their time online. Encourage them to use app locks that block the app at certain times of the day. You can also consider putting your teen’s display on grayscale, especially at bedtime, to make notifications and apps less enticing.
- Set a time for offline activities. Playing sports, dancing, reading, and listening to music are a few offline activities that teens can indulge in daily. Doing so will help them stay away from social media and focus on self-improvement. Encourage your teen to take up some hobbies that can keep them engaged away from electronic gadgets and provide opportunities to meet new people and learn new skills.
 Quick tip
Quick tipIf your teen is struggling to stay away from social media or social media is affecting their overall health even after persistent guidance and monitoring, you should speak to your healthcare professional. The doctor will devise a de-addiction plan based on the social media addiction intensity and issues faced by the teen.
Social media use among teenagers is ubiquitous. While its responsible and guided use can provide entertainment and help stay connected with other people, its overuse can cause addiction. Teenage social media addiction is linked to mental health problems and functional impairment that can affect a teen’s quality of life. Thus, parents and educators should monitor and guide teens’ social media activities. Following simple measures to have healthy social media use can help teens reap its benefits without the risk of getting addicted to it.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What age group is most addicted to social media?
A US survey in 2019 noted that about 40% of people aged 18 to 22 years admitted to being somewhat to completely addicted to social media. It indicated an age group where maximum individuals acknowledged their social media addiction even if it was mild addiction (12).
2. How long do teens spend on social media?
On average, teenagers spend about nine hours daily on social media, which may include various social media websites (13).
3. What resources are available for teenagers and their families who are struggling with social media addiction?
Professional help from therapists or counselors specializing in addiction and mental health can help individuals and families understand the underlying causes of addiction, develop coping strategies and work towards healthier social media habits. Support groups and organizations like Social Media Anonymous offer support groups specifically focused on social media addiction. Digital well-being apps and parental control software, such as Net Nanny, are additional ways teenagers and parents can combat social media addiction.
4. Are certain social media platforms more addictive for teens than others?
Addiction to a social media platform may vary from one individual to another. However, certain characteristics and features of platforms make them more addictive than others. For instance, some platforms allow infinite scrolling to entertain and engage the user. Many offer like, comment, and share options for instant gratification and social validation. Targeted advertising based on user data and preferences and gamification elements, such as badges and rewards, provide users with a sense of achievement that raises their potential for addictive behaviors.
Infographic: How Does Usage Of Social Media Affect Teen’s Life?
In today’s era of technological advancement, social media has become a boon to connect with everyone, despite their distances. However, it also has some negative impacts. Read through the infographic below to learn about social media’s positive and negative effects on teens.
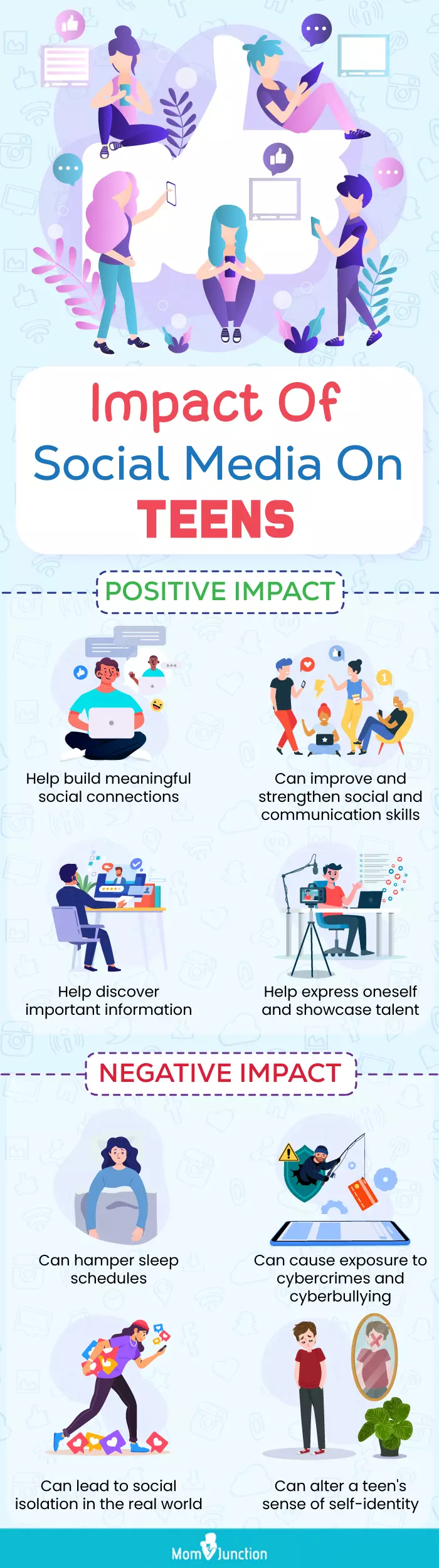
Illustration: Momjunction Design Team
Illustration: Teenage Addiction To Social Media: Causes And Tips To Deal

Image: Stable Diffusion/MomJunction Design Team
In today’s world, social media has become a necessity, but you should be aware of its negative side as well. This video explores the effects of social media on adolescent brains through an NIH study tracking the impact.
Personal Experience: Source
MomJunction articles include first-hand experiences to provide you with better insights through real-life narratives. Here are the sources of personal accounts referenced in this article.
1. The mobile cleanse (Teenage addition)https://medium.com/@parnikapuri/the-mobile-cleanse-teenage-addition-42f77b764557
References
- Teens, Social Media and Technology 2018.
https://www.pewresearch.org/internet/2018/05/31/teens-social-media-technology-2018/ - Social media’s growing impact on our lives.
https://www.apa.org/members/content/social-media-research - Hogan H. Lee et al.; (2017); Differences by Sex in Association of Mental Health With Video Gaming or Other Nonacademic Computer Use Among US Adolescents.
https://www.cdc.gov/pcd/issues/2017/17_0151.htm - Speaking of Psychology: How social media affects teens’ mental health and well-being, with Linda Charmaraman, PhD.
https://www.apa.org/news/podcasts/speaking-of-psychology/social-media-teens - Should I Worry About Social Media Addiction?
https://americanaddictioncenters.org/blog/social-media-addiction - Is social media bad for teens’ mental health?
https://www.unicef.org/stories/social-media-bad-teens-mental-health - Social Media and Mental Health.
https://www.helpguide.org/mental-health/wellbeing/social-media-and-mental-health - Daria J. Kuss and Mark D. Griffiths; (2017); Social Networking Sites and Addiction: Ten Lessons Learned.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5369147/ - The Growing Case for Social Media Addiction.
https://www.calstate.edu/csu-system/news/Pages/Social-Media-Addiction.aspx - Impact of Social Media on Youth Mental Health: Statistics, Tips & Resources.
https://www.unr.edu/public-health/degrees/online-mph - Anjali Singh et al.; (2020); Impact of Social Media on Adolescent’s Mental Health.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/343205479_Impact_of_Social_Media_on_Adolescent’s_Mental_Health - Are you addicted to social media?
https://www.leehealth.org/health-and-wellness/healthy-news-blog/mental-health/are-you-addicted-to-social-media - Are instagram and other social media bad for your teen’s mental health?
https://flushinghospital.org/newsletter/do-teenagers-spend-too-much-time-on-social-media/#:~:text=Studies%20show%20that%20teens%20spend,can%20affect%20their%20mental%20health. - Social Media changed the way introverts engage.
https://networkconference.netstudies.org/2021/2021/04/27/social-media-changed-the-way-introverts-engage/ - How parents and educators can support healthy teen use of social media.
https://www.kqed.org/mindshift/58624/how-parents-and-educators-can-support-healthy-teen-use-of-social-media
Community Experiences
Join the conversation and become a part of our nurturing community! Share your stories, experiences, and insights to connect with fellow parents.
Read full bio of Angela Karanja
Read full bio of Swati Patwal
Read full bio of Rohit Garoo
Read full bio of Dr. Joyani Das